- Home
- About
- Deals
-
Products
-
Crawl Space & Basement Dehumidifiers
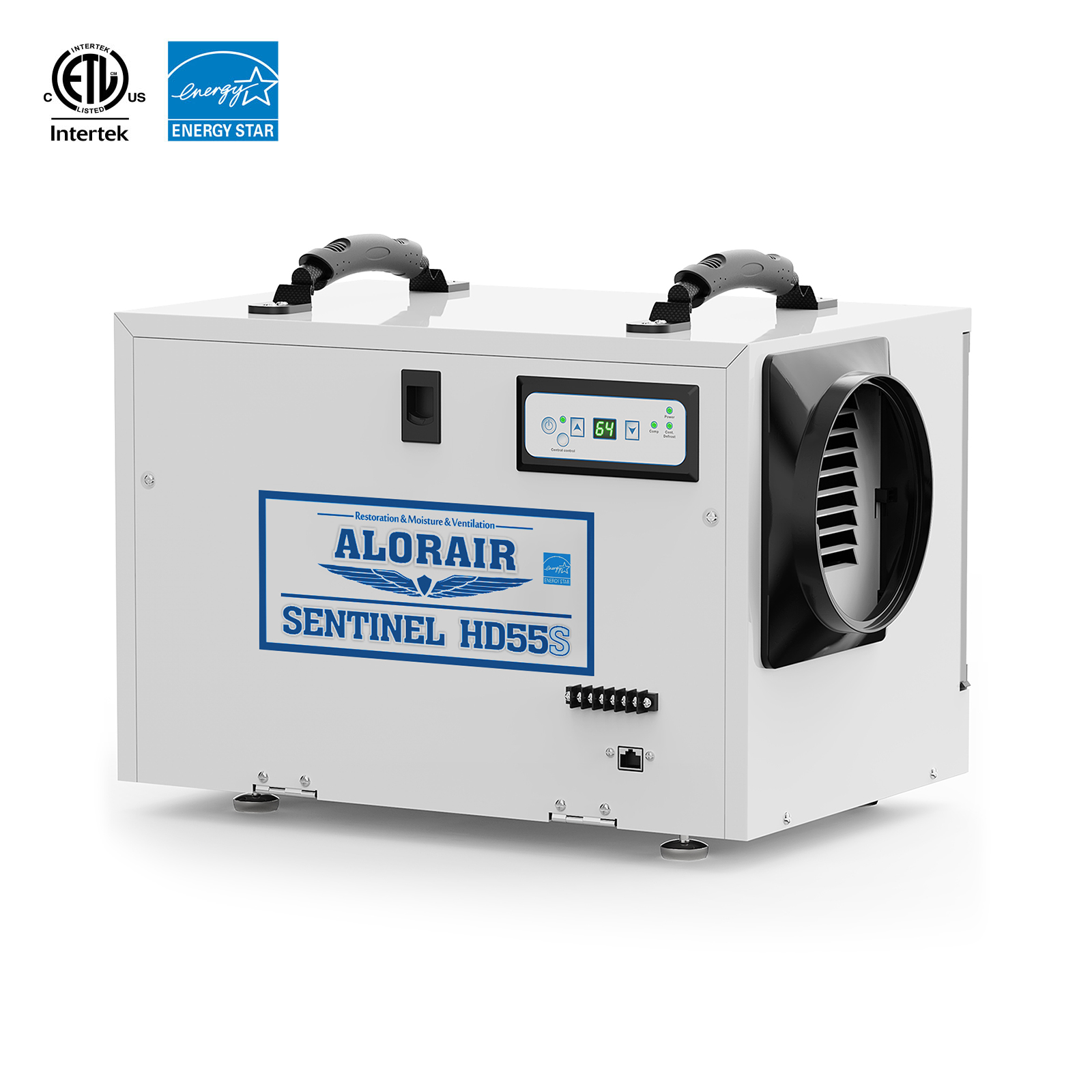
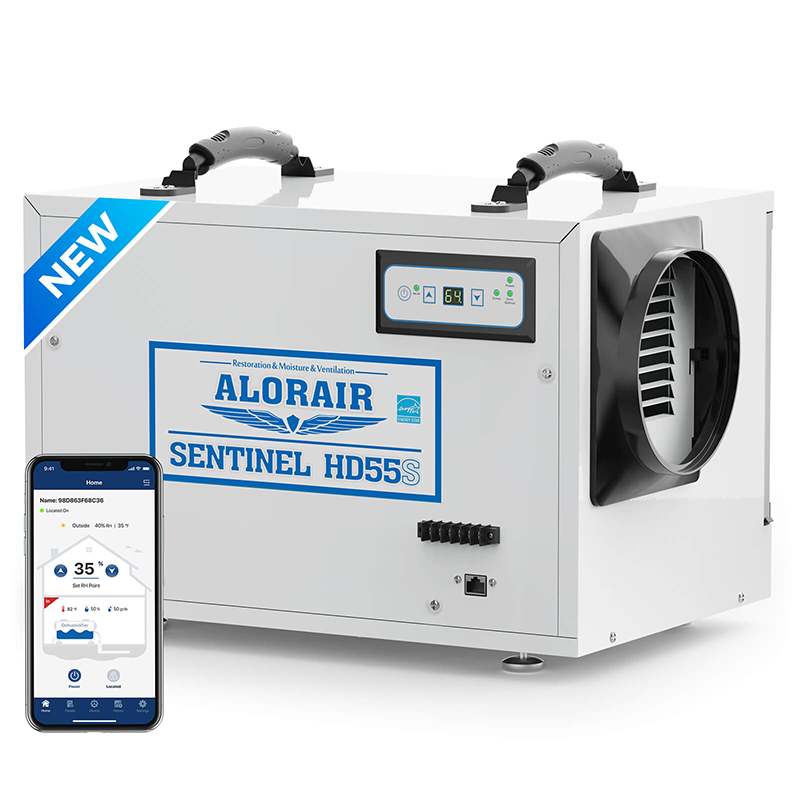
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S with WiFi
- Alorair Sentinel HDi65S Black WIFI
- AlorAir® Sentinel HS35
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD35P
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD55P
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD55
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S (Gold)
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S (White)
- AlorAir® Sentinel HDi90 (Built-in Pump)
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD90
- AlorAir® Sentinel HDi90 (Duct-able)
- AlorAir® Sentinel HDi 100
- AlorAir® Sentinel HDi 120
- AlorAir® Galaxy 60P
- Sentinel HD35P WIFI
- AlorAir® Sentinel HD55 Blue WIFI
- AlorAir Sentinel HDi90 WIFI
- AlorAir® Galaxy 60
- AlorAir® Galaxy 85P
- Whole House Dehumidifiers
-
Commercial & Industrial Dehumidifiers
- AlorAir® Sentinel Pro 55X
- AlorAir® Sentinel Pro 35X
- AlorAir® Sentinel SLGR 1400X
- AlorAir® Storm 80X
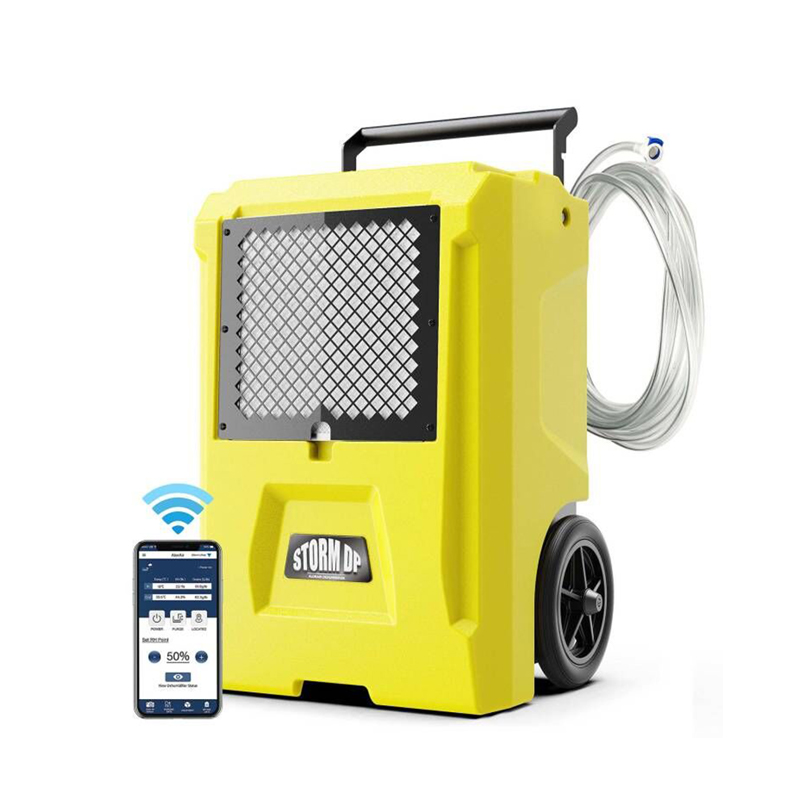
- AlorAir® Storm DP Single-Voltage
- AlorAir® Storm Ultra
- AlorAir® Storm Elite
- AlorAir® Storm Pro Dehumidifier
- AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250
- AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250X
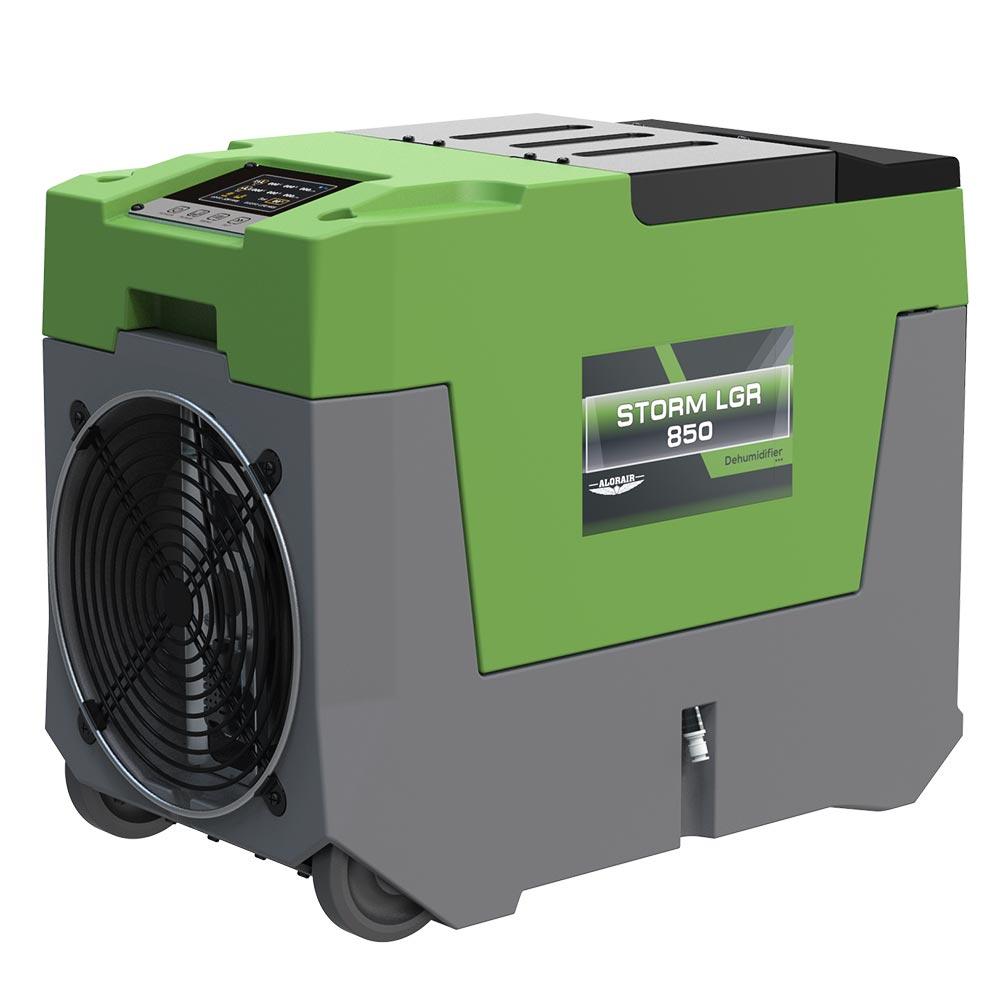
- AlorAir® Storm LGR 850
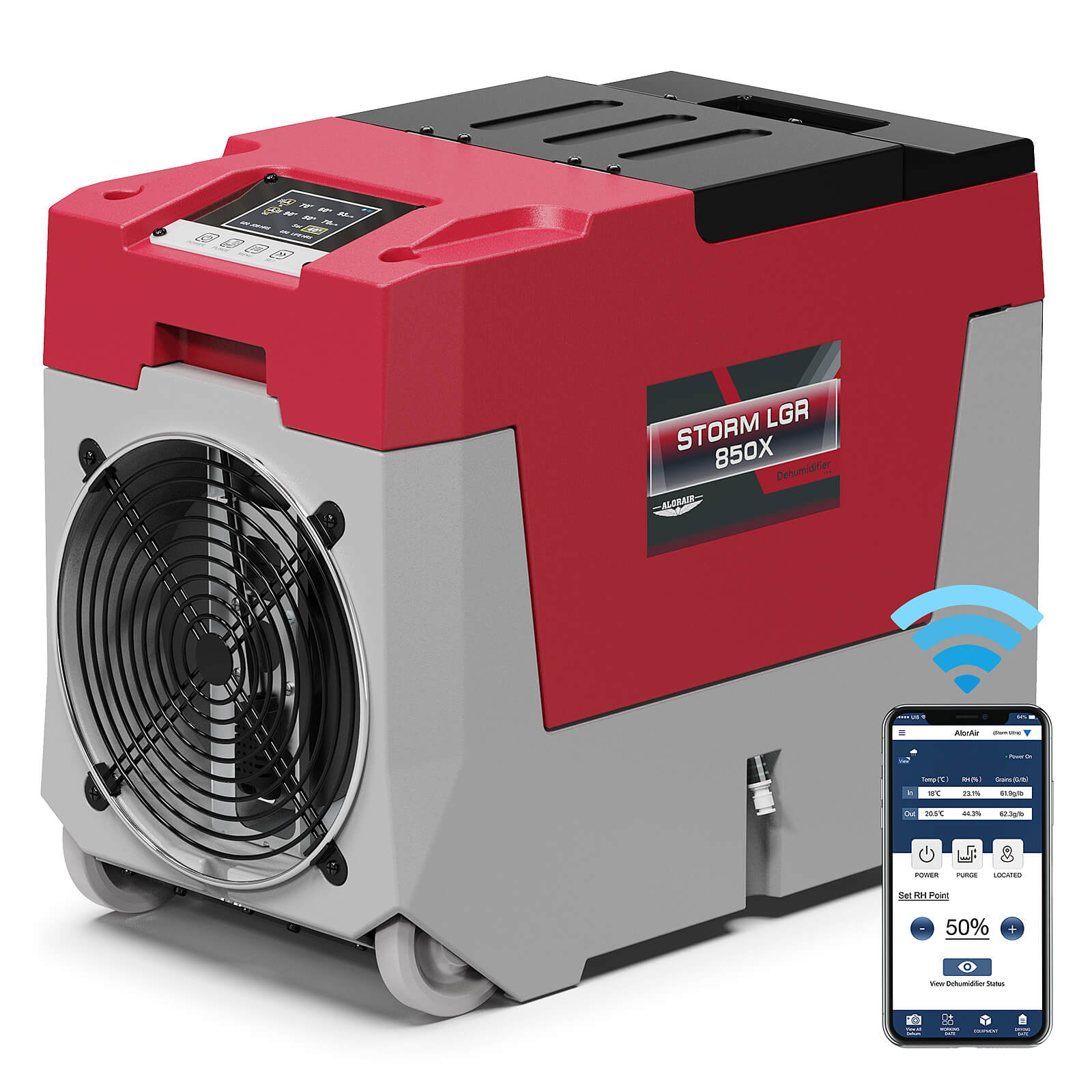
- AlorAir® Storm LGR 850X
- AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme Smart App Control
- AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme (Hot Sale)
-
Commercial HEPA Air Scrubbers
- AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 970
- AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 870
- AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 770
- AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 970
- AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 870
- AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 770
- AlorAir® Cleanshield HEPA 550 (Hot Sale)
- Purisystems S1 UVIG Air Scrubber
- Purisystems S1 UV Air Scrubber
- Purisystems S1 Air Scrubber
- Purisystems HEPA 600 UVIG (Medical Grade)
- Purisystems HEPA Pro UVIG (Industrial Grade)
- Purisystems S2 Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)
- Purisystems S2 UV Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)
- Purisystems S2 UVIG Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)
-
Woodshop Air Filtration System
- AlorAir® Purecare 1050IG
- AlorAir® Purecare 1050
- AlorAir® Purecare 780S
- AlorAir® Purecare 1080IG
- AlorAir® Purecare 1080
- AlorAir® Purecare 780IG
- AlorAir® Purecare 780
- AlorAir® Purecare 1350IG
- AlorAir® Purecare 1350
- Purisystems Puricare 1100
- Purisystems Puricare 1100IG
- Purisystems Puricare 500
- Purisystems Puricare 500IG
-
Air Mover
- AlorAir® Zeus Extreme Axial Air Mover
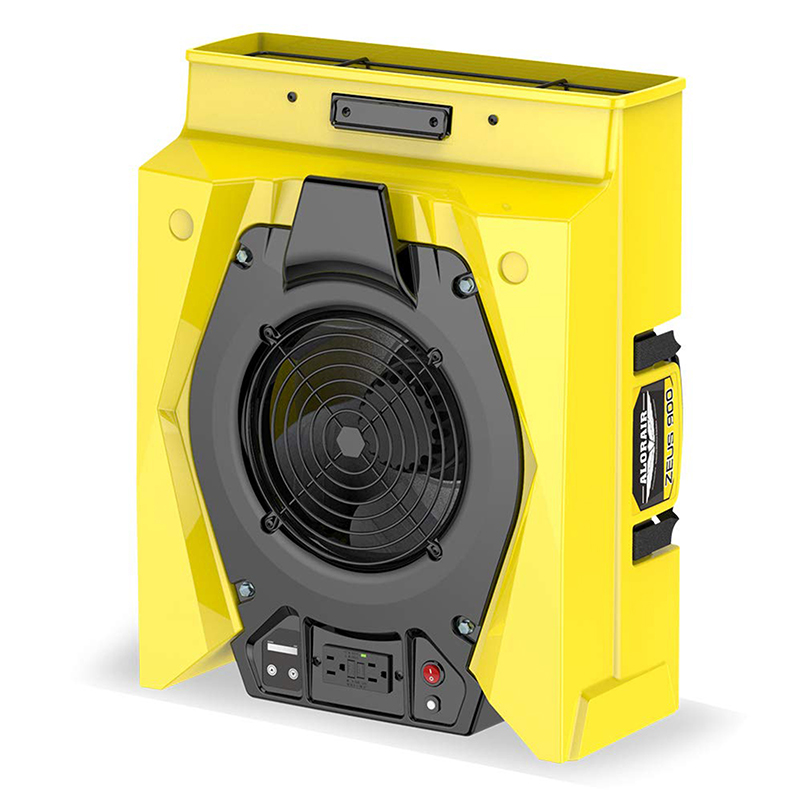
- AlorAir® Zeus 900 Air Mover
- AlorAir® 600 CFM Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE4000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE4000HTC Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE4000TC Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE3000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE4000T Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE3000HTC Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE3000TF Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE3000T Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE2000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE2000TF Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® GE2000T Air Mover Blower Fan
- AlorAir® Air Drying System
- SLGR Dehumidifiers
-
Ventilation Fans
- AlorAir® Ventirpro 720
- AlorAir® Ventirpro 540
- AlorAir® Ventirpro 260
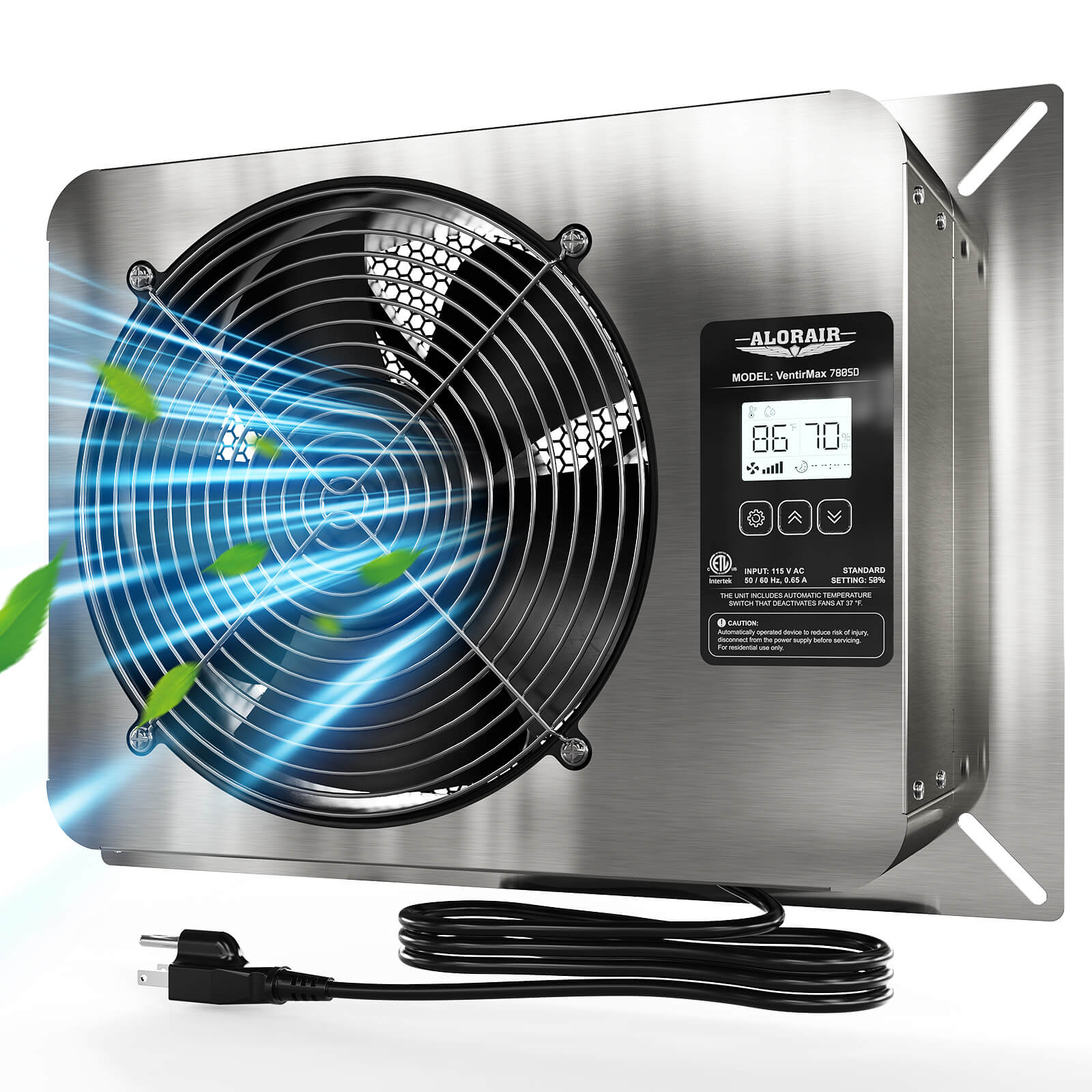
- AlorAir® VentirMax 780SD
- AlorAir® VentirMax 570SD
- AlorAir® VentirMax 300SD
- AlorAir® VentirPro-S2
- AlorAir® VentirPro 260S
- AlorAir® VentirPro 540S
- AlorAir® VentirPro 720S
- AlorAir® VentirMax 300S
- AlorAir® VentirMax 570S
- AlorAir® VentirMax 780S
- Electric Heat Drying Systems
- Crawl Space Encapsulation and Repair
-
Wifi Dehumidifier
-
Crawl Space & Basement Dehumidifiers
- Shop
- Crawl Space & Basement Dehumidifiers
- Whole House Dehumidifiers
- Commercial & Industrial Dehumidifiers
- Commercial HEPA Air Scrubbers
- Woodshop Air Filtration System
- Air Mover
- SLGR Dehumidifiers
- Ventilation Fans
- Electric Heat Drying Systems
- Filter & Other Accessories
- Crawl Space Encapsulation and Repair
- Wifi Dehumidifier
-
Applications
- Managing Air
- Basement Dehumidification
- Carpet Cleaning
- Crawl Space Dehumidification
- Fire Damage Restoration
- Flood Dehumidification
- Mold Removal
- Water Damage Restoration
- Indoor Swimming Pool
- Grow Room & Tent Optimization
- Pharmaceutical Production
- Supermarket Grocery & Retail
- Warehouse & Storage
- Laboratory & Cleanrooms
- Basement Wine Cellar
- Gyms & Fitness Center
- Guest Rooms & Hotels
- Support
- Learning
- Community
- Blog
- Distributor
- Login/Register
- About
-
Deals

- Products
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S with WiFi
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S with WiFi]()
Capacity
120 PPD at Saturation, 55 PPD at AHAM
Size for
1300 sq.ft
Draining
Gravity Drainage
Unit Dimensions
12.2"D x 19.2"W x 13.3"H
-
Alorair Sentinel HDi65S Black WIFI
![Alorair Sentinel HDi65S Black WIFI]()
Capacity
120 PPD at Saturation, 55 PPD at AHAM
