In order to properly understand the concept of the provision of appropriate humidity control in a cold room or storage area, it would be necessary to sort them out into two broad categories.
- Active stores
- Passive stores

Active cold stores are warehouses that are refrigerated and they are needed for dynamic storage appliances. While passive stores are designed for the storage of perishable cargos for both a medium and long period of time, and they are most times meant for the storage of vegetables and fresh fruits.

The warehouses undergo regular movements of goods on a daily basis. In addition to this, the diverse temperate zones are structured in the same warehouse for the purpose of storing all sorts of products that require different temperatures. While it is quite effortless to construct refrigeration systems meant for passive cold storage, a number of variables need to be considered when designing an active cold store.
- Ensure that wet floors are not present
- Avoid the accumulation of ice on evaporator coils in order to step down the defrosting cycles which would, in turn, improve the productivity of the refrigeration systems
- Remove the build-up of frost close to the loading docks for a clear sight to make sure that the cargo in the warehouse are handled in order to ensure that accidents do not occur
In conventional small cold stores which are used by laboratories, restaurants, and the likes, the high relative humidity is most times the cause of such problems. When a moist store enters a cold store, ice and frost are formed.
A layman’s view of cold storage suggests that it would not be disturbed by humidity-related issues since the entirety is frozen. On the contrary, the cold situation is a huge problem which humidity presents in cold storage amenities, and this can, in turn, cause a couple of issues. Controlling humidity in cold storage and storage area, in general, is quintessential in regulating and eventually eradicating the damage done to products. Also, it ensures that there is a safe and sound working environment.
The difficulty of humidity control in cold storage
One of the major reasons why humidity control in cold storage is difficult is because, the spaces where the storage areas are situated, is firmly constructed and sealed in order to properly utilize the productivity of the cooling system. So, water finds its way in through infiltration either when the doors are opened, or through the occupant’s and product’s off-gassing, water can also be introduced through the wash- down activities which eventually gets it stuck in the air-tight room.
Since there is no HVAC system or ventilation in place, the water is unable to leave the cold space, this, in turn, makes it impossible for the cold storage to control the level of humidity without the aid of a ventilation system or the use of commercial dehumidification.
Challenges of cold rooms and storage areas
Quite often, cold rooms and storage areas situated adjacent to bigger areas, stay at warmer temperatures. One good instance is the situation of a cold storage structure next to a dock, where all sorts of items are conveyed from a refrigerated truck across a warehouse, into the storage area.