Coverage
1300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump drainage/Gravity drain
Unit Dimensions
12.2" D X19.2" W X13.3" H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HS35
![AlorAir® Sentinel HS35]()
Capacity
70 PPD at Saturation, 35 PPD@AHAM
Size for
1000 sq.ft
Draining
Gravity drainage
Unit Dimensions
15.35 × 11.2 × 11.4 in
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HD35P
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD35P]()
Capacity
70 PPD at Saturation, 35 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
1000 sq.ft
Draining
Pump drainage/Gravity drain
Unit Dimensions
15.35 × 11.2 × 11.4 in
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HD55P
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD55P]()
Capacity
120 PPD at Saturation, 55 PPD@AHAM
Size for
1500 sq.ft
Draining
Pump drainage/Gravity drain
Unit Dimensions
17.64 x 11.69 x 11.85in
-
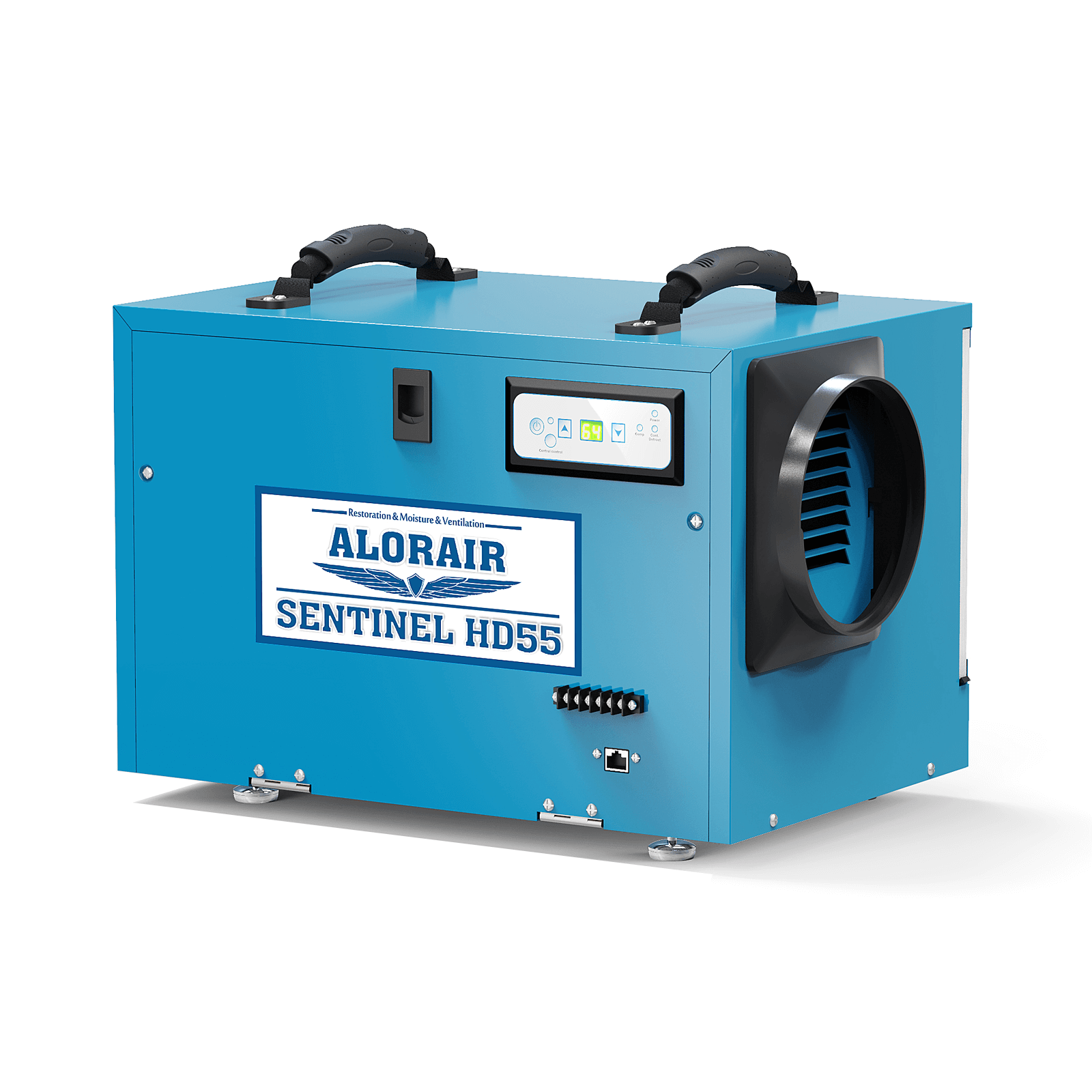
AlorAir® Sentinel HD55
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD55]()
Capacity
113 PPD at Saturation, 53PPD@AHAM
Size for
1200 sq.ft
Draining
Gravity Drainage
Unit Dimensions
12.2"D x 19.2"W x 13.3"H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S (Gold)
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S (Gold)]()
Capacity
120 PPD at Saturation, 55 PPD@AHAM
Size for
1300 sq.ft
Draining
Gravity Drainage
Unit Dimensions
12.2" D X19.2" W X13.3" H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S (White)
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD55S (White)]()
Capacity
120 PPD at Saturation, 55 PPD@AHAM
Size for
1300 sq.ft
Draining
Gravity Drainage
Unit Dimensions
12.2"D x 19.2"W x 13.3"H
-
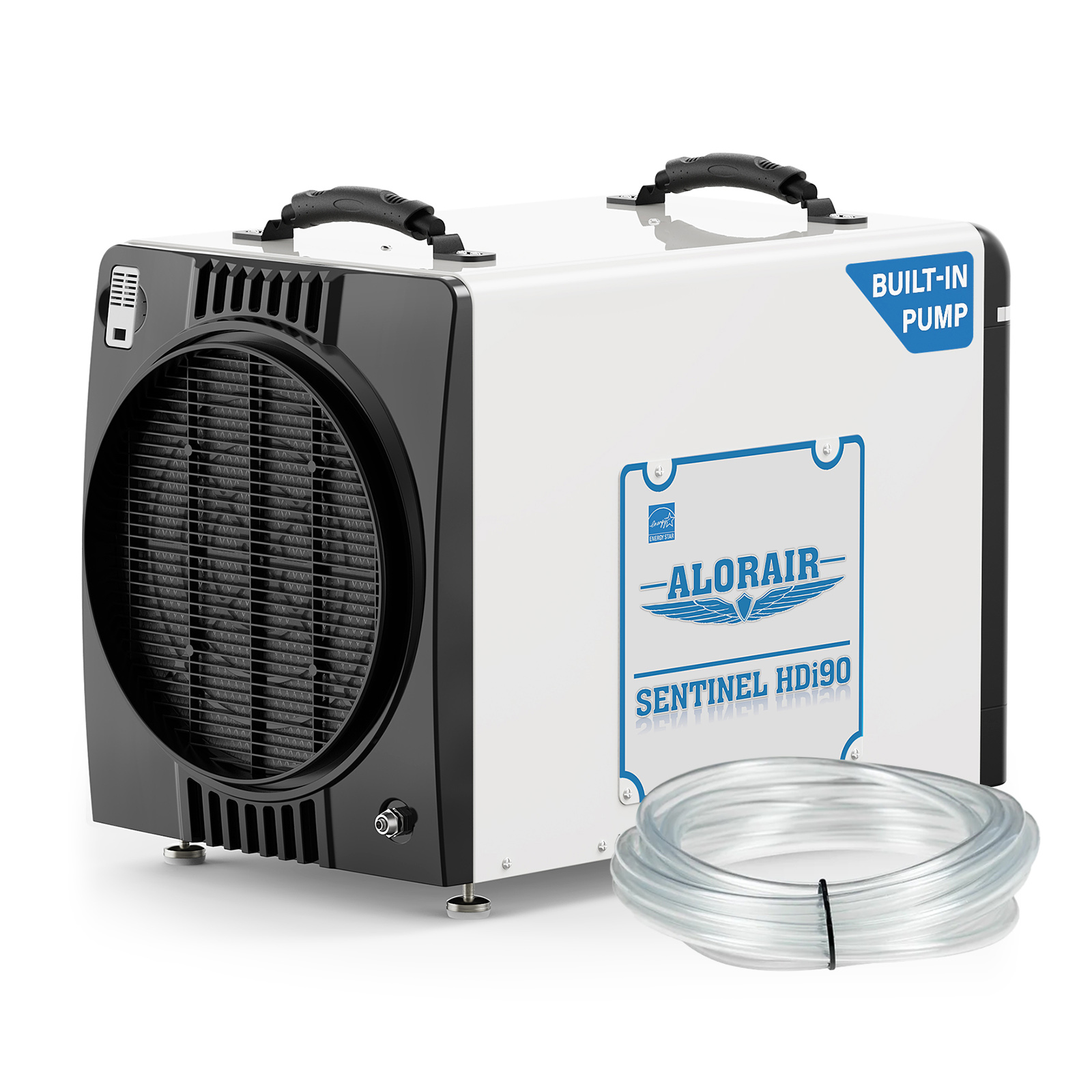
AlorAir® Sentinel HDi90 (Built-in Pump)
![AlorAir® Sentinel HDi90 (Built-in Pump)]()
Capacity
198 PPD at Saturation, 90 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2600 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
15.2" D x 23.2" W x 17.7" H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HD90
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD90]()
Capacity
198 PPD at Saturation, 90 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2600 sq.ft
Draining
Gravity Drainage
Unit Dimensions
15.2" D x 23.2" W x 17.7" H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel HDi90 (Duct-able)
![AlorAir® Sentinel HDi90 (Duct-able)]()
Capacity
198 PPD at Saturation, 90 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2600 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
15.2" D x 23.2" W x 17.7" H
-
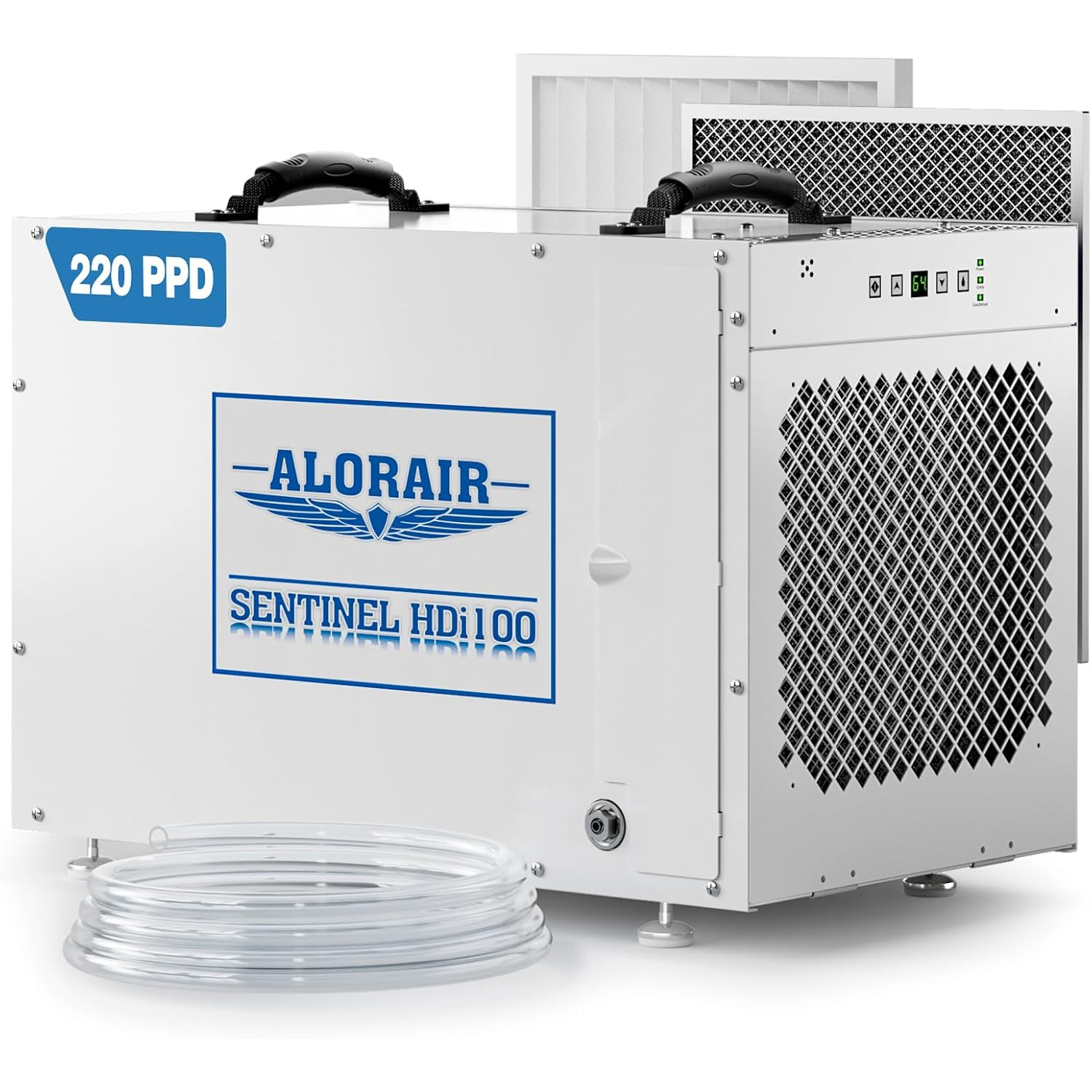
AlorAir® Sentinel HDi 100
![AlorAir® Sentinel HDi 100]()
Capacity
220 PPD at Saturation, 100 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2900 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
14.7" D x 23.8" W x 17.9" H
-
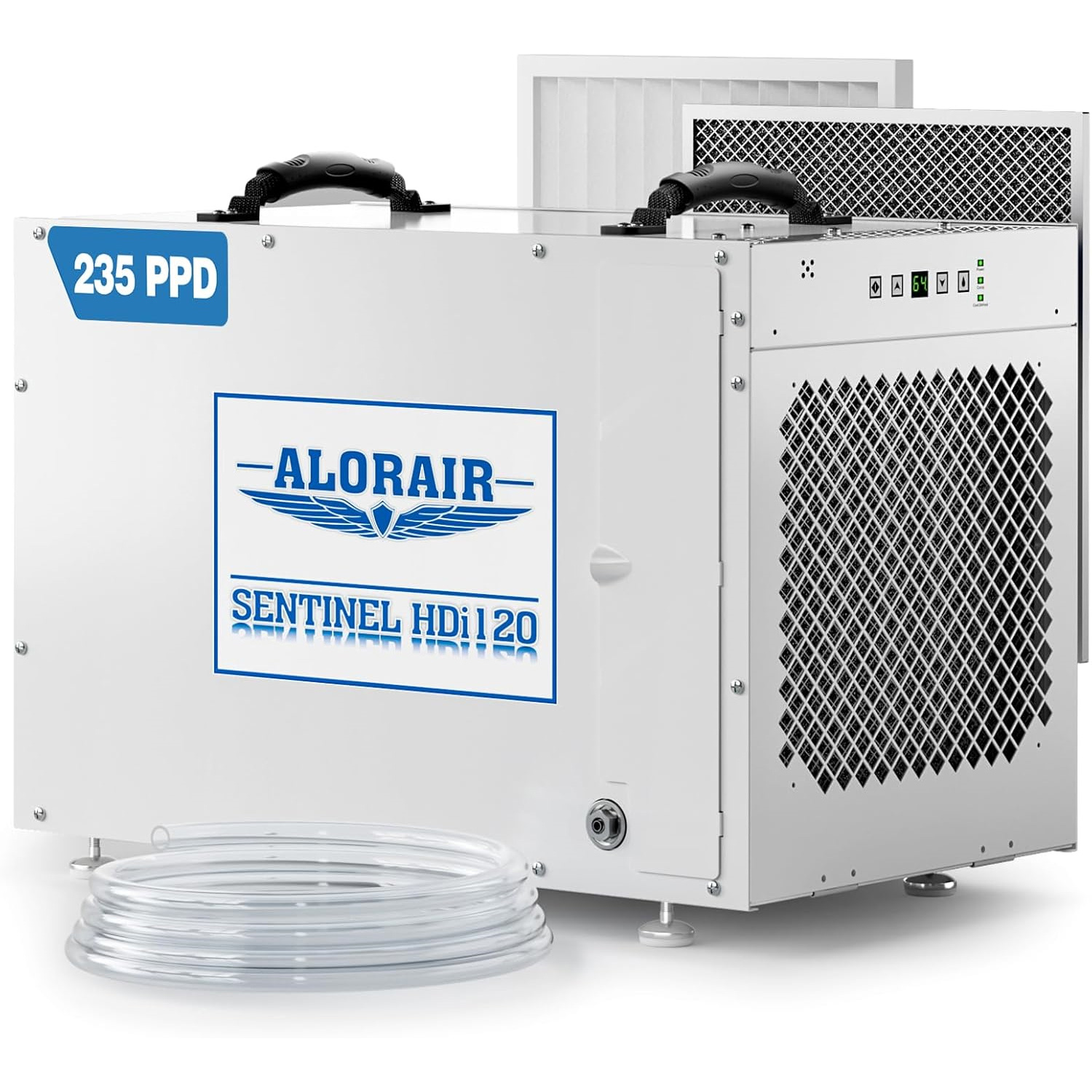
AlorAir® Sentinel HDi 120
![AlorAir® Sentinel HDi 120]()
Capacity
235 PPD at Saturation, 120 PPD@AHAM
Size for
3300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
14.7" D x 23.8" W x 17.9" H
-
AlorAir® Galaxy 60P
![AlorAir® Galaxy 60P]()
Capacity
145 PPD at Saturation
Size for
1800 sq.ft
Unit Dimensions
21.3"D x 14.1"W x 11.7"H
-
Sentinel HD35P WIFI
![Sentinel HD35P WIFI]()
Capacity
70 PPD at Saturation, 35 PPD at AHAM
Coverage
1000 sq.ft
Draining
Pump drainage/Gravity drain
Unit Dimensions
15.35 × 11.2 × 11.4 in
-
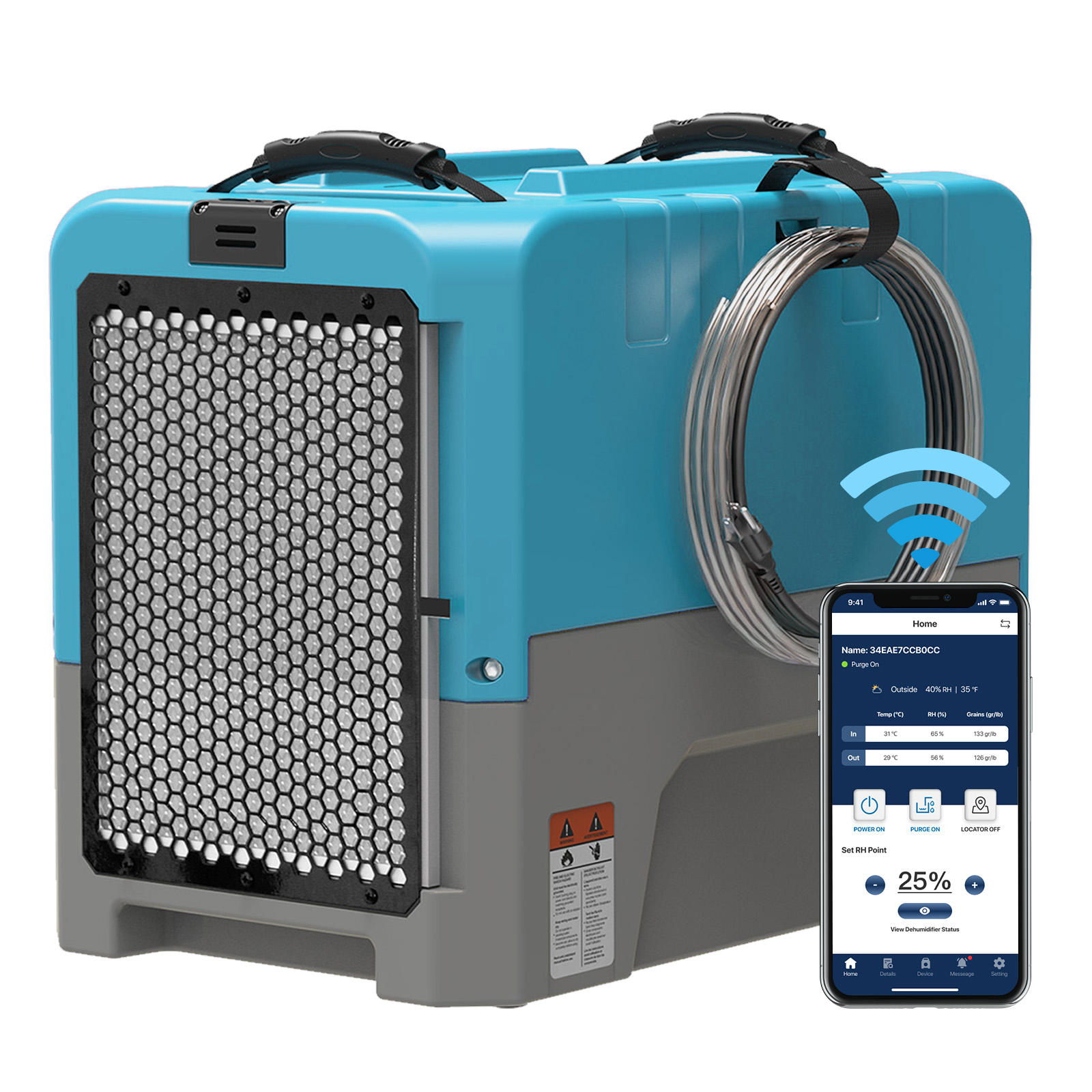
AlorAir® Sentinel HD55 Blue WIFI
![AlorAir® Sentinel HD55 Blue WIFI]()
-
AlorAir Sentinel HDi90 WIFI
![AlorAir Sentinel HDi90 WIFI]()
Capacity
198 PPD at Saturation, 90 PPD at AHAM
Coverage
2600 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
15.2" D x 23.2" W x 17.7" H
-
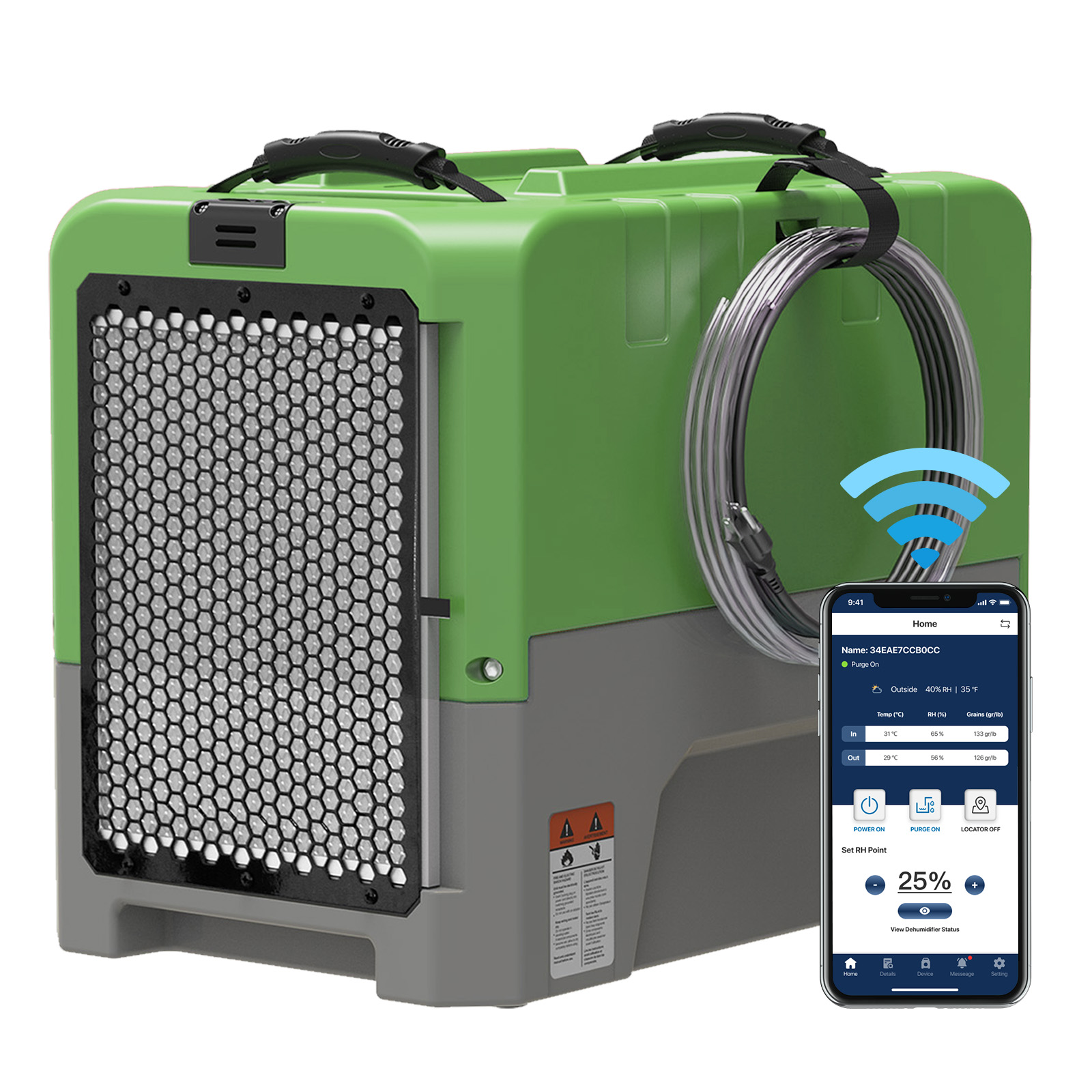
AlorAir® Galaxy 60
![AlorAir® Galaxy 60]()
Capacity
145 PPD at Saturation
Size for
1800 sq.ft
Unit Dimensions
21.3"D x 14.1"W x 11.7"H
-
AlorAir® Galaxy 85P
![AlorAir® Galaxy 85P]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation
Size for
2300 sq.ft
Unit Dimensions
21.3"D x 14.1"W x 11.7"H
Crawl Space & Basement Dehumidifiers
-
AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 100
![AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 100]()
Size for
2300 Sq.Ft
AHAM, (80°F, 60% RH)(Pints)
90 Pints
Airflow
229CFM, 309CFM
Unit Dimensions
22.64"D x 14.65"W x 19.88"H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 120
![AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 120]()
Size for
3000 Sq.Ft
AHAM, (80°F, 60% RH)(Pints)
104 Pints
Airflow
229CFM, 309CFM
Unit Dimensions
22.64"D x 14.65"W x 19.88"H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 150
![AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 150]()
Size for
3500 Sq.Ft
AHAM, (80°F, 60% RH)(Pints)
140 Pints
Airflow
309CFM, 383CFM
Unit Dimensions
37.3"D x 23.4"W x 24.3"H
-
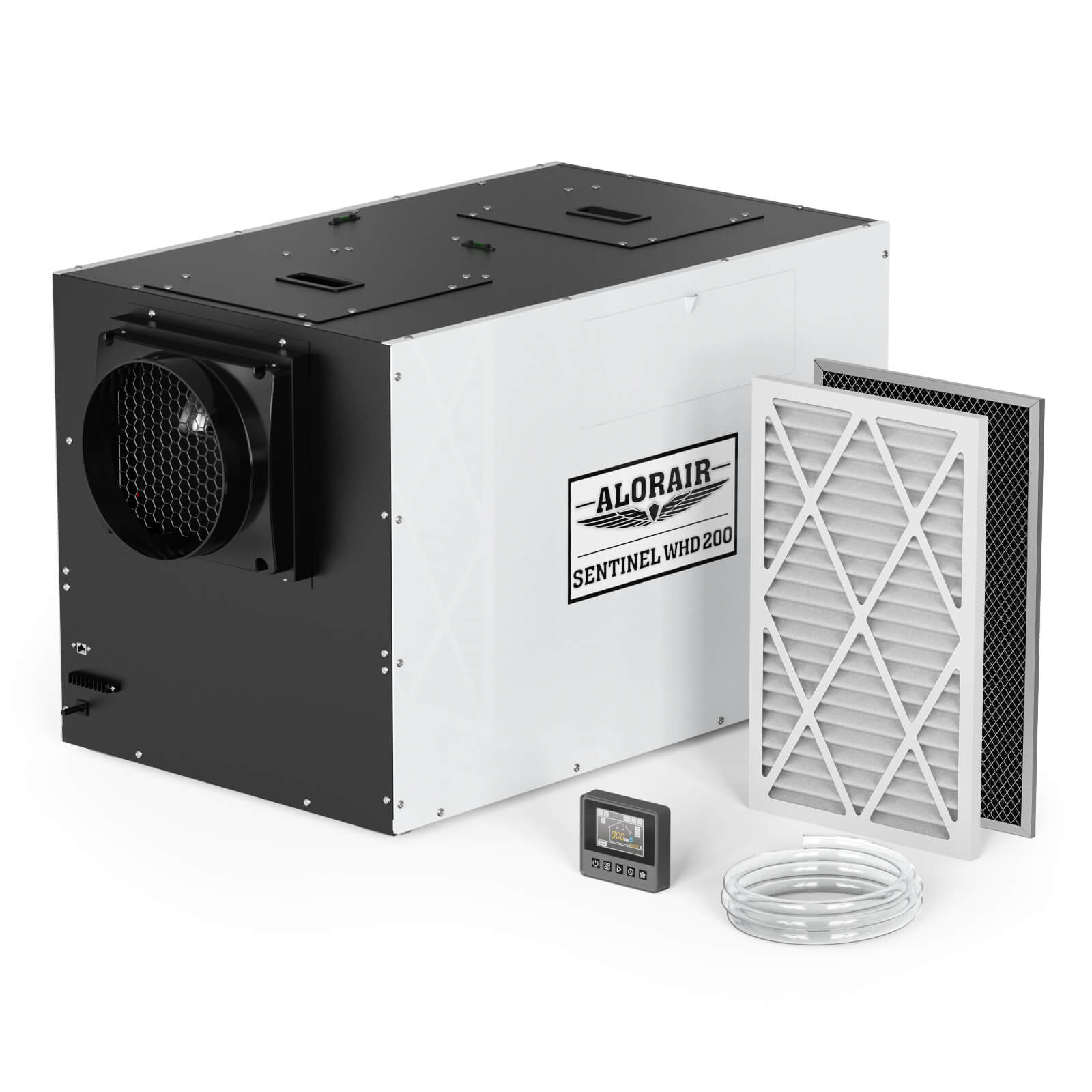
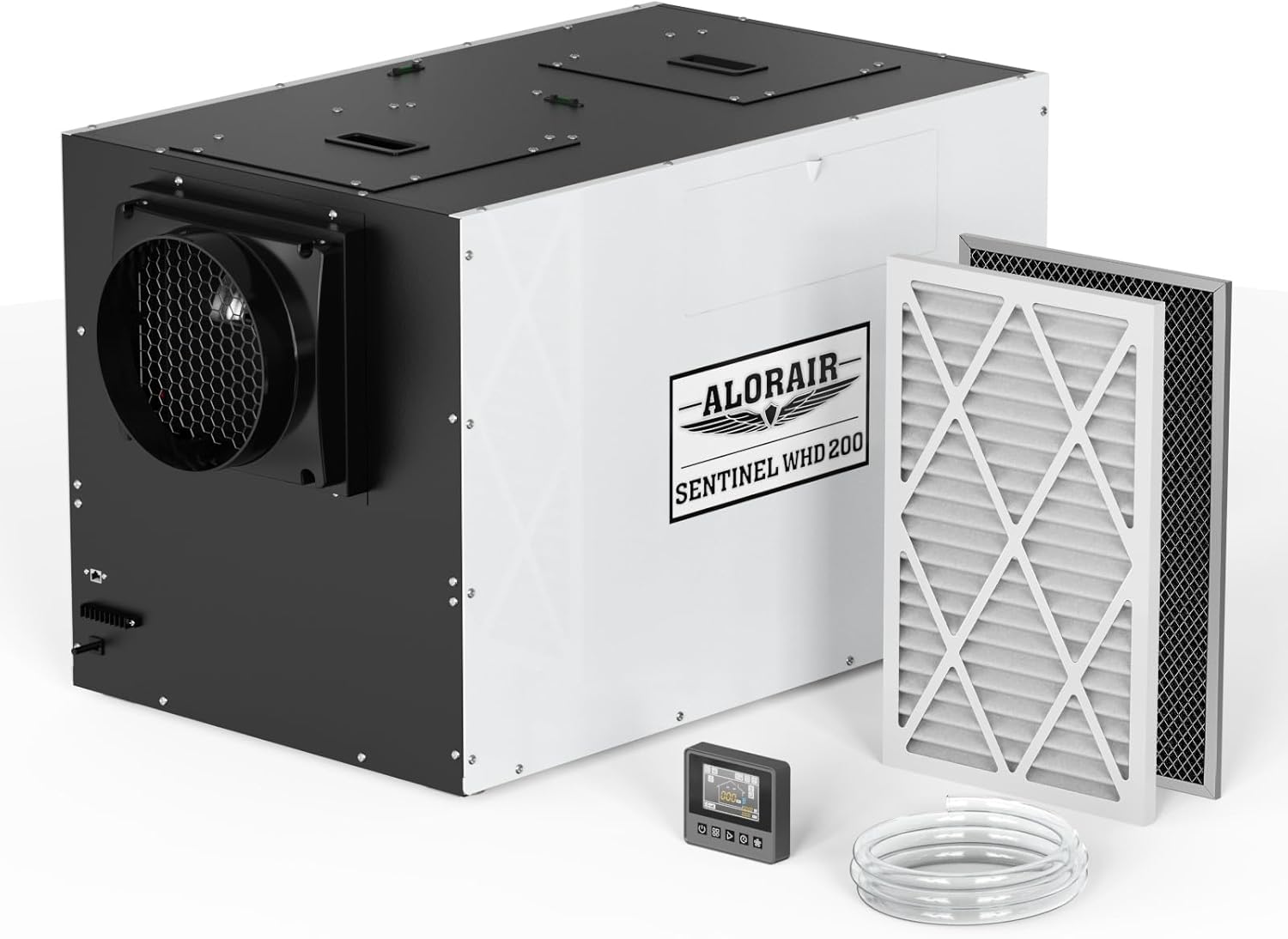
AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 200
![AlorAir® Sentinel WHD 200]()
Size for
4500 Sq.Ft
AHAM, (80°F, 60% RH)(Pints)
165 Pints
Airflow
309CFM, 413CFM
Unit Dimensions
37.3"D x 23.4"W x 24.3"H
Whole House Dehumidifiers
-
AlorAir® Sentinel Pro 55X
![AlorAir® Sentinel Pro 55X]()
Capacity
120 PPD at Saturation, 55 PPD@AHAM
Size for
1500 sq.ft
Air Flow
187 CFM/318CMH
Unit Dimensions
12.9"D x 14.14"W x 24.55"H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel Pro 35X
![AlorAir® Sentinel Pro 35X]()
Capacity
70 PPD at Saturation, 35 PPD@AHAM
Size for
1000 sq.ft
Air Flow
180 CFM/306CMH
Unit Dimensions
12.9"D x 14.14"W x 24.55"H
-
AlorAir® Sentinel SLGR 1400X
![AlorAir® Sentinel SLGR 1400X]()
Capacity
275 PPD at Saturation, 140 PPD@AHAM
Size for
3800 sq.ft
Air Flow
440 CFM, 680 CMH
Unit Dimensions
15.2"D x 14.4"W x 24.8"H
-
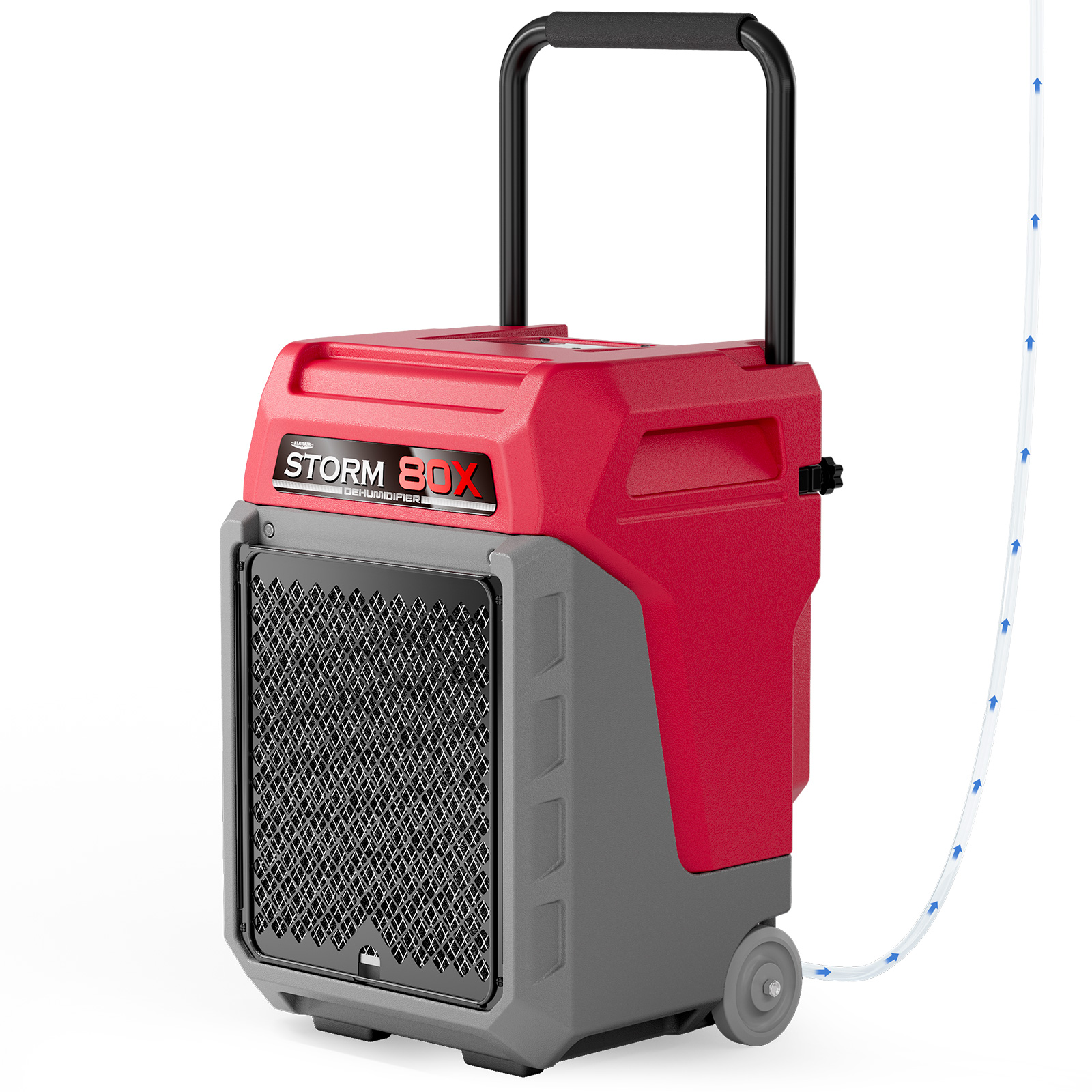
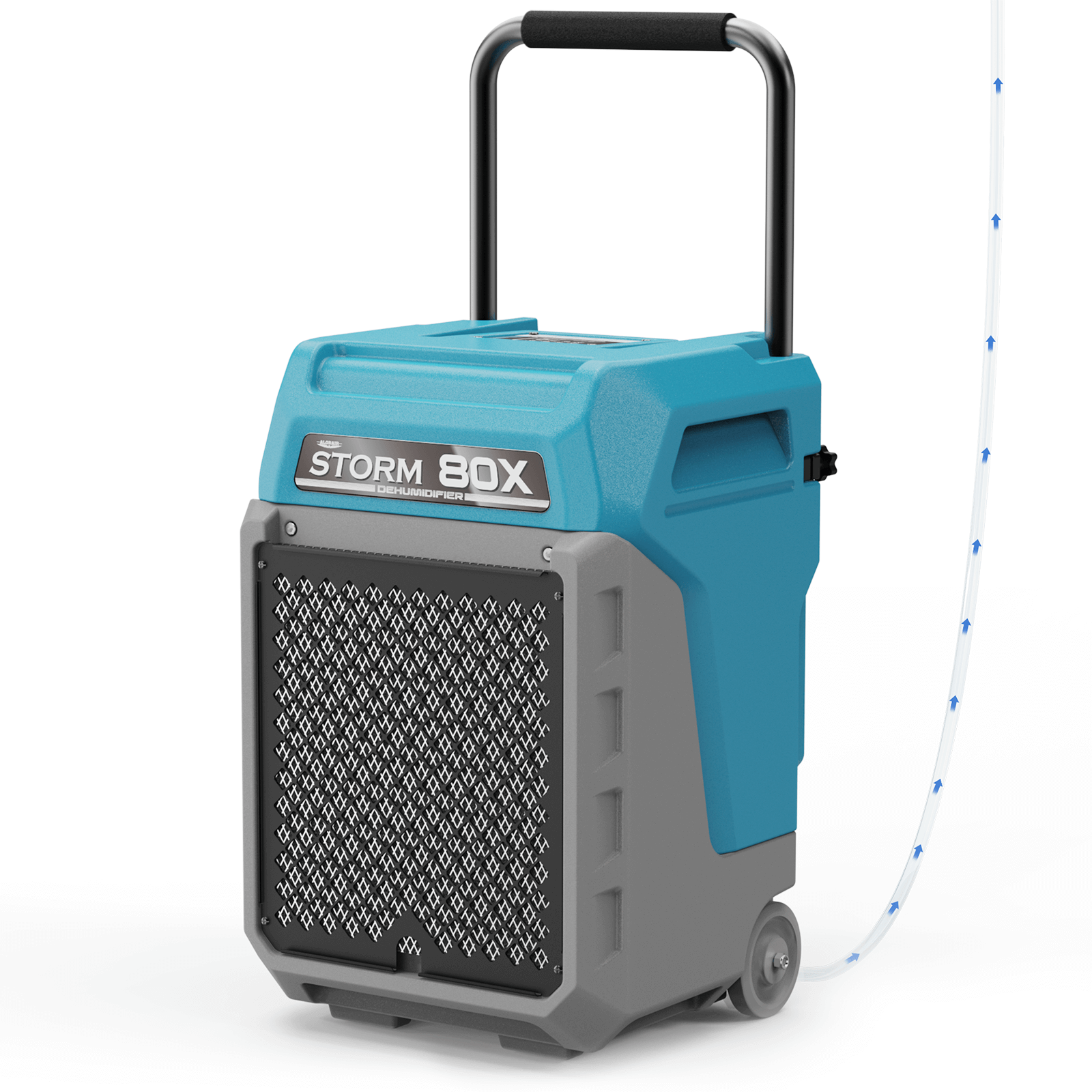
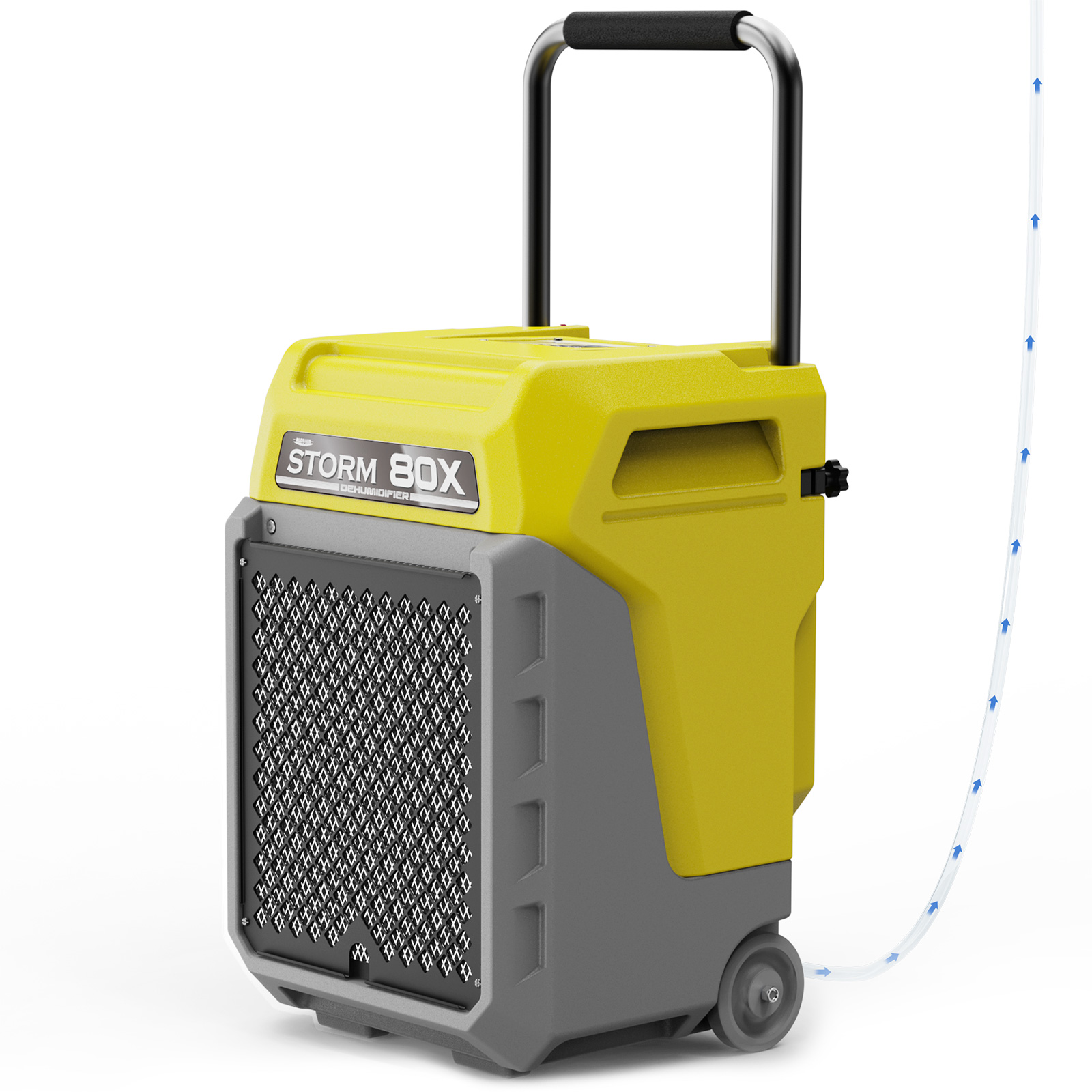
AlorAir® Storm 80X
![AlorAir® Storm 80X]()
![AlorAir® Storm 80X]()
![AlorAir® Storm 80X]()
![AlorAir® Storm 80X]()
Capacity
170 PPD at Saturation, 80 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2100 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
15.2"D x 14.4"W x 24.8"H
-
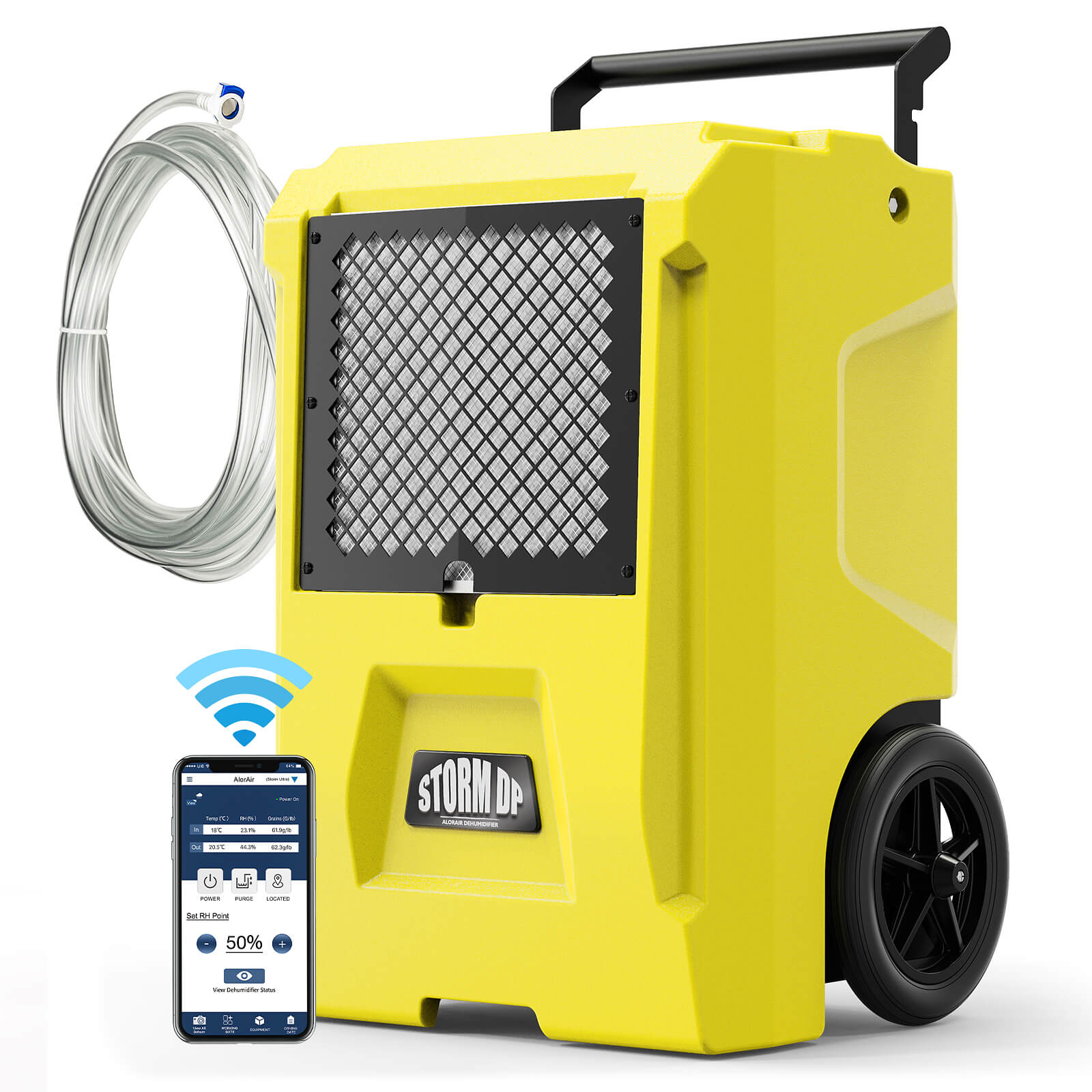
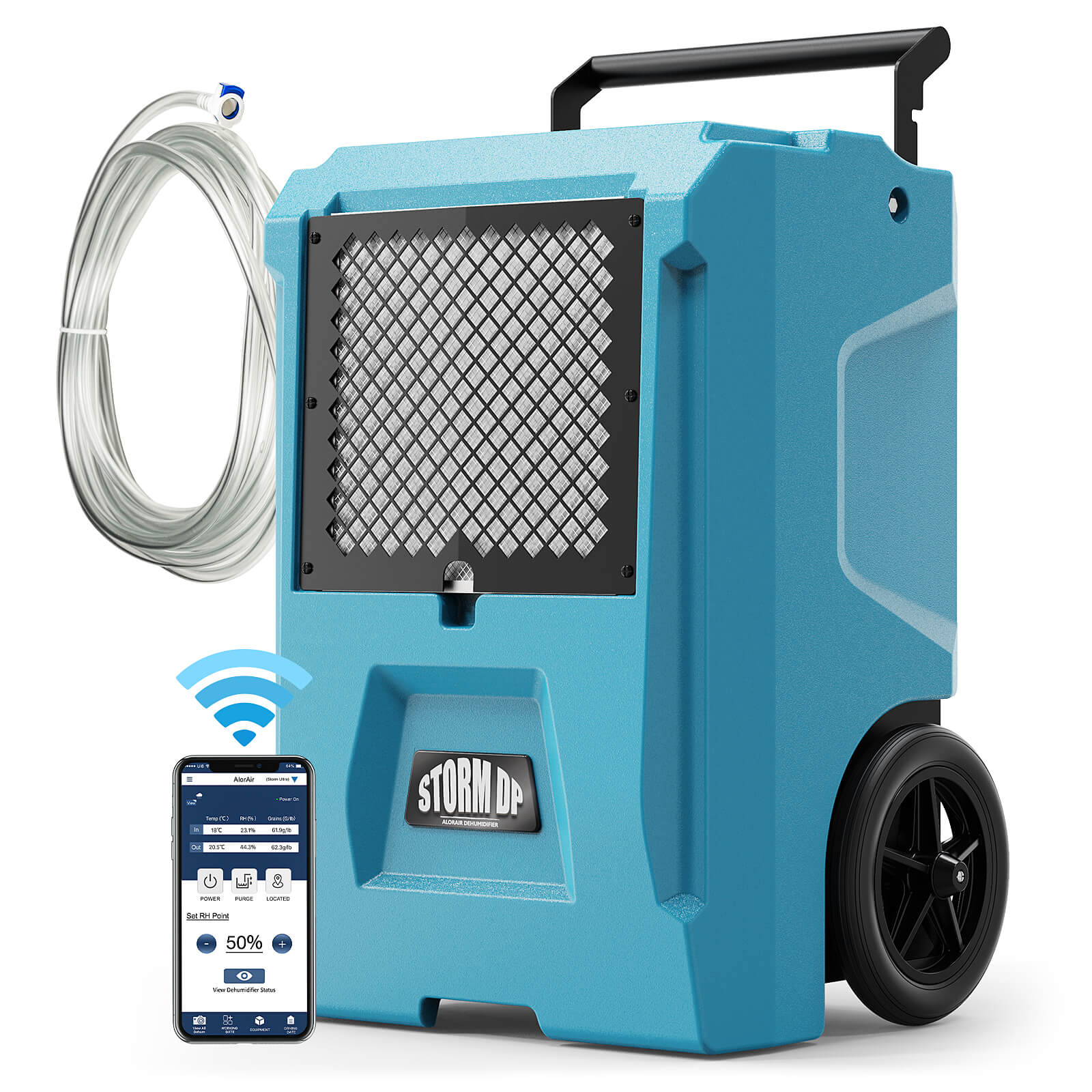
AlorAir® Storm DP Single-Voltage
![AlorAir® Storm DP Single-Voltage]()
![AlorAir® Storm DP Single-Voltage]()
Capacity
110 PPD at Saturation, 50 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
1300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
14" D x 17" W x 23.1" H
-
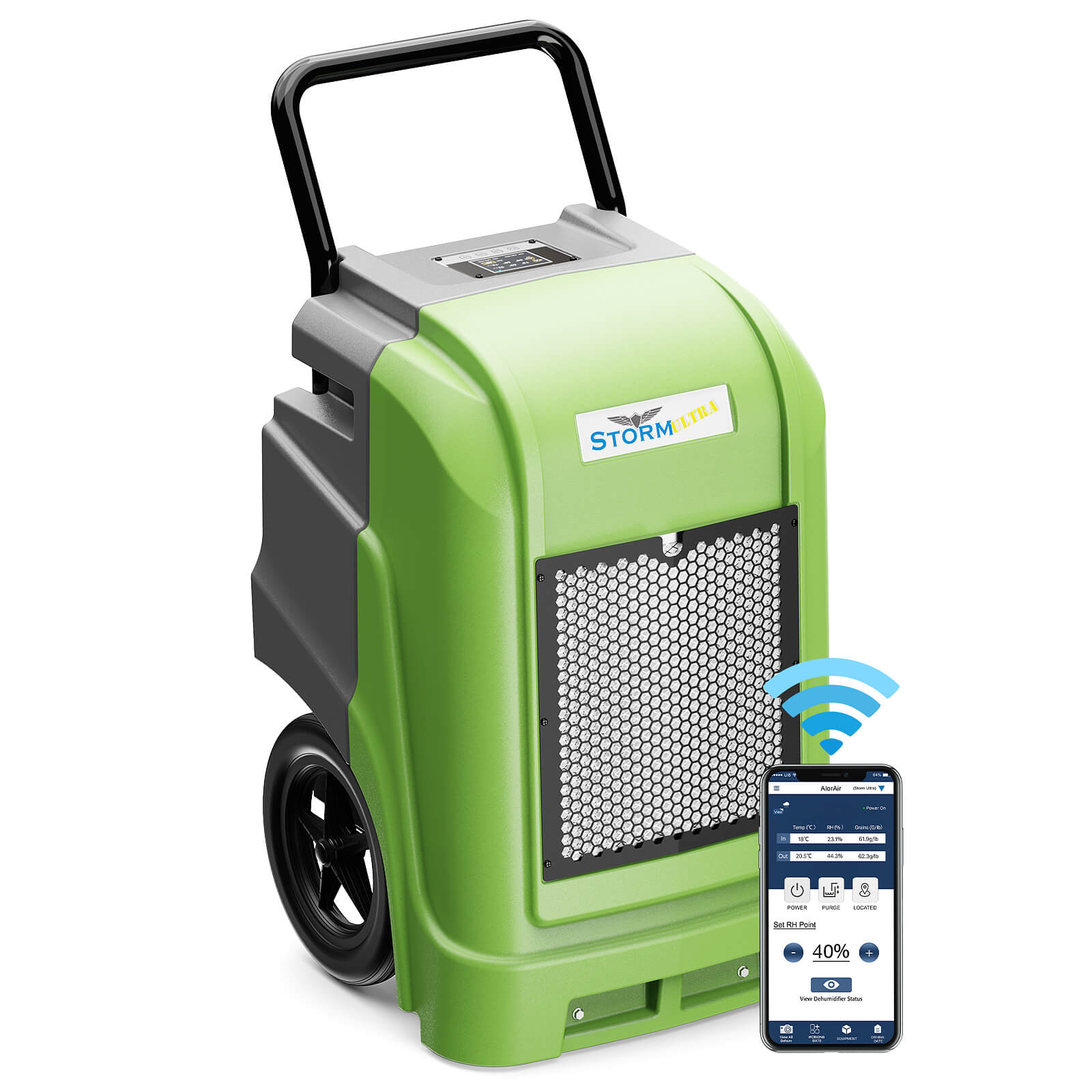
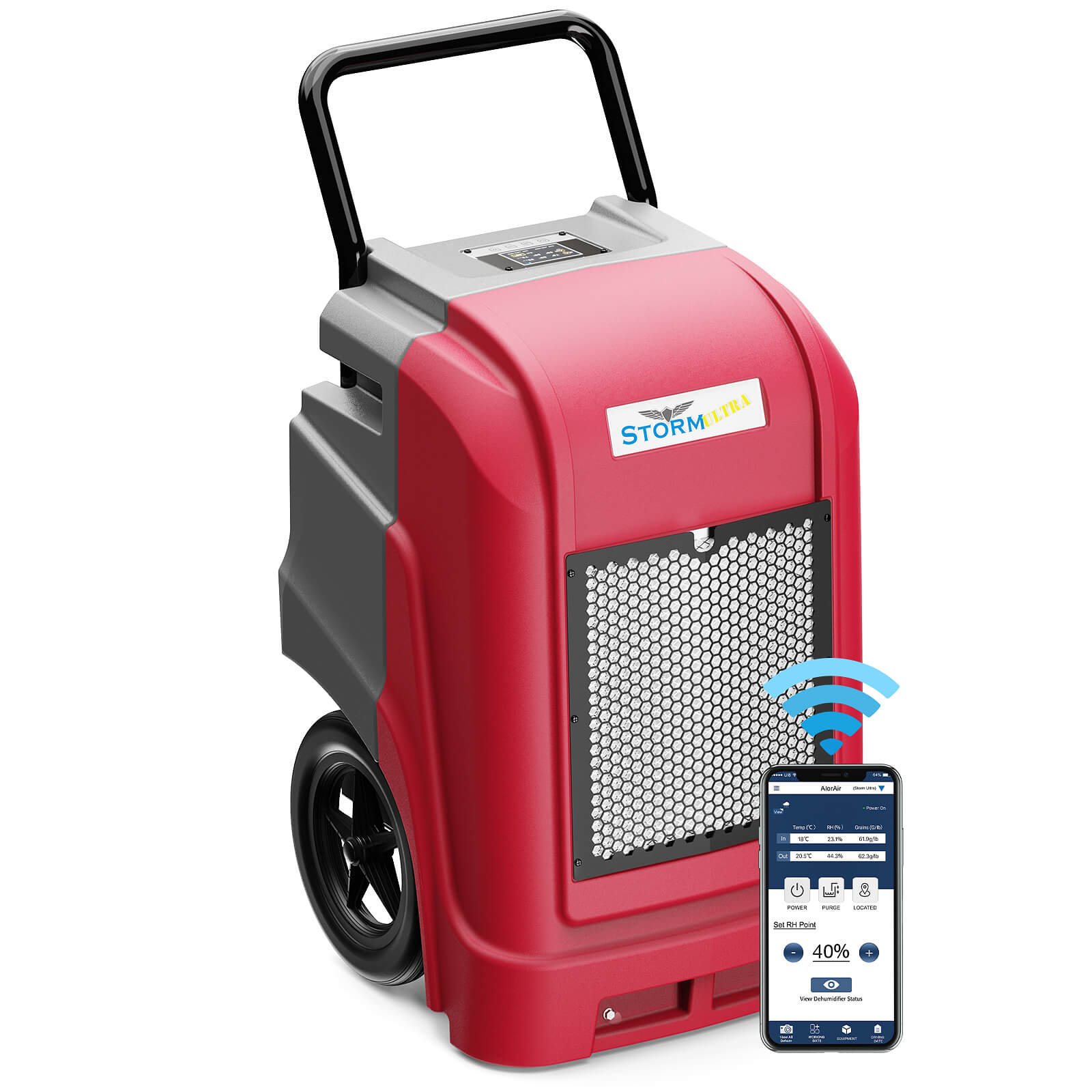
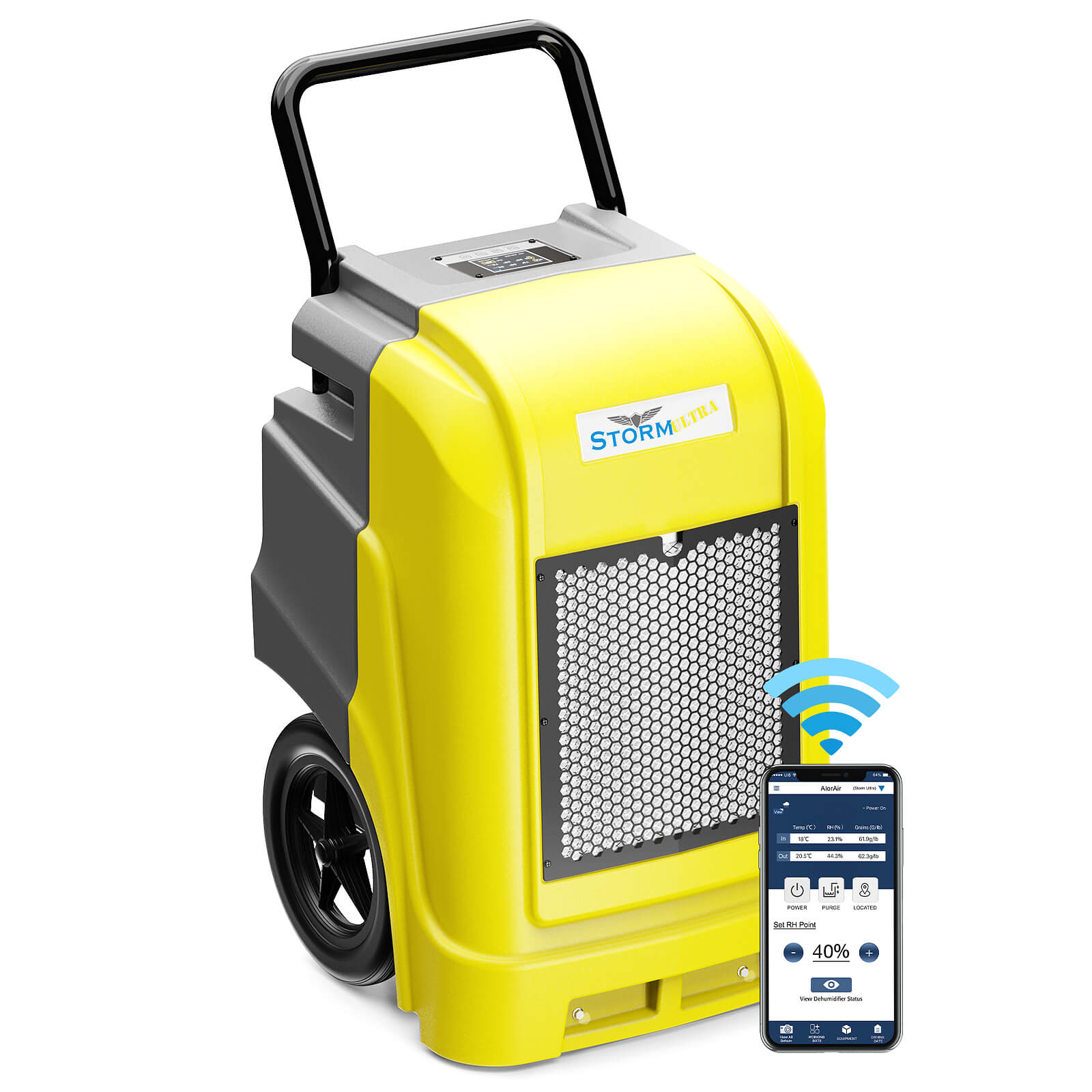
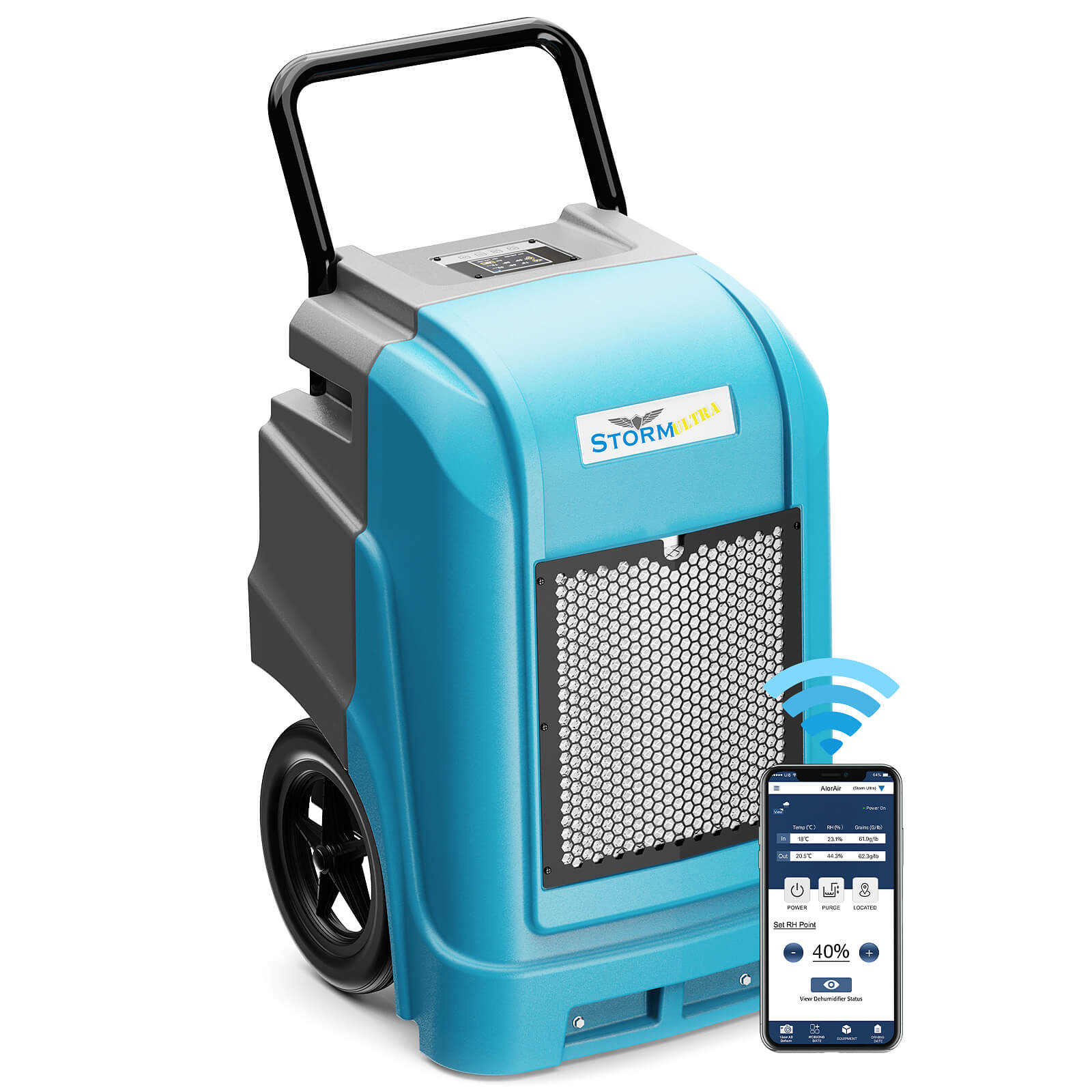
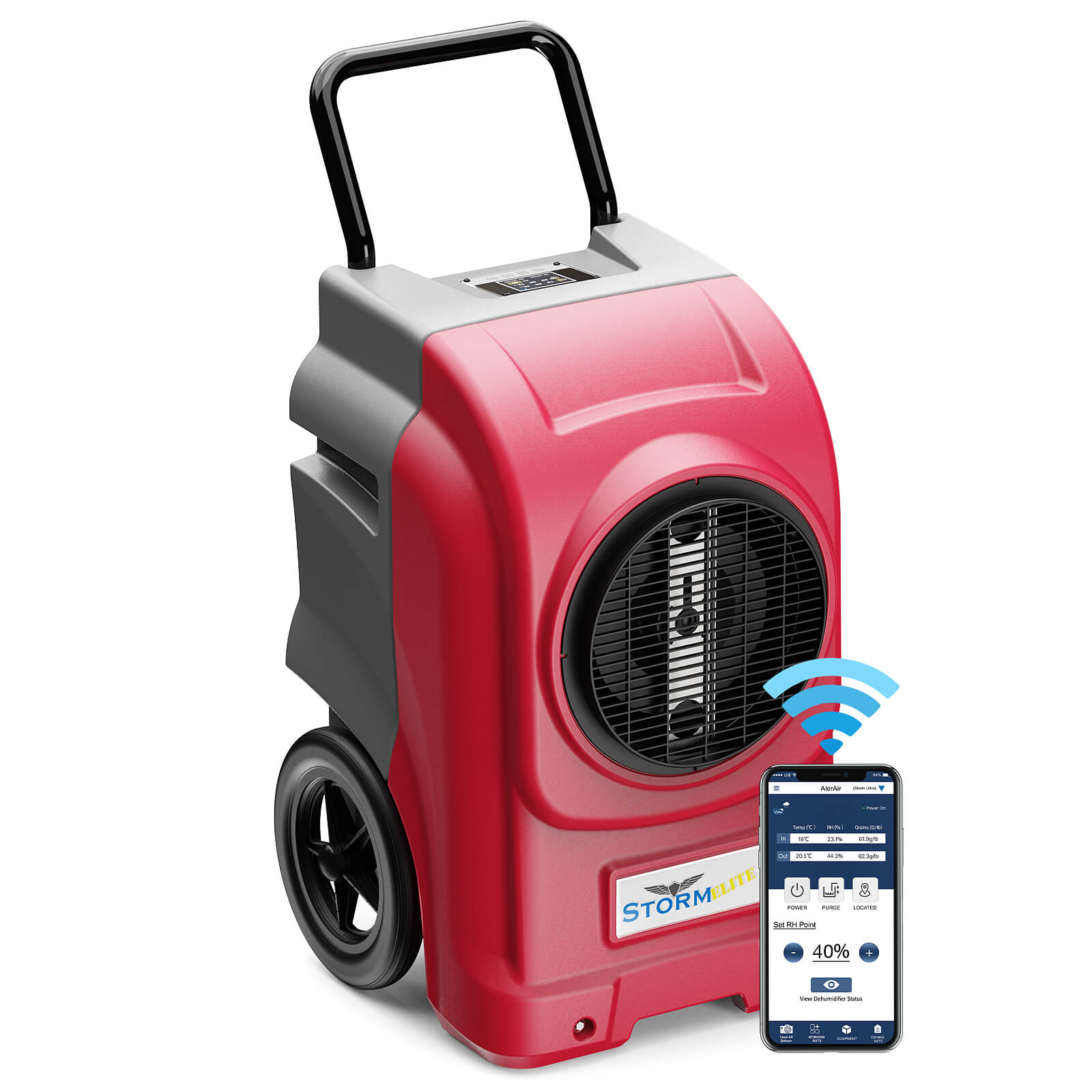
AlorAir® Storm Ultra
![AlorAir® Storm Ultra]()
![AlorAir® Storm Ultra]()
![AlorAir® Storm Ultra]()
![AlorAir® Storm Ultra]()
Capacity
190 PPD at Saturation, 90 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
2600 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
21.2" D×22" W×38" H
-
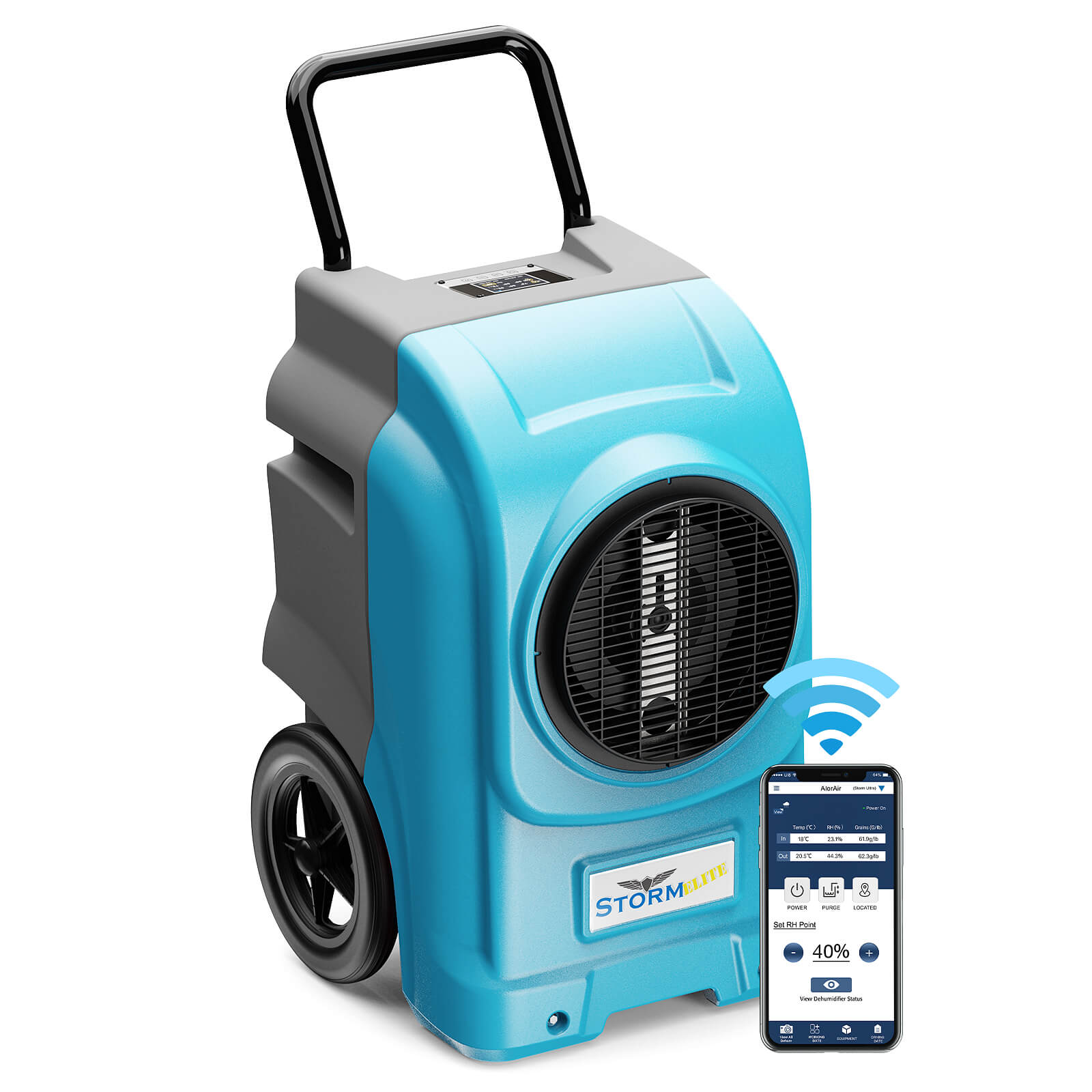
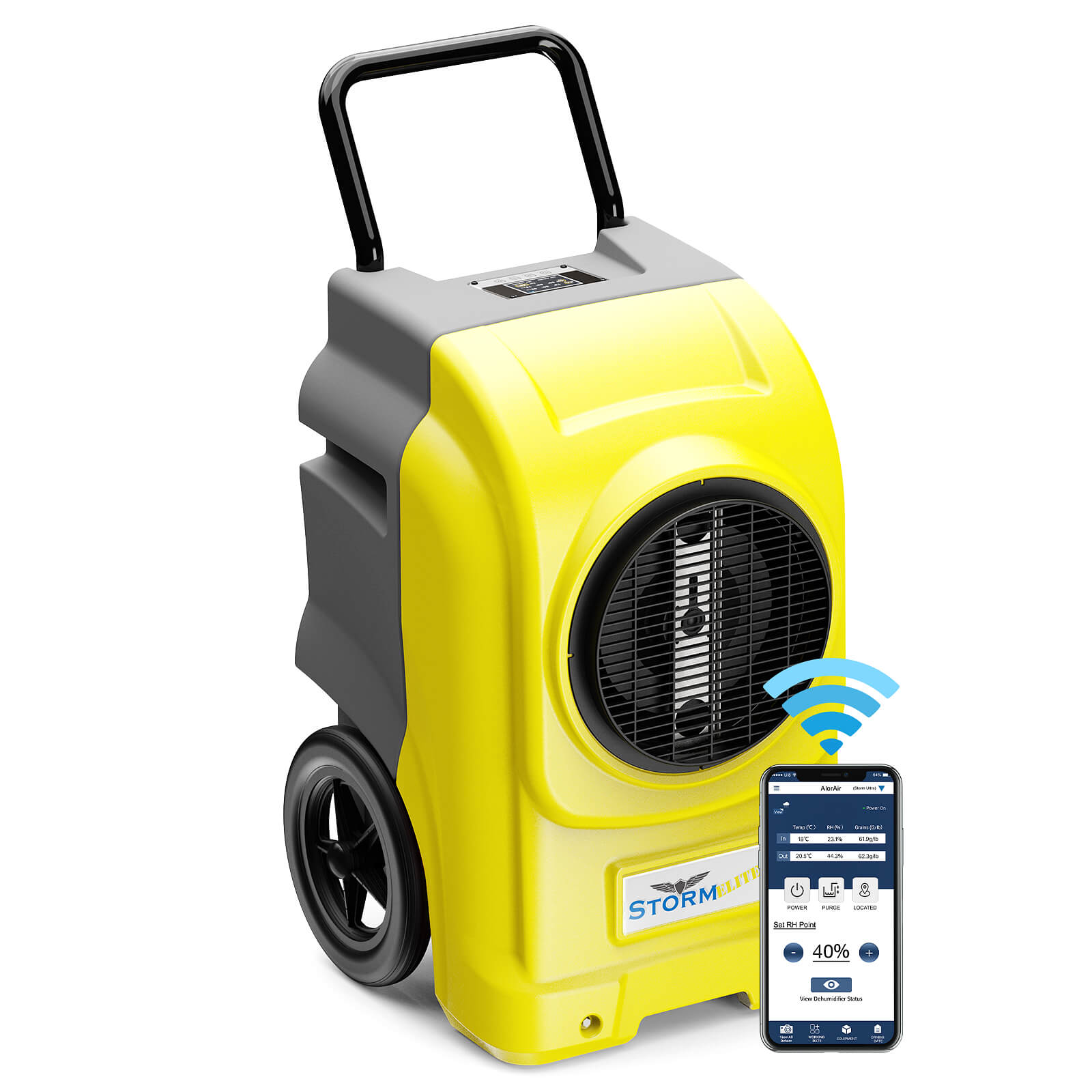
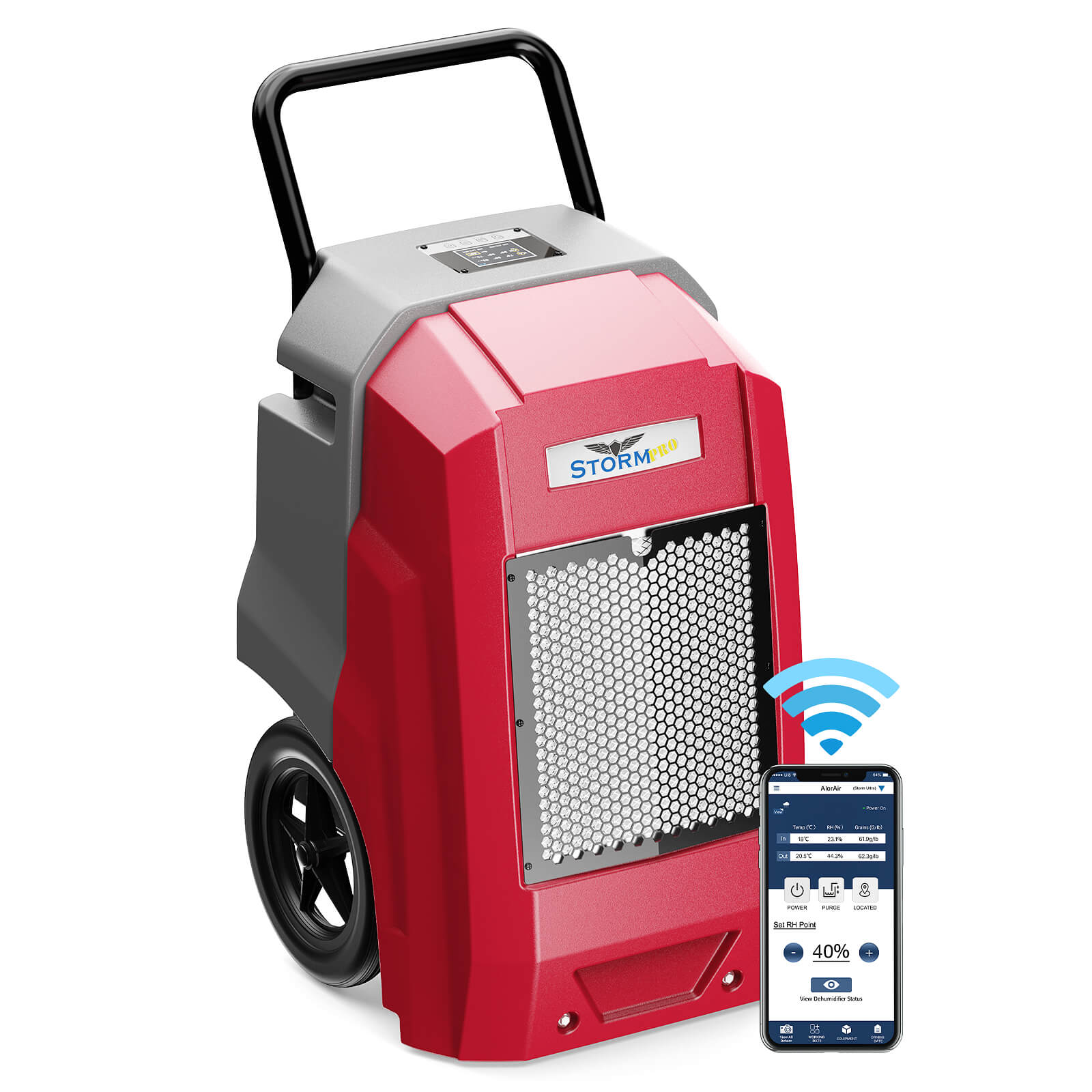
AlorAir® Storm Elite
![AlorAir® Storm Elite]()
![AlorAir® Storm Elite]()
![AlorAir® Storm Elite]()
![AlorAir® Storm Elite]()
Capacity
270 PPD at Saturation, 125 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
3000 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
22.3" D×23.6" W×39.7" H
-
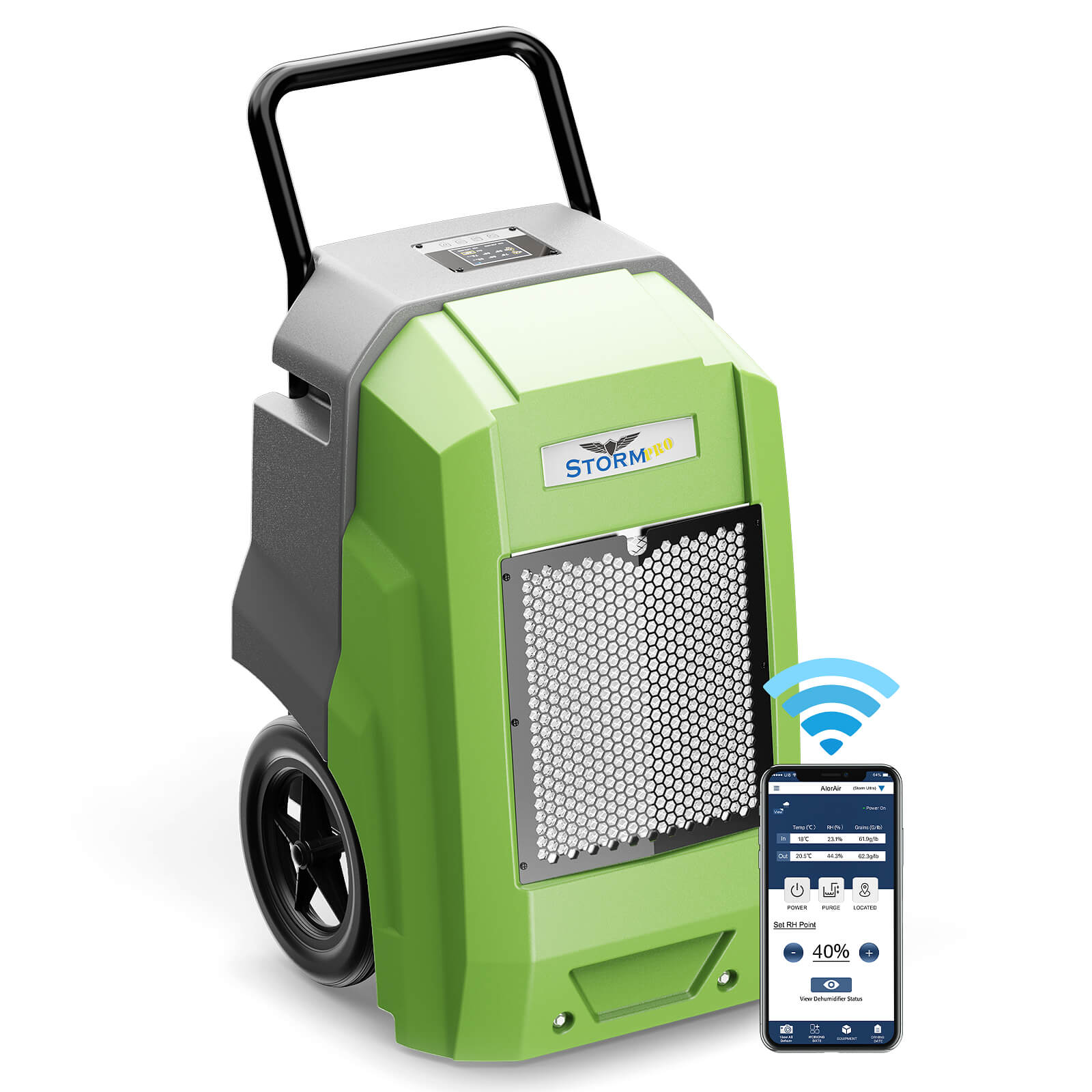
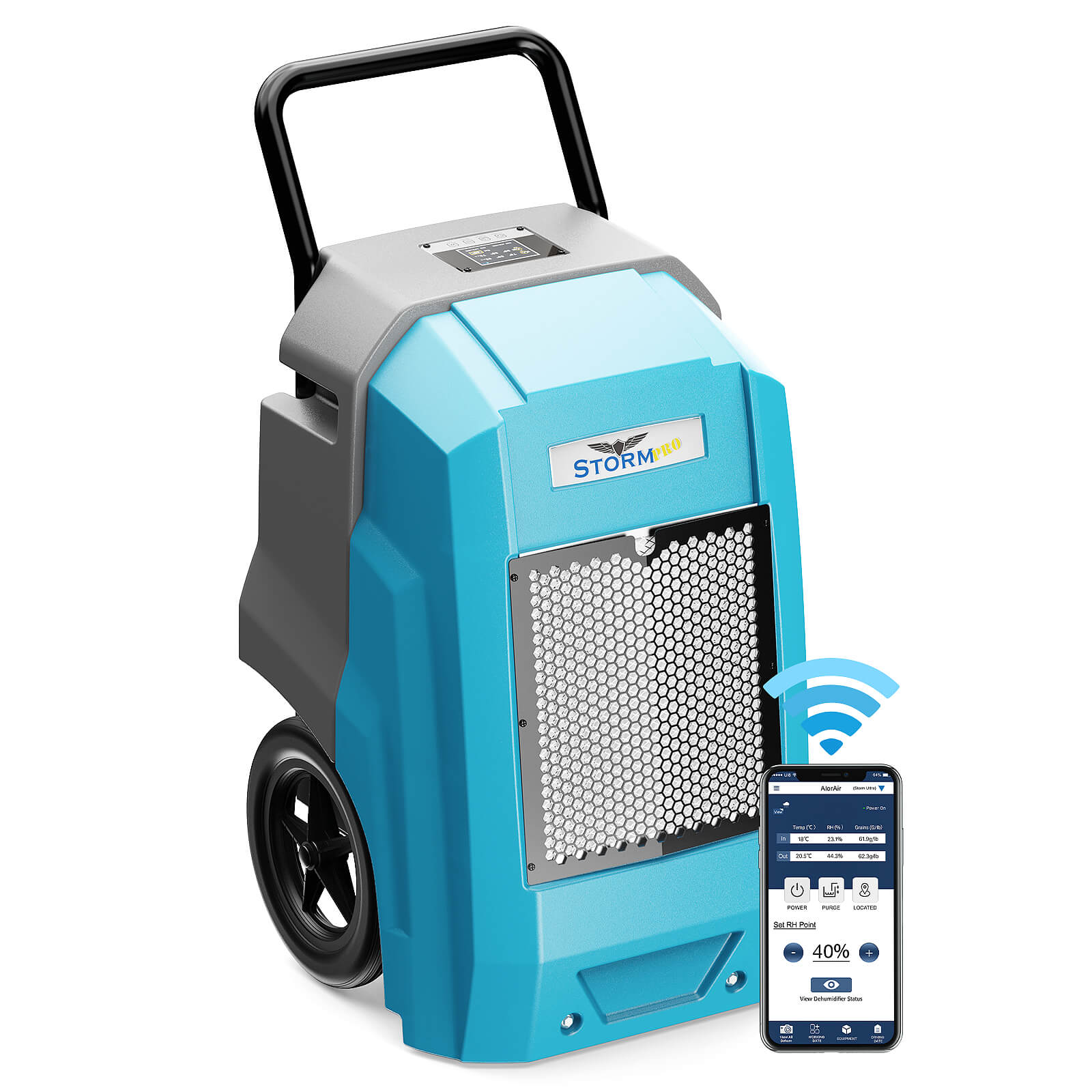
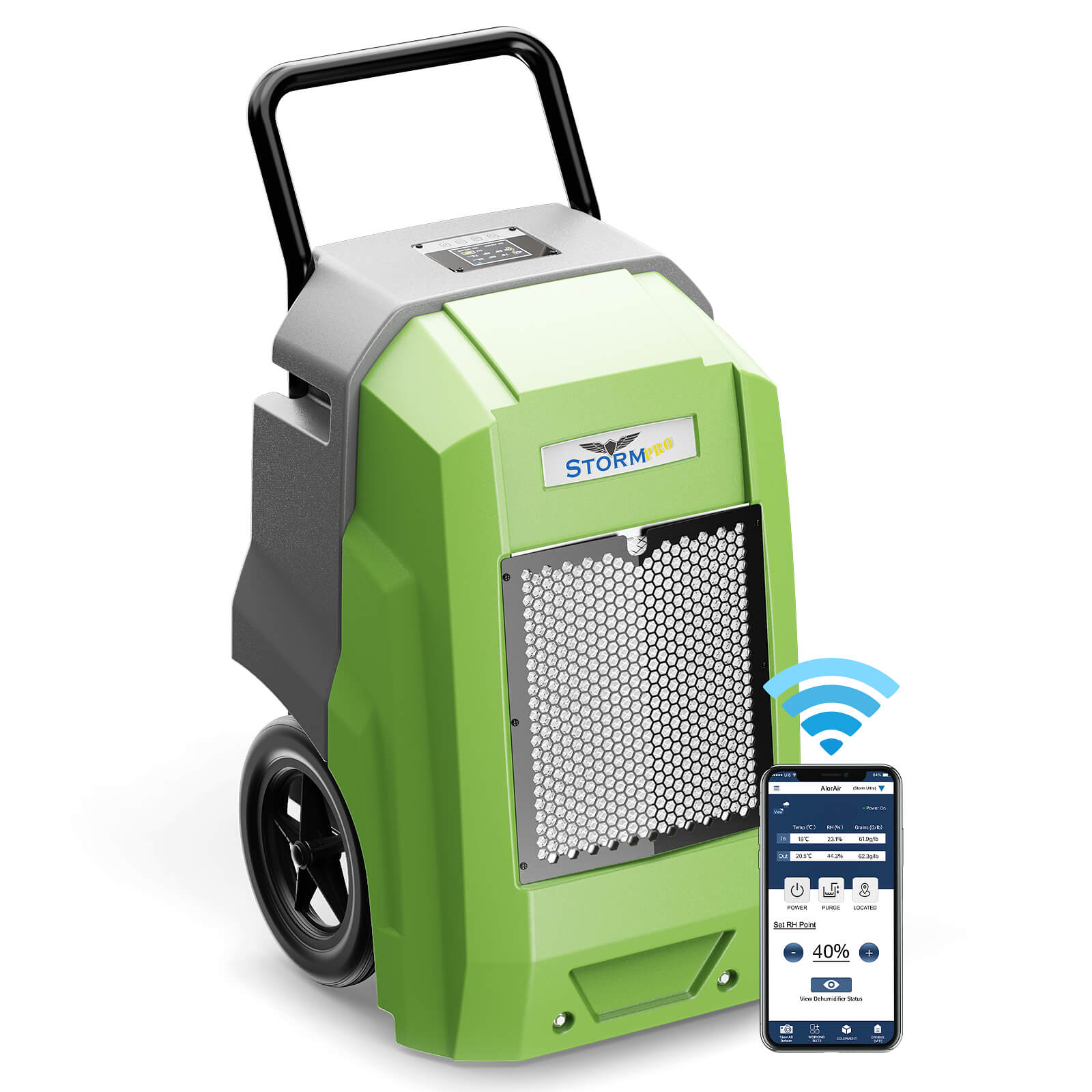
AlorAir® Storm Pro Dehumidifier
![AlorAir® Storm Pro Dehumidifier]()
![AlorAir® Storm Pro Dehumidifier]()
![AlorAir® Storm Pro Dehumidifier]()
![AlorAir® Storm Pro Dehumidifier]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation, 85 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
2300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
21.2" D×22" W×38" H
-
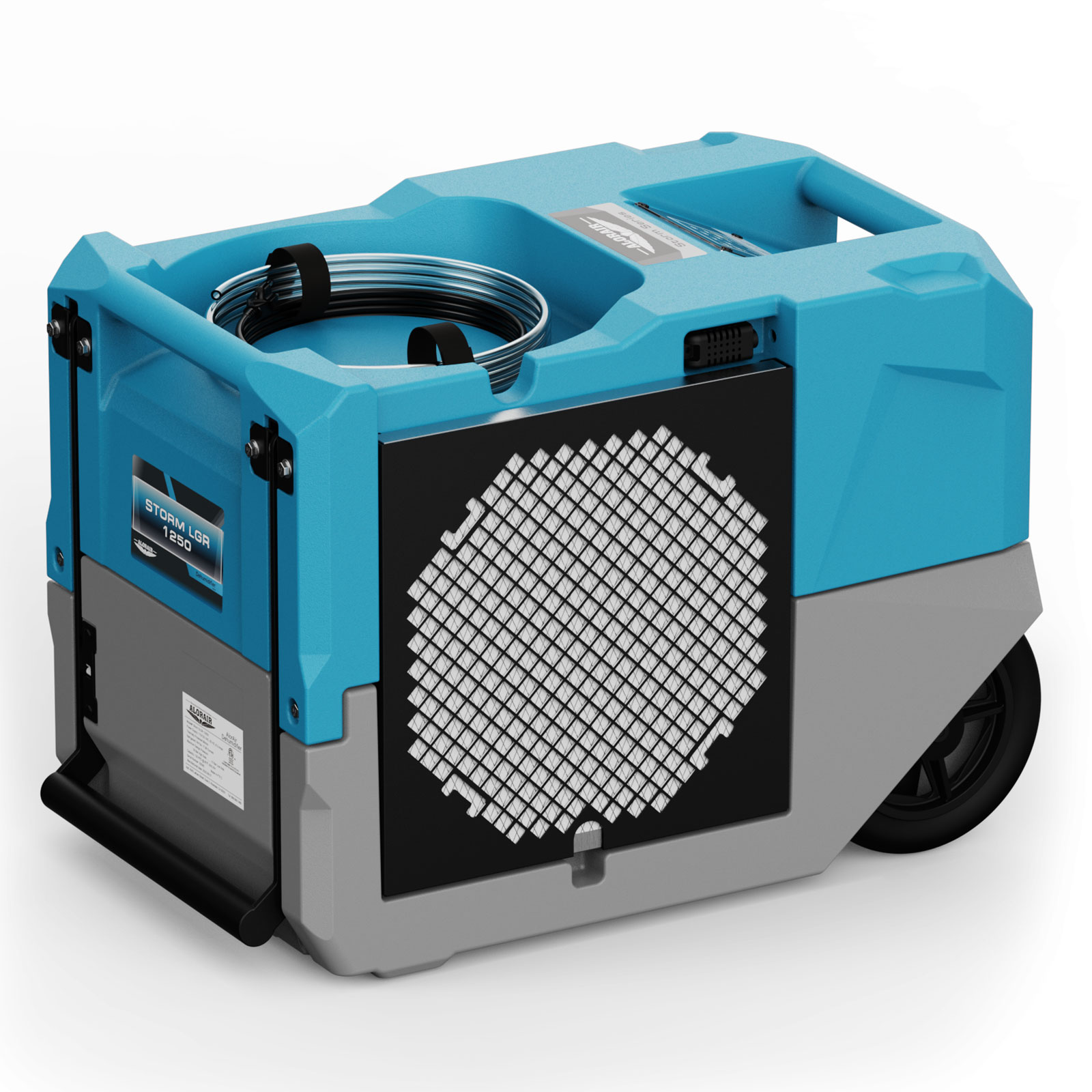
AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250
![AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250]()
Capacity
264 PPD at Saturation, 125 PPD@AHAM
Size for
3000 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
26.1" D x15.5" W x17.6" H
-
AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250X