Each time the door is opened in the midst of these areas, the pressure change moves the moist and warmer air into the cold storage region. Then, a reaction occurs in which condensation forms on walls, ceilings, stored items, and even floors.
Solving the cold storage problem
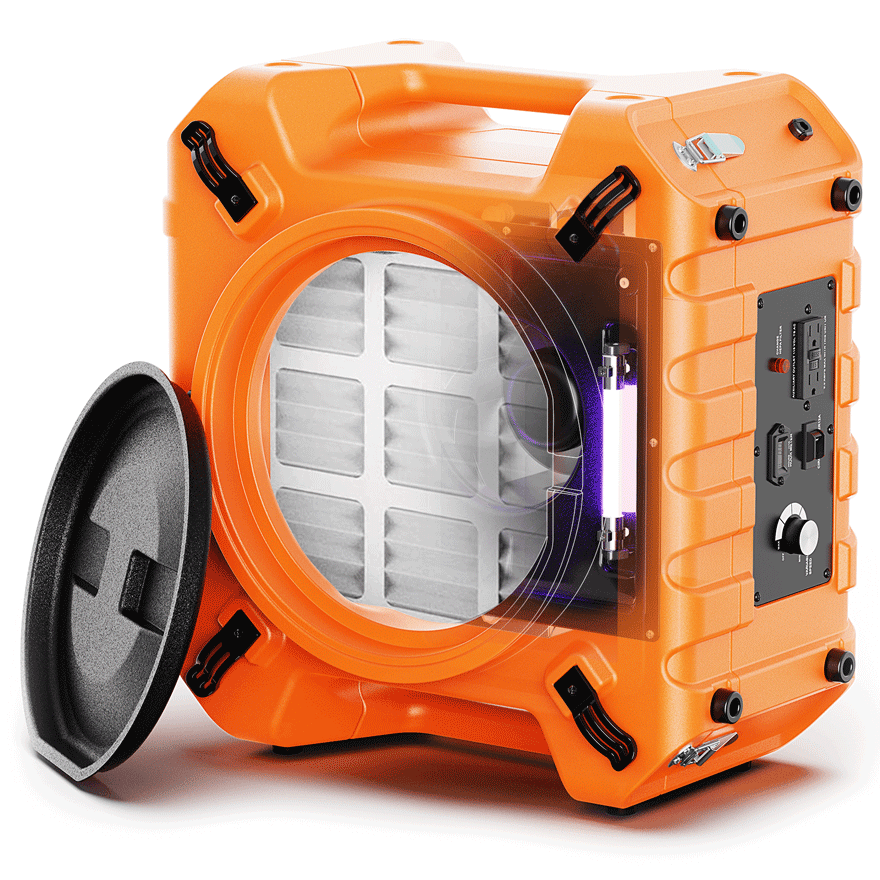
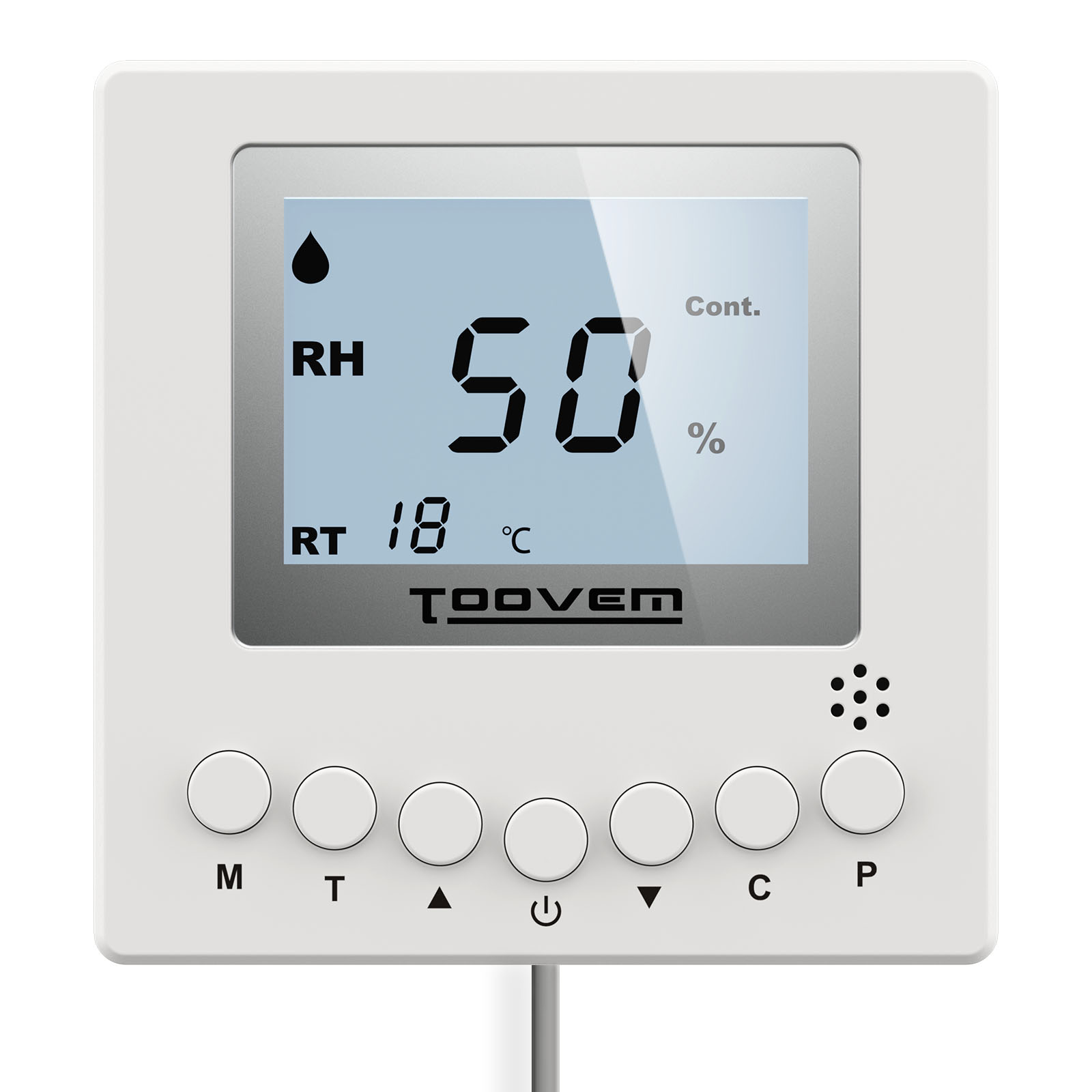
What is needed, is the installation of a commercial dehumidifier which would function by drawing moisture from the climate of the indoor air. When it takes in the water vapor and dissipates it, the indoor