![AlorAir® Storm LGR 1250X]()
Capacity
264 PPD at Saturation, 125 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
3000 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
26.1" D x15.5" W x17.6" H
-
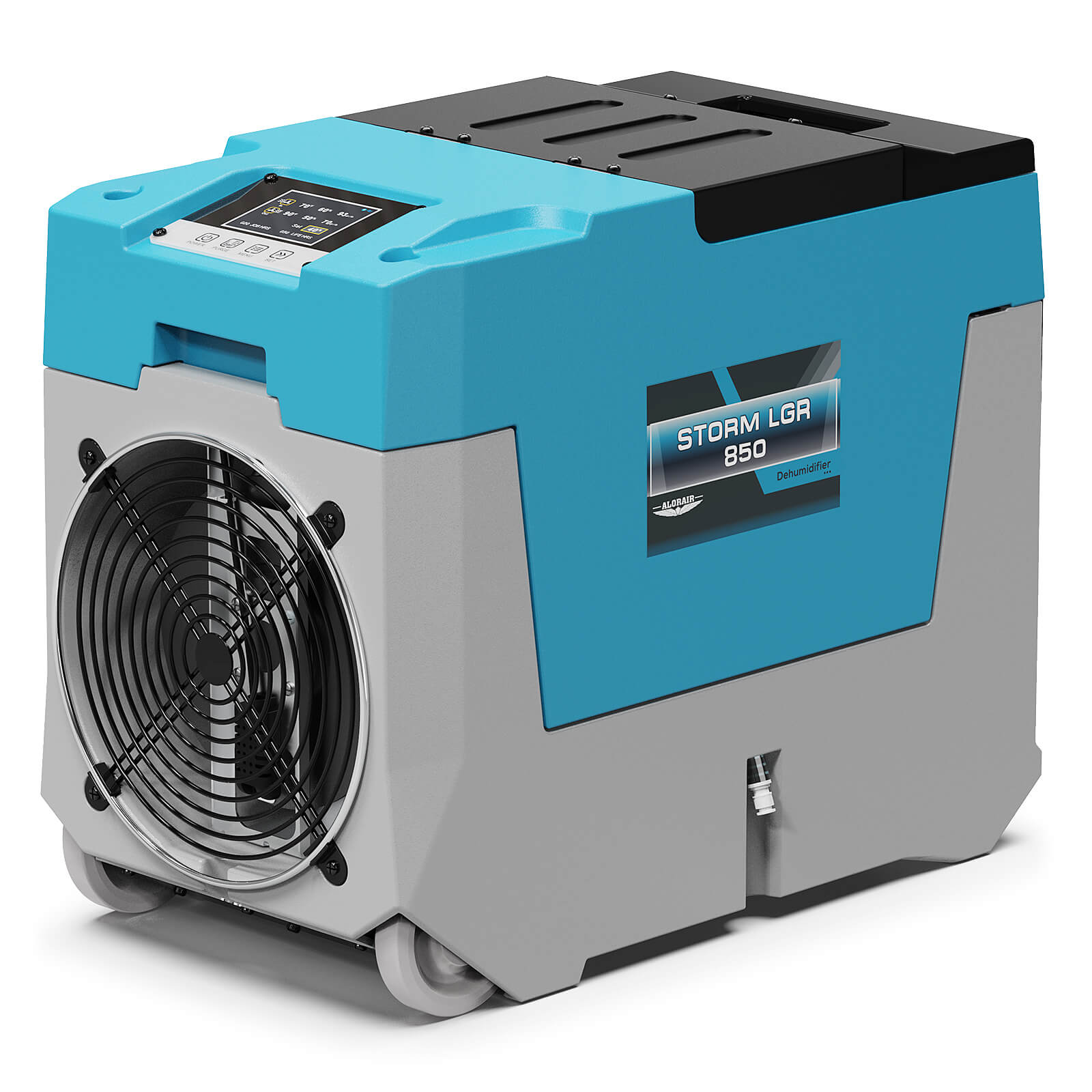
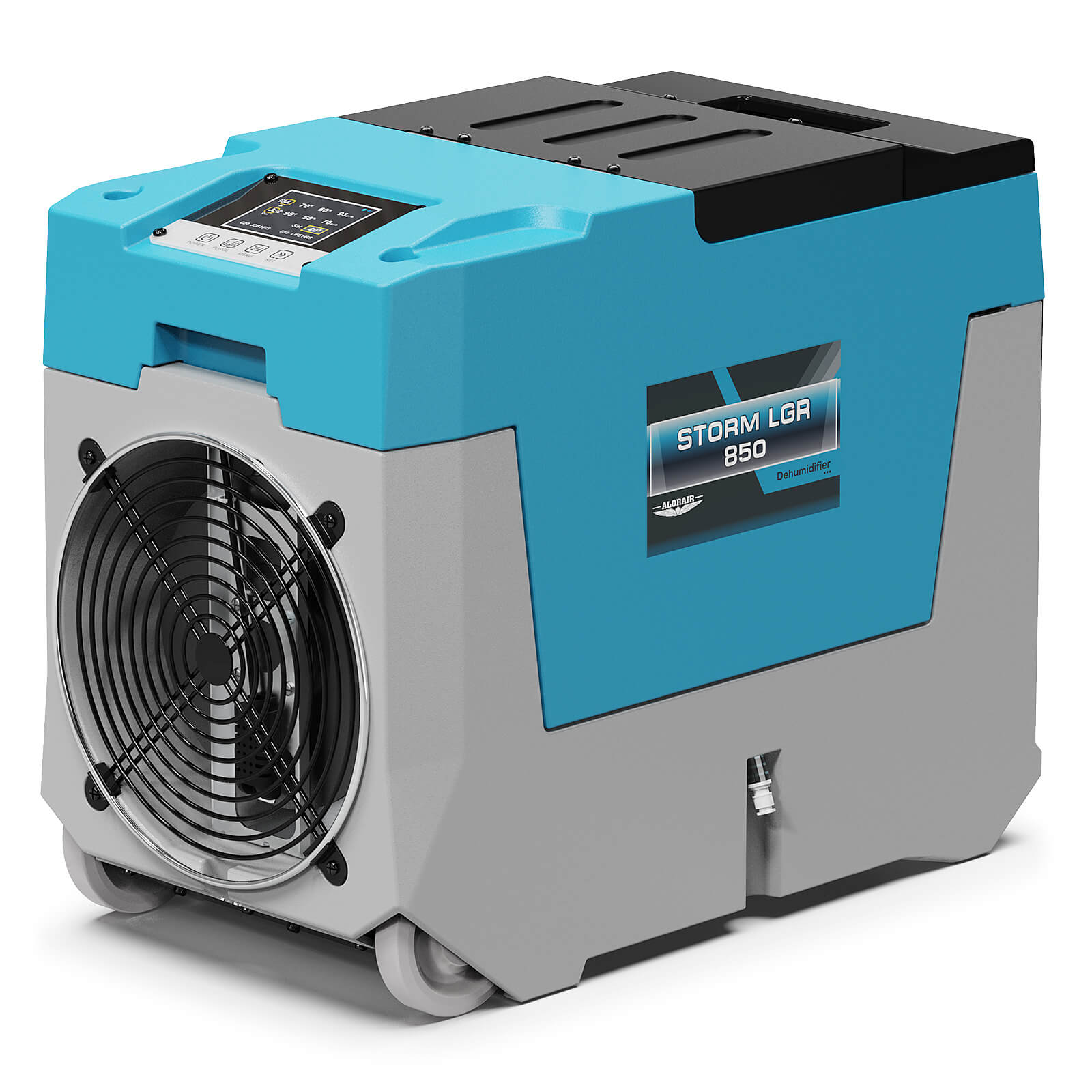
AlorAir® Storm LGR 850
![AlorAir® Storm LGR 850]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR 850]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation, 85 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
21" D×11.6" W ×17.3" H
-
AlorAir® Storm LGR 850X
![AlorAir® Storm LGR 850X]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation, 85 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
2300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
21" D×11.6" W ×17.3" H
-
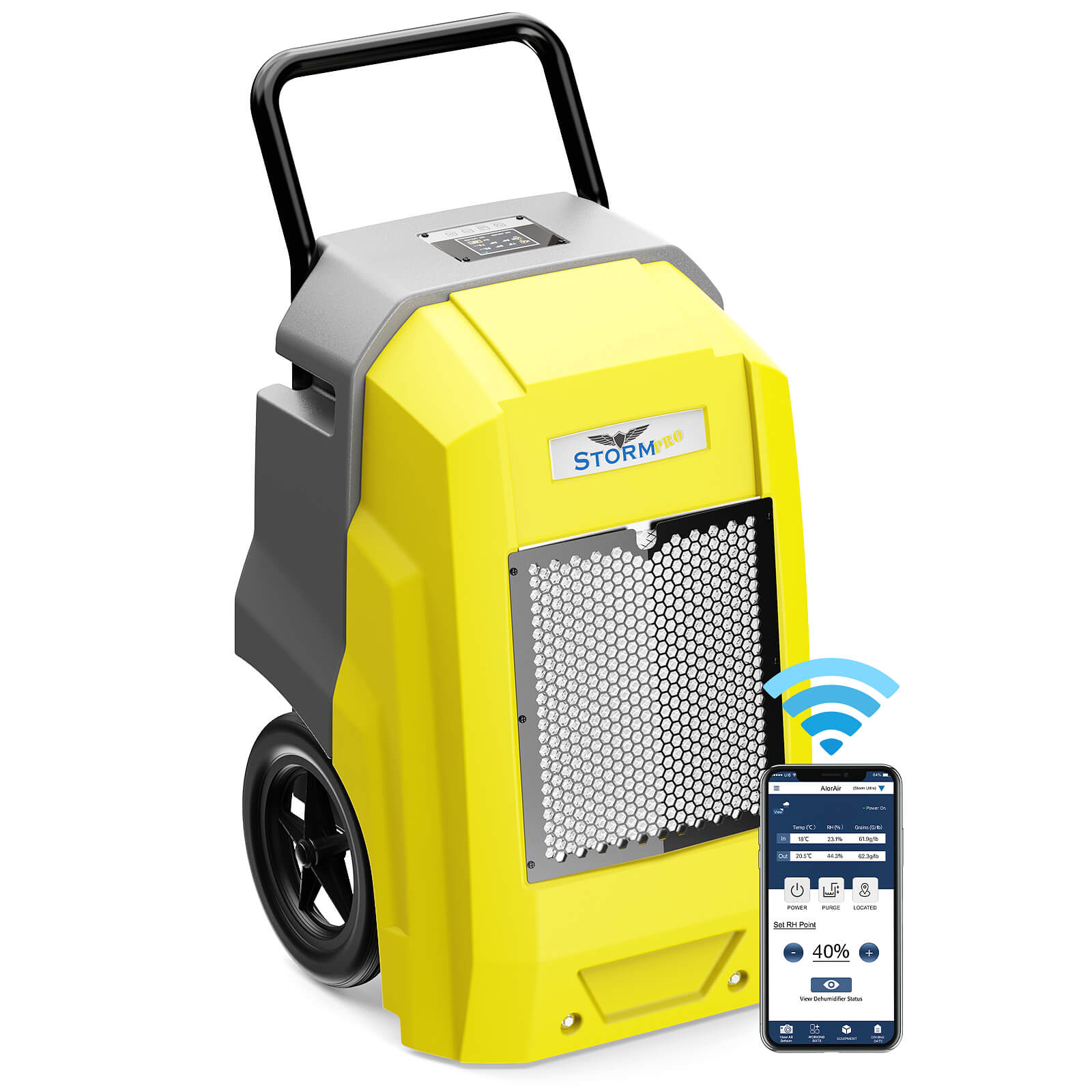
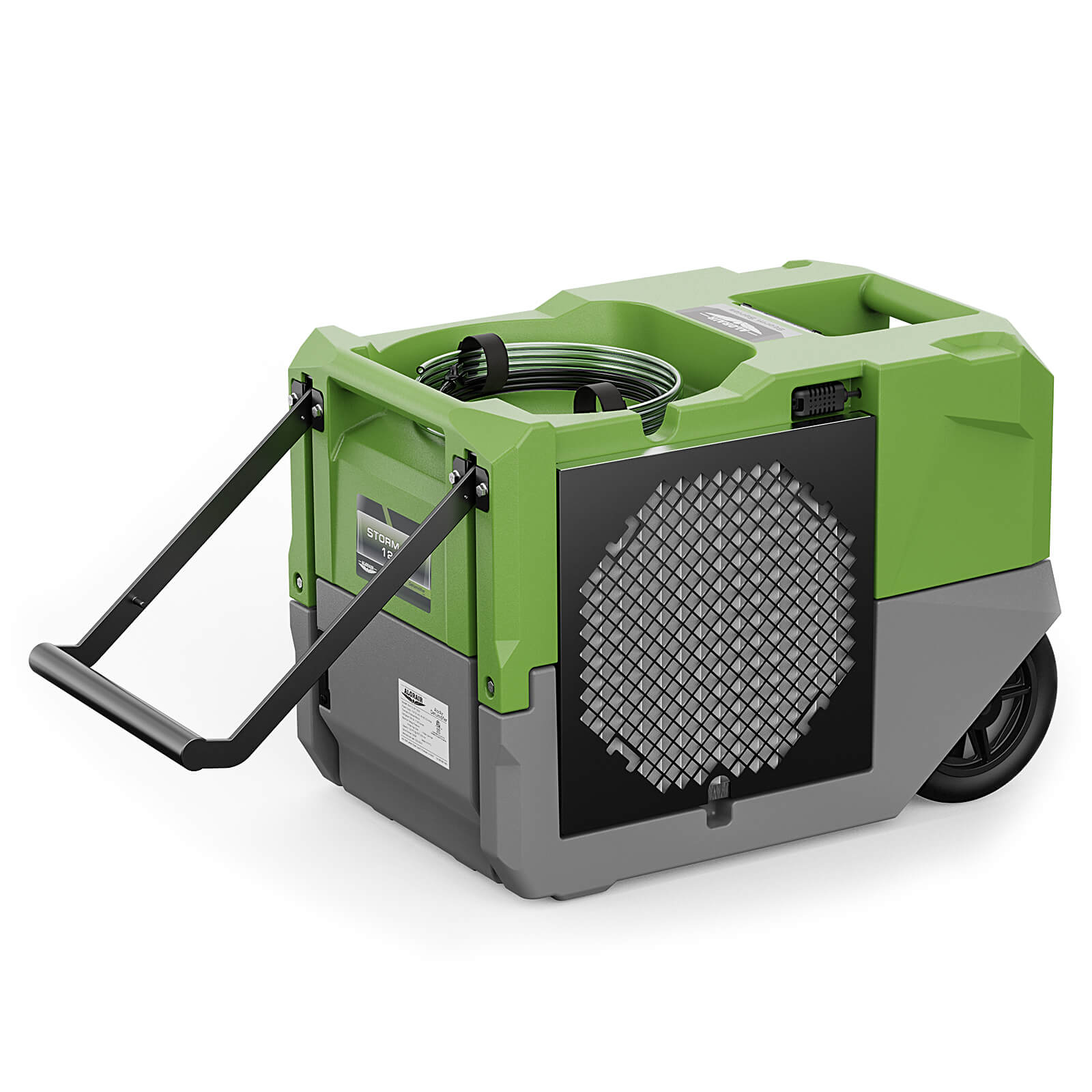
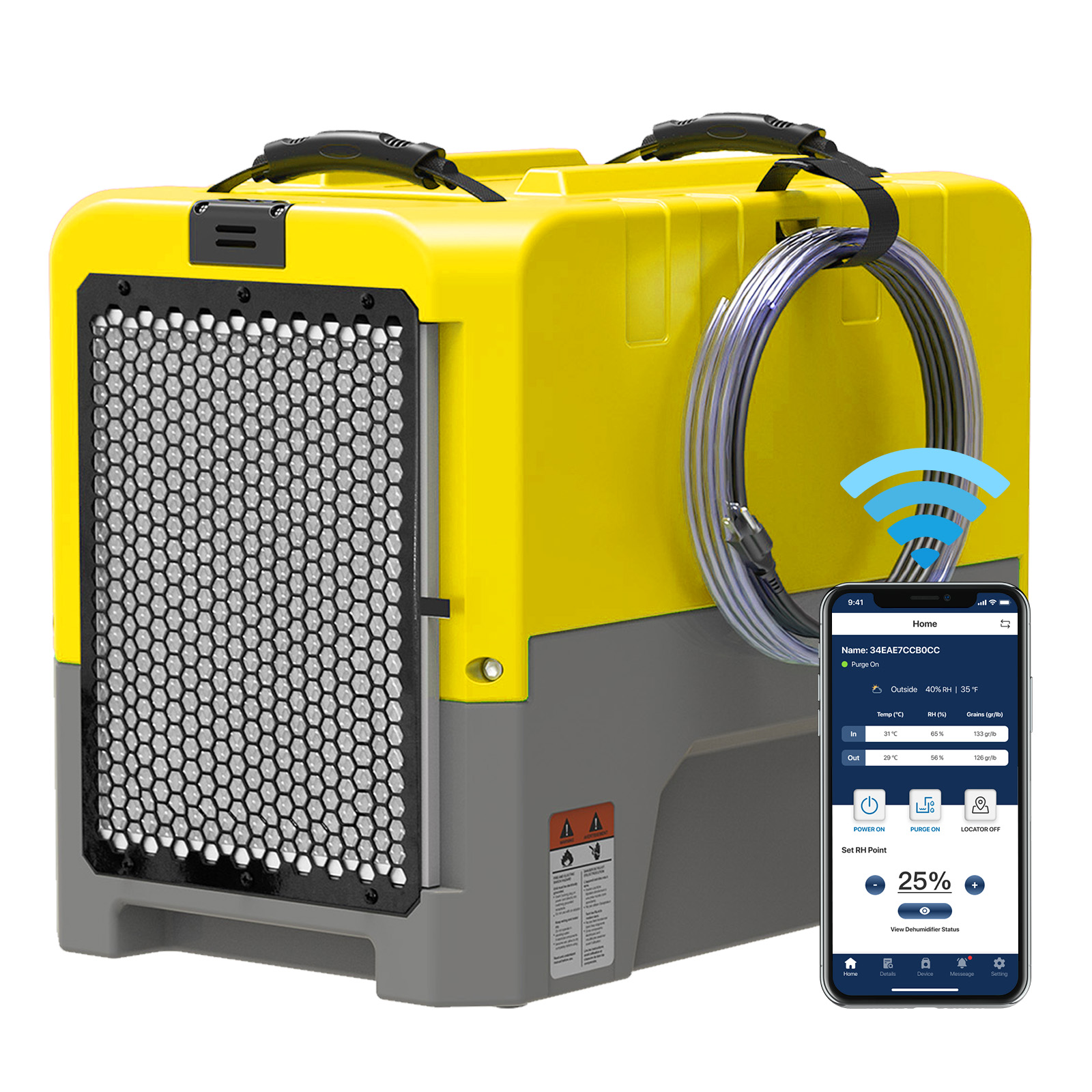
AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme Smart App Control
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme Smart App Control]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme Smart App Control]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme Smart App Control]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme Smart App Control]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation, 85 PPD@AHAM
Coverage
2300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
22.8" D ×13.7" W ×17.3" H
-
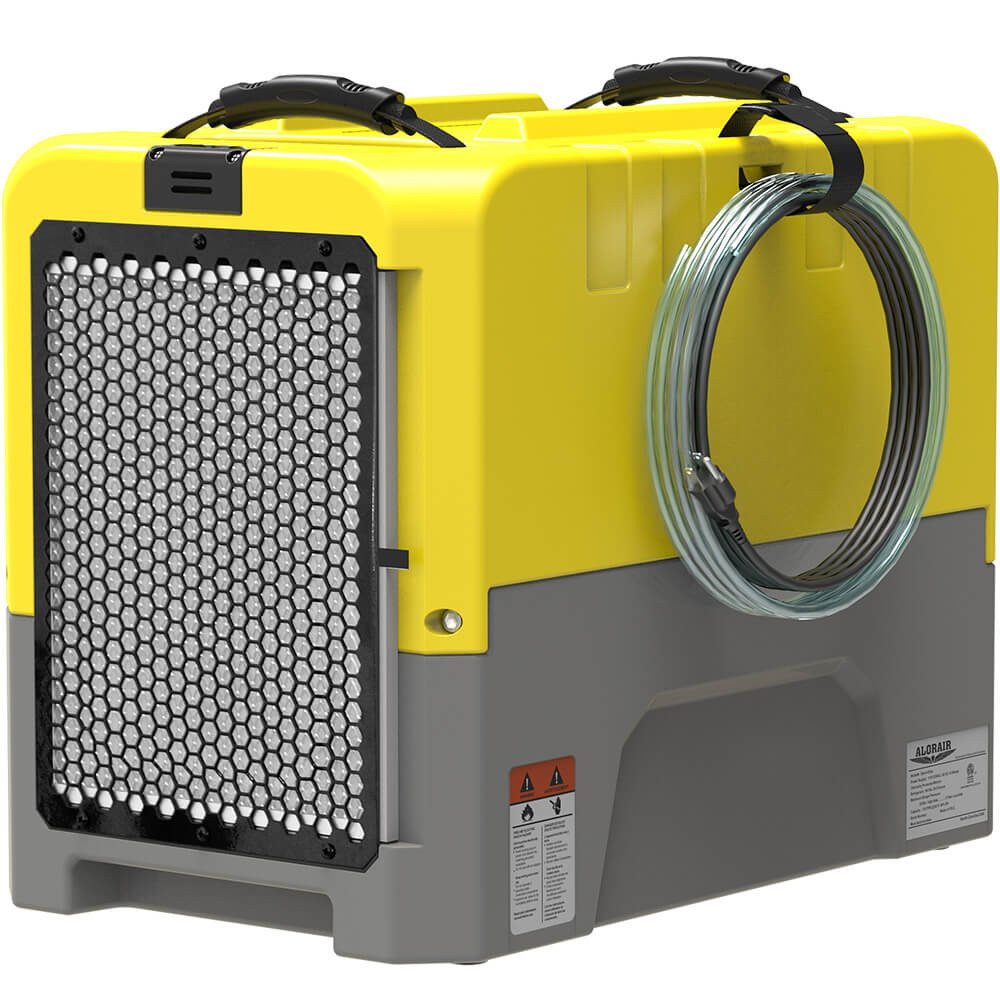
AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme (Hot Sale)
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme (Hot Sale)]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme (Hot Sale)]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme (Hot Sale)]()
![AlorAir® Storm LGR Extreme (Hot Sale)]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation, 85 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
22.8" D ×13.7" W ×17.3" H
Commercial & Industrial Dehumidifiers
-
AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 970
![AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 970]()
Built-in UV-C light
Yes
Airflow
270-750 CFM
Size for
1100 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 870
![AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 870]()
Built-in UV-C light
Yes
Airflow
270-550 CFM
Size for
800 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 -filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 770
![AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Max 770]()
Built-in UV-C light
No
Airflow
270-550 CFM
Size for
800 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 970
![AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 970]()
Built-in UV-C light
Yes
Airflow