humidity levels are lowered by the system, and it is done in an effective and affordable manner.
In contrast to residential systems, commercial dehumidifiers are designed to last for a long period due to the nature of the environment in which they would function. Also, they can also be linked to HVAC systems which are already in place, for prompt and automatic removal of the water vapor and total control of the climate.
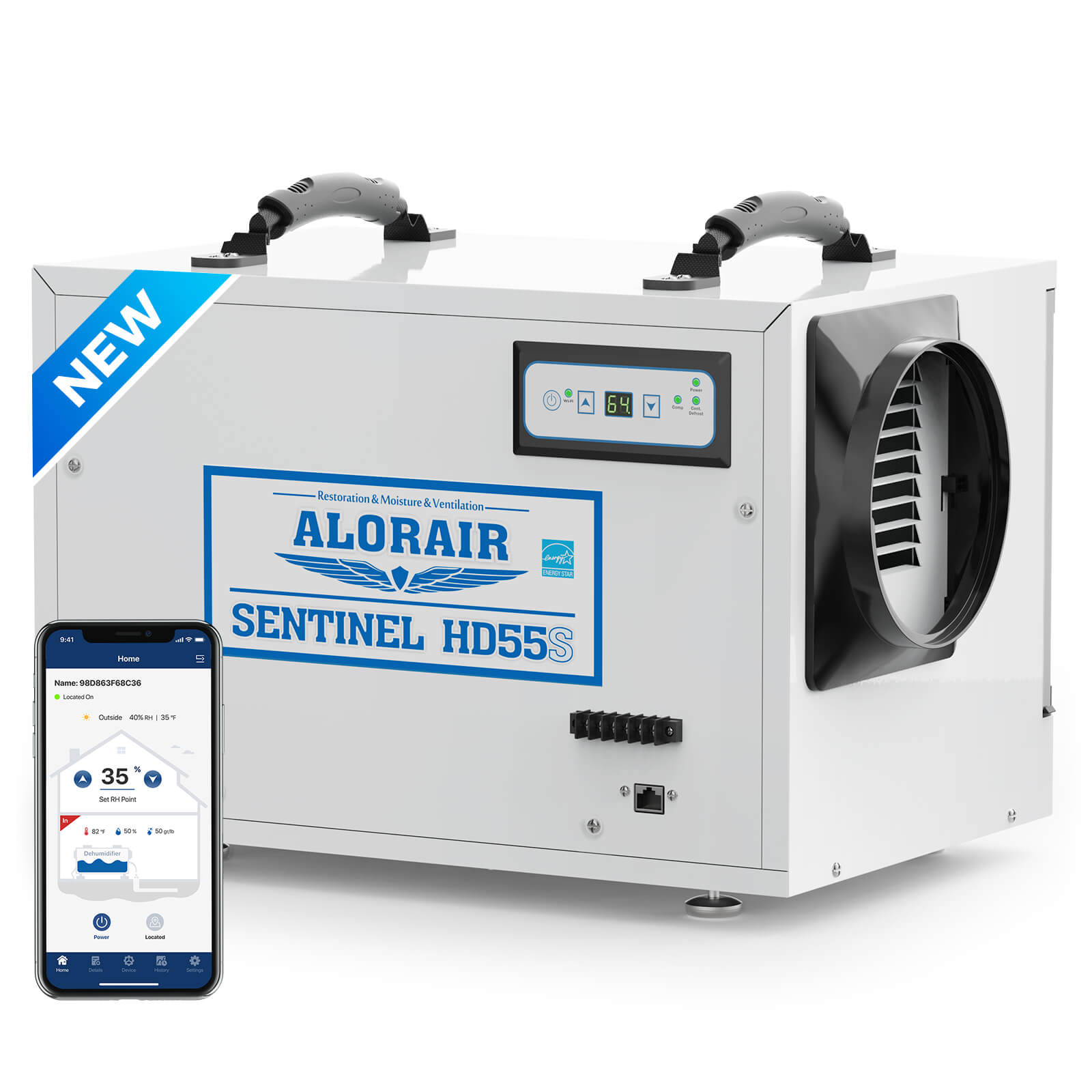
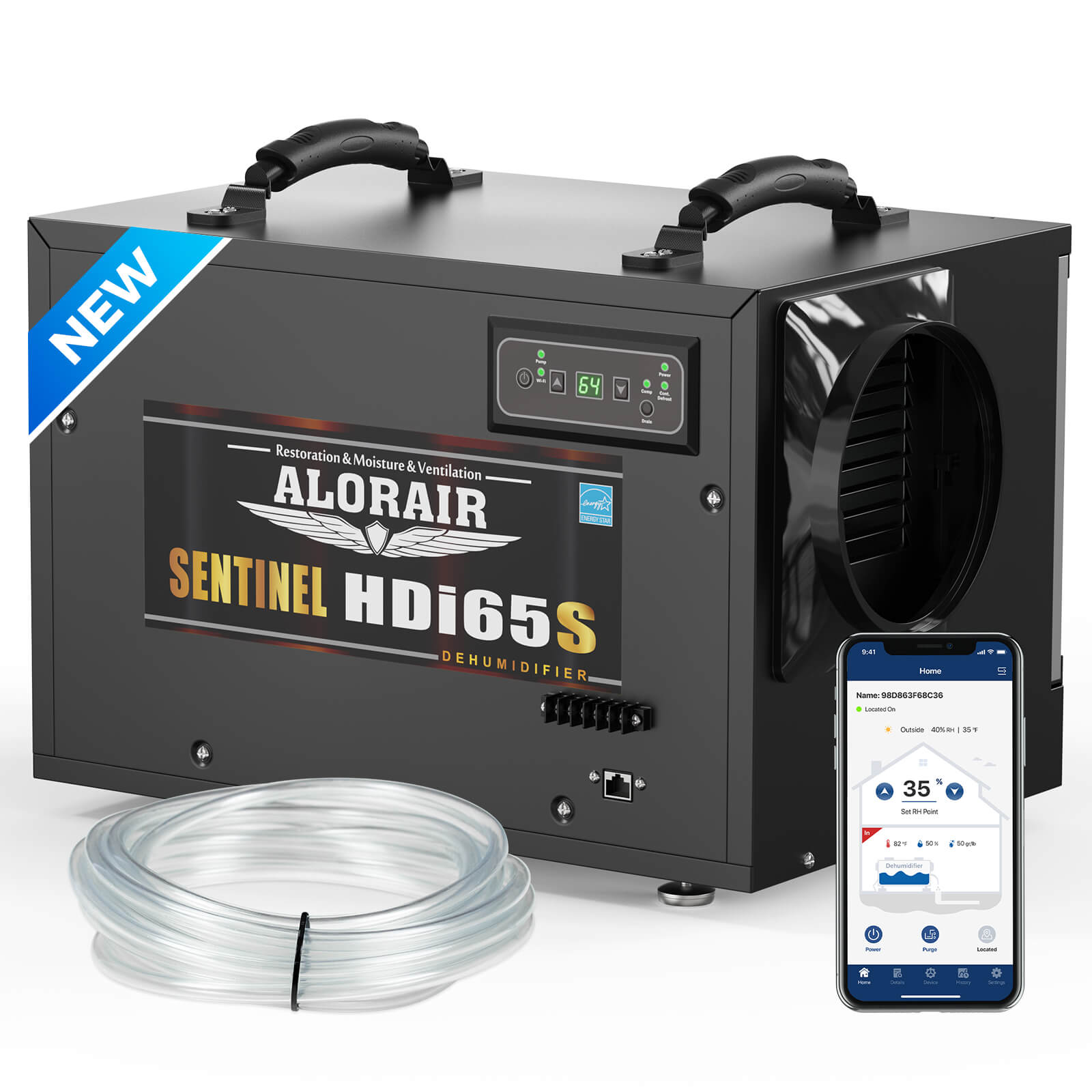
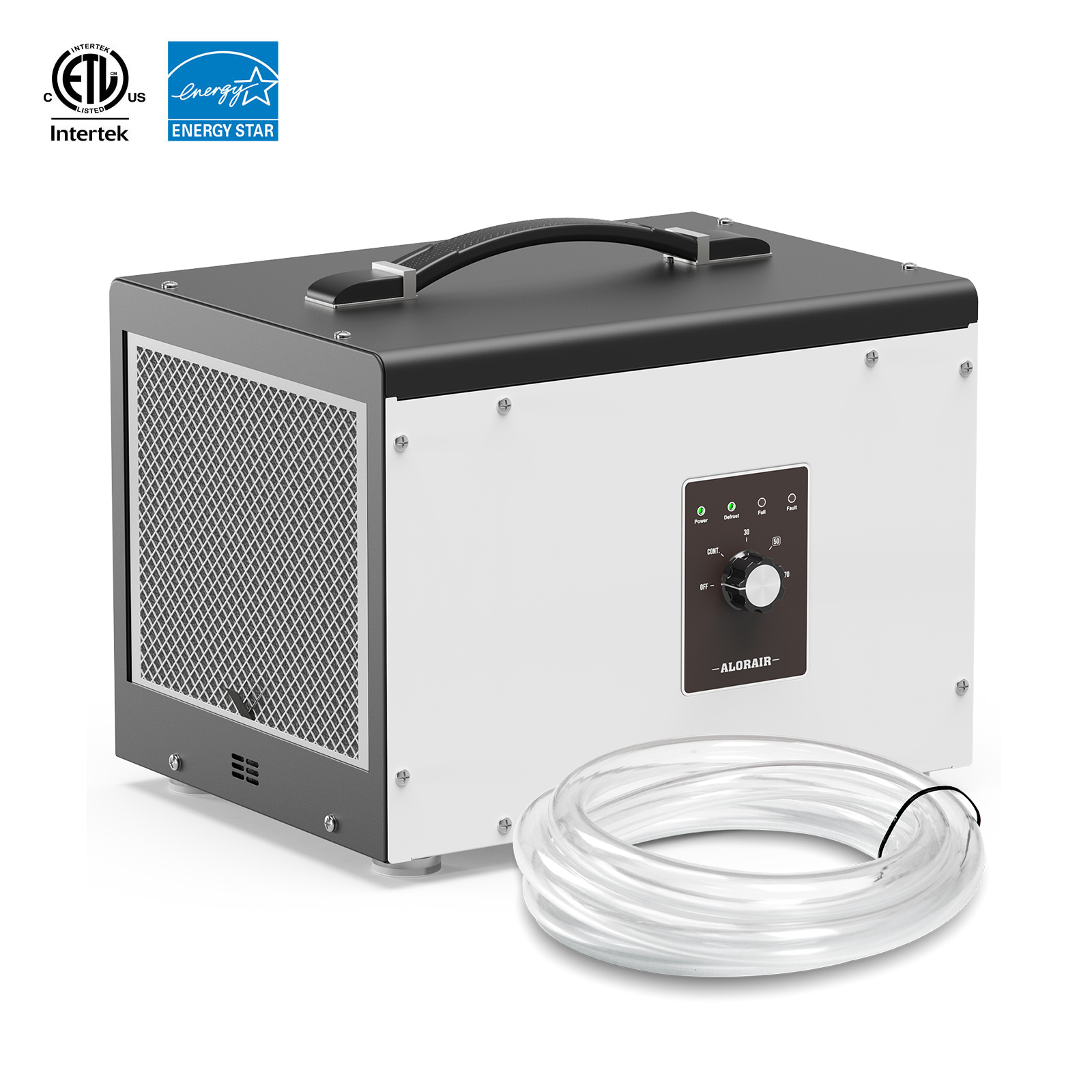