270-750 CFM
Size for
1100 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 870
![AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 870]()
Built-in UV-C light
Yes
Airflow
270-550 CFM
Size for
800 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 770
![AlorAir® PureAiro HEPA Pro 770]()
Built-in UV-C light
No
Airflow
270-550 CFM
Size for
800 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
AlorAir® Cleanshield HEPA 550 (Hot Sale)
![AlorAir® Cleanshield HEPA 550 (Hot Sale)]()
![AlorAir® Cleanshield HEPA 550 (Hot Sale)]()
![AlorAir® Cleanshield HEPA 550 (Hot Sale)]()
![AlorAir® Cleanshield HEPA 550 (Hot Sale)]()
Built-in UV-C light
No
Airflow
270-550 CFM
Size for
800 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 filter and HEPA/activated carbon filter
-
Purisystems S1 UVIG Air Scrubber
![Purisystems S1 UVIG Air Scrubber]()
New Tech
Built-in UV-C light and ionizer
Airflow
200-900 CFM
Size for
1100 sq.ft
Filtration system
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
-
Purisystems S1 UV Air Scrubber
![Purisystems S1 UV Air Scrubber]()
Built-in UV-C light
Yes
Airflow
200-900 CFM
Size for
1100 sq.ft
Filtration system
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
-
Purisystems S1 Air Scrubber
![Purisystems S1 Air Scrubber]()
Built-in UV-C light
No
Airflow
200-900 CFM
Size for
1100 sq.ft
Filtration system
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
-
Purisystems HEPA 600 UVIG (Medical Grade)
![Purisystems HEPA 600 UVIG (Medical Grade)]()
New Tech
Built-in UV-C light and lonizer
Airflow
270-600 CFM
Size for
800 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-10 Filter and HEPA/Activated Carbon Filter
-
Purisystems HEPA Pro UVIG (Industrial Grade)
![Purisystems HEPA Pro UVIG (Industrial Grade)]()
New Tech
Built-in UV-C light and ionizer
Airflow
800-2000 CFM
Size for
2500 sq.ft
Filtration system
MERV-8 Filter and H13 Clapboard Filter
-
Purisystems S2 Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)
![Purisystems S2 Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)]()
Built-in UV-C light
No
Airflow
800-2000 CFM
Size for
2500 sq.ft
Filtration system
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
-
Purisystems S2 UV Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)
![Purisystems S2 UV Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)]()
Built-in UV-C light
Yes
Airflow
800-2000 CFM
Size for
2500 sq.ft
Filtration system
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
-
Purisystems S2 UVIG Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)
![Purisystems S2 UVIG Air Scrubber (Industrial Grade)]()
New Tech
Built-in UV-C light and ionizer
Airflow
800-2000 CFM
Size for
2500 sq.ft
Filtration system
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
Commercial HEPA Air Scrubbers
-
AlorAir® Purecare 1050IG
![AlorAir® Purecare 1050IG]()
Built-in Ionizer
No
AirFlow
850-1050 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
58 DBA
Filters
MERV-13
-
AlorAir® Purecare 1050
![AlorAir® Purecare 1050]()
Built-in Ionizer
No
AirFlow
850-1050 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
58 DBA
Filters
MERV-13
-
AlorAir® Purecare 780S
![AlorAir® Purecare 780S]()
Built-in Ionizer
No
AirFlow
580-780 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
58 DBA
Filters
MERV-13
-
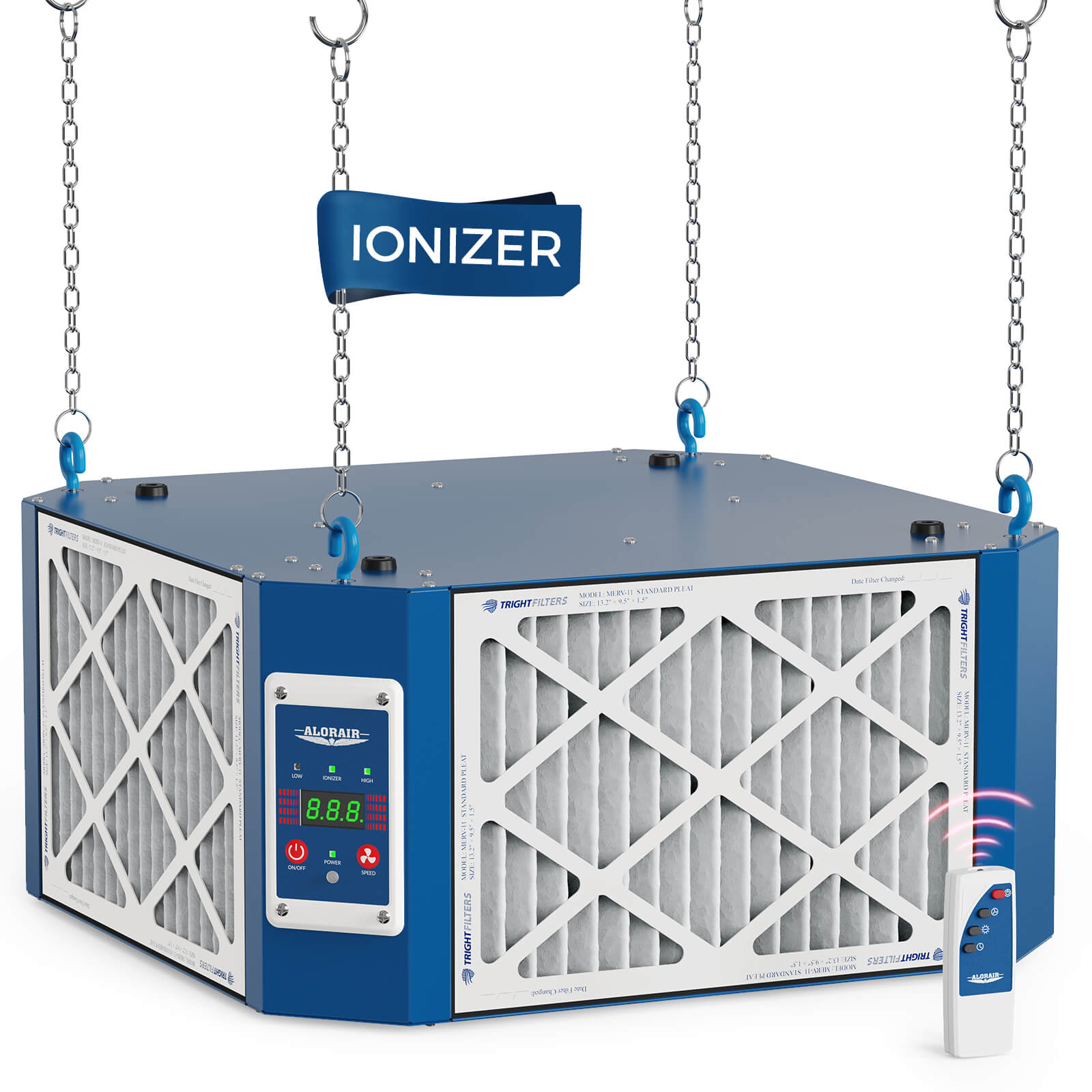
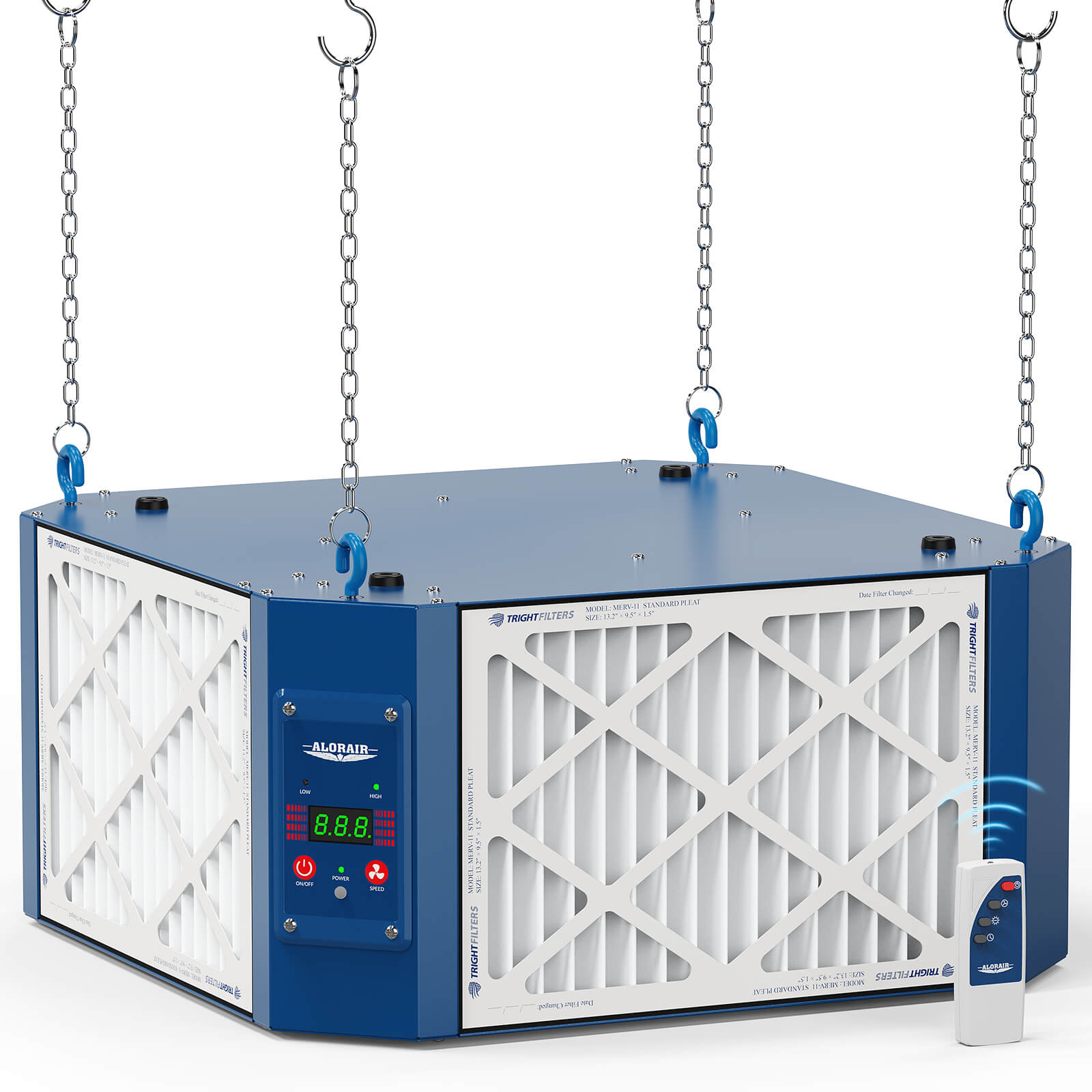
AlorAir® Purecare 1080IG
![AlorAir® Purecare 1080IG]()
Built-in Ionizer
Yes
AirFlow
780/1080CFM
Sound Pressure Level
60 DBA
Filters
3 X MERV-11
-
AlorAir® Purecare 1080
Built-in Ionizer
No
AirFlow
780/1080CFM
Sound Pressure Level
60 DBA
Filters
3 X MERV-11
-
AlorAir® Purecare 780IG
![AlorAir® Purecare 780IG]()
Built-in Ionizer
Yes
AirFlow
580/780CFM
Sound Pressure Level
50 DBA
Filters
3 X MERV-11
-
AlorAir® Purecare 780
![AlorAir® Purecare 780]()
Built-in Ionizer
No
AirFlow
580/780CFM
Sound Pressure Level
50 DBA
Filters
3 X MERV-11
-
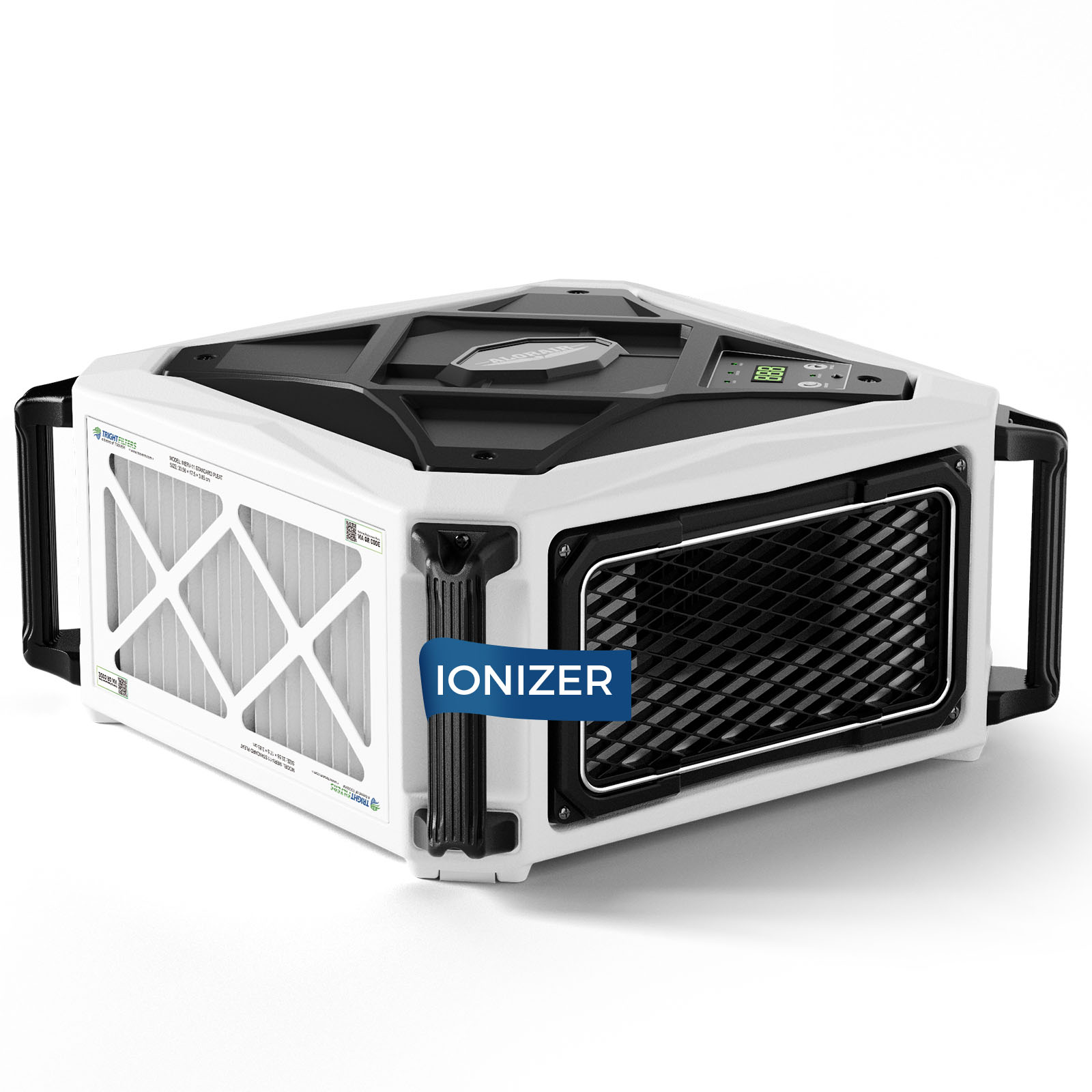
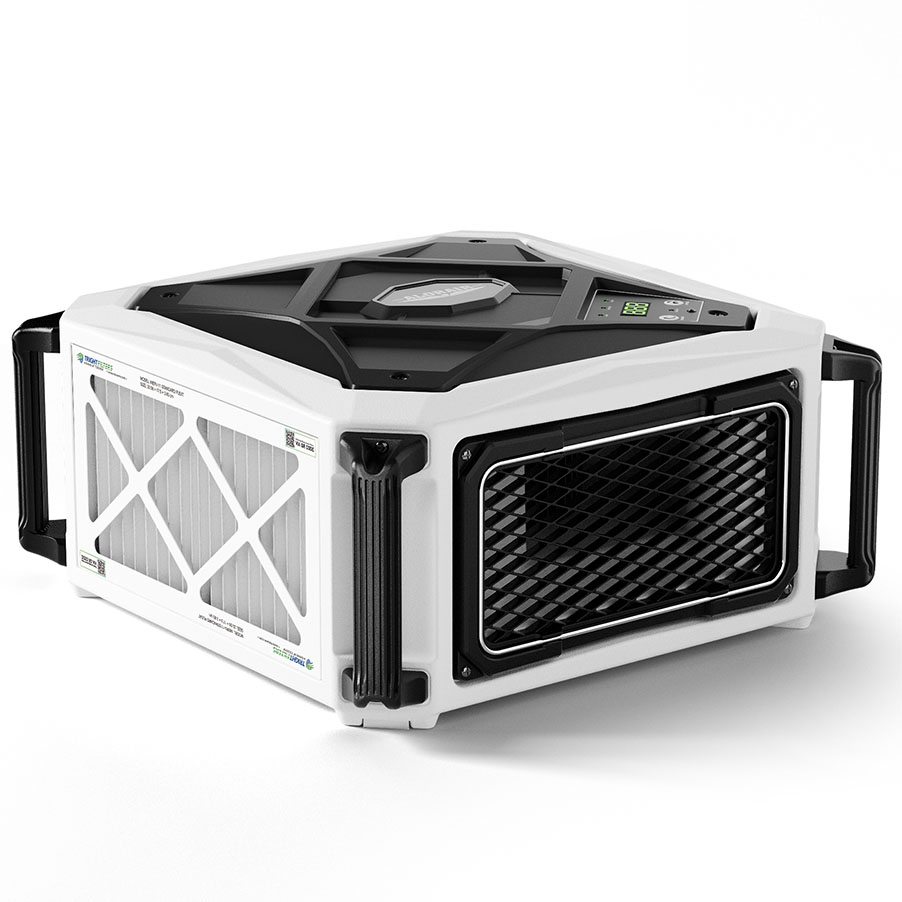
AlorAir® Purecare 1350IG
![AlorAir® Purecare 1350IG]()
Built-in Ionizer
Yes
AirFlow
1050-1350 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
69 DBA
Filters
4 X MERV-11
-
AlorAir® Purecare 1350
![AlorAir® Purecare 1350]()
Built-in Ionizer
No
AirFlow
1050-1350 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
69 DBA
Filters
4 X MERV-11
-
Purisystems Puricare 1100
![Purisystems Puricare 1100]()
Built-in lonizer
No
AirFlow
1100 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
66 DBA
Filters
5-Micron Filter (Outer), 1-Micron Filter (Inner)
-
Purisystems Puricare 1100IG
![Purisystems Puricare 1100IG]()
Built-in lonizer
Yes
AirFlow
1100 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
66 DBA
Filters
5-Micron Filter, 1-Micron Filter
-
Purisystems Puricare 500
![Purisystems Puricare 500]()
Built-in lonizer
No
AirFlow
500 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
61 DBA
Filters
5-Micron Filter, 1-Micron Filter
-
Purisystems Puricare 500IG
![Purisystems Puricare 500IG]()
Built-in lonizer
Yes
AirFlow
500 CFM
Sound Pressure Level
61 DBA
Filters
5-Micron Filter (Outer), 1-Micron Filter (Inner)
Woodshop Air Filtration System
-
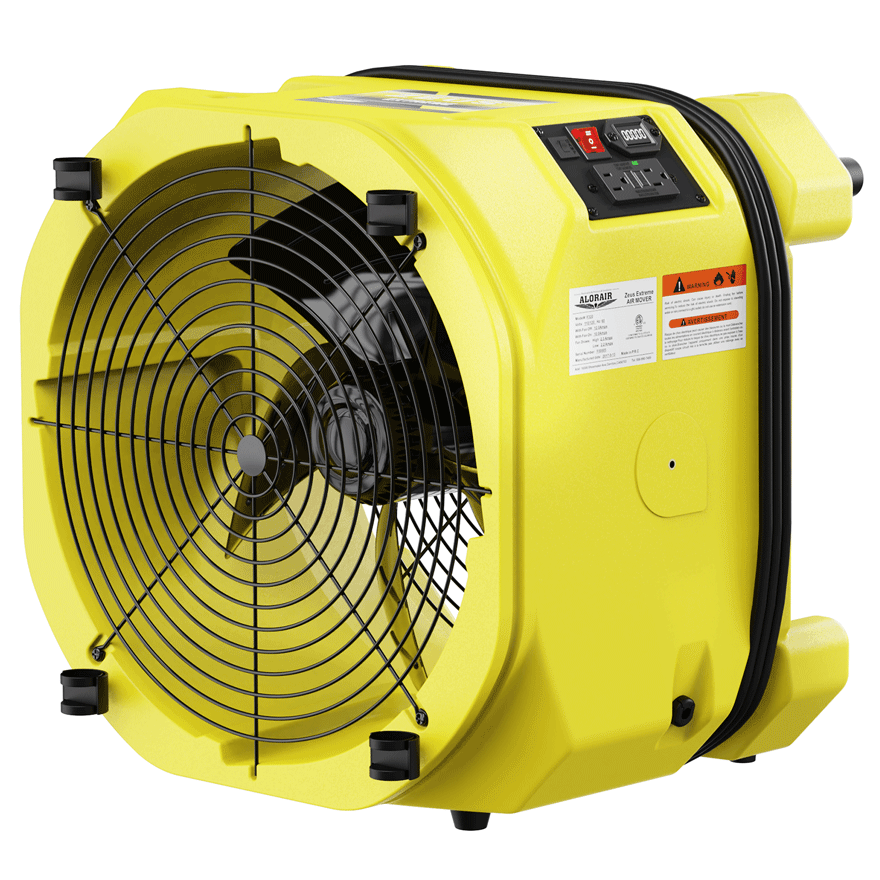
AlorAir® Zeus Extreme Axial Air Mover
![AlorAir® Zeus Extreme Axial Air Mover]()
Air Flow
3000cfm
Power
2.3 Amps
Speed Control
2-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
20.1" D x 20.1" W x 16.1" H
-
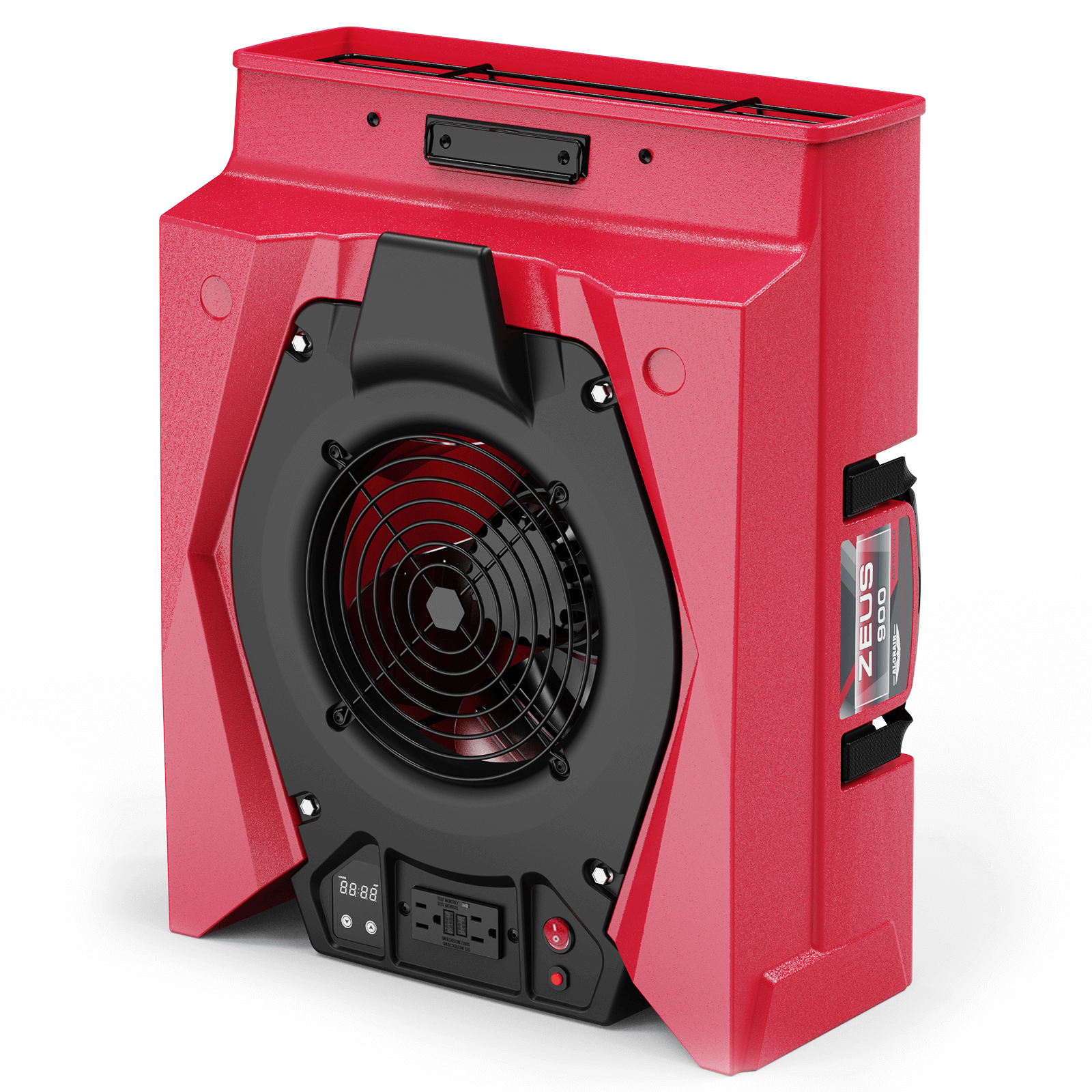
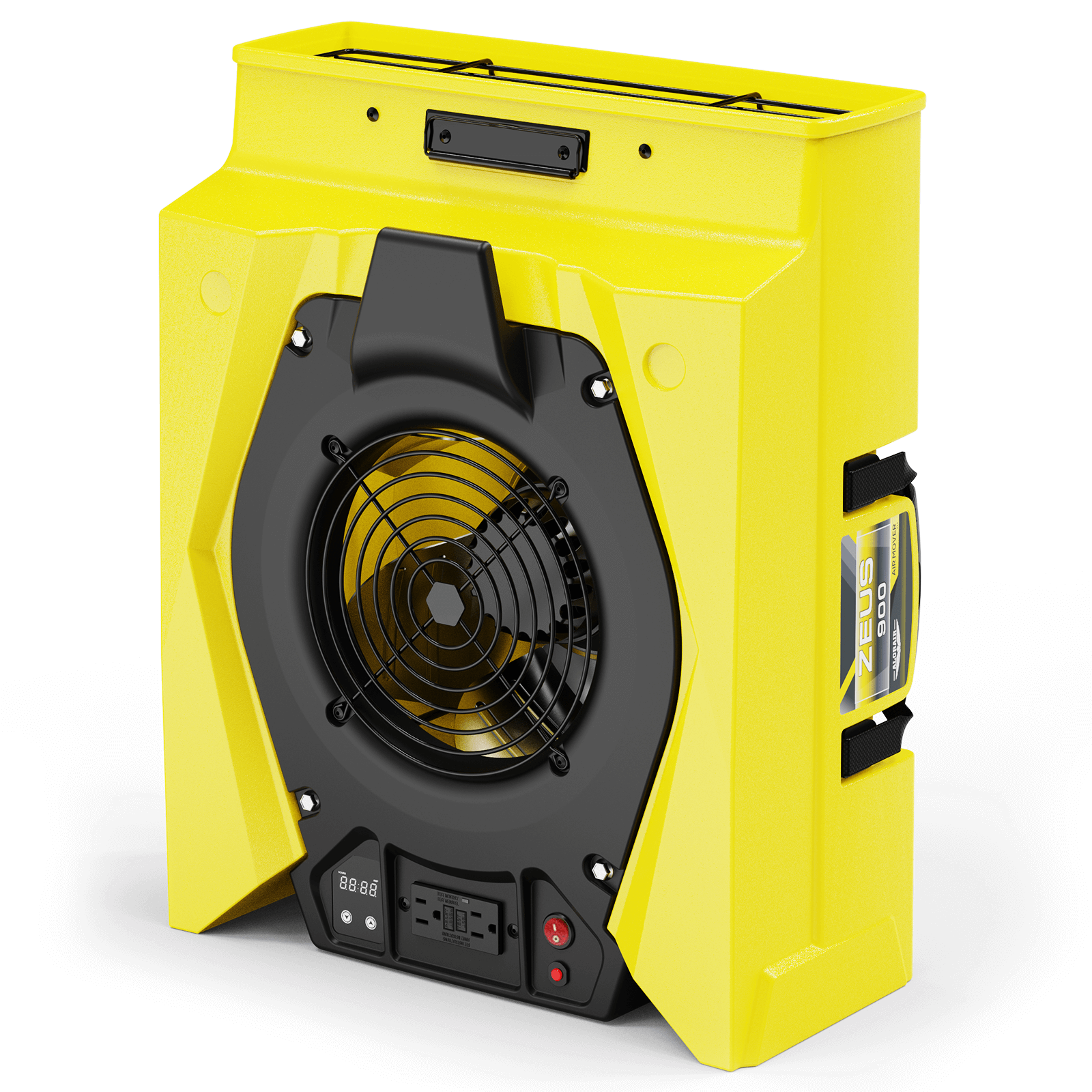
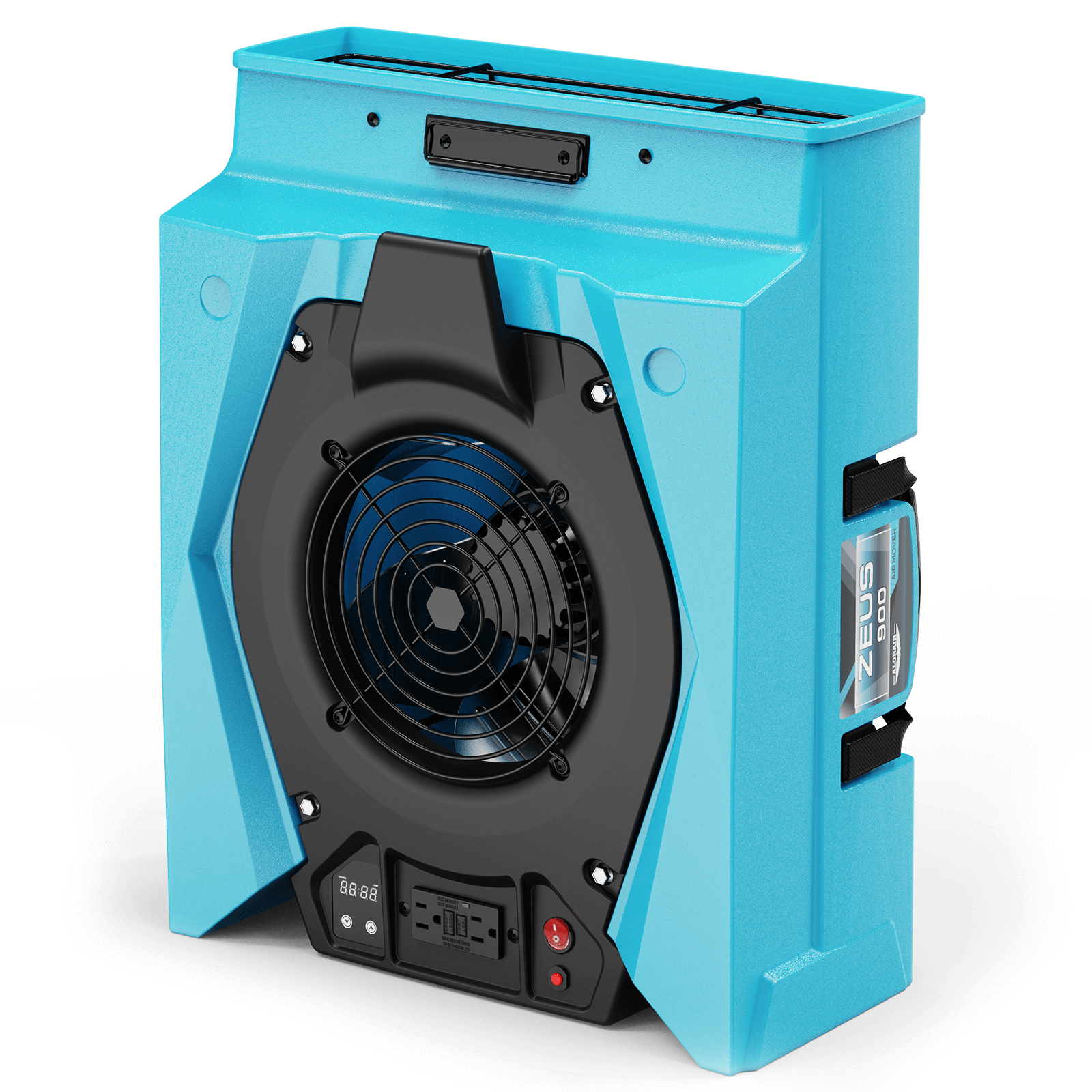