.jpg)
.jpg)
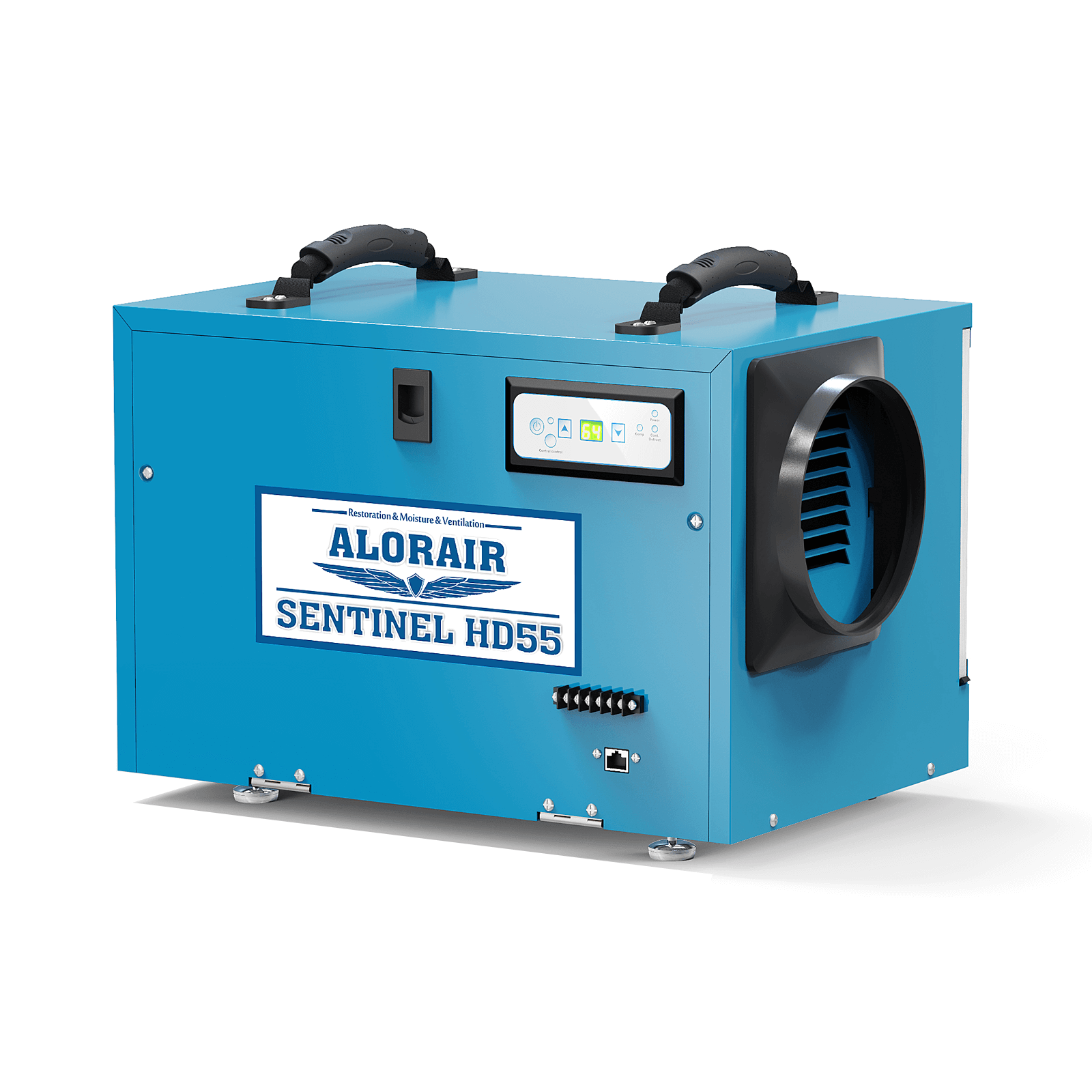

.jpg)
.jpg)
.HDi90.png)
.HD90.png)









.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)








.jpg)
.jpg)








.jpg)
.jpg)






















.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)
















-.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)


























 Exclusive offers
promotions
Exclusive offers
promotions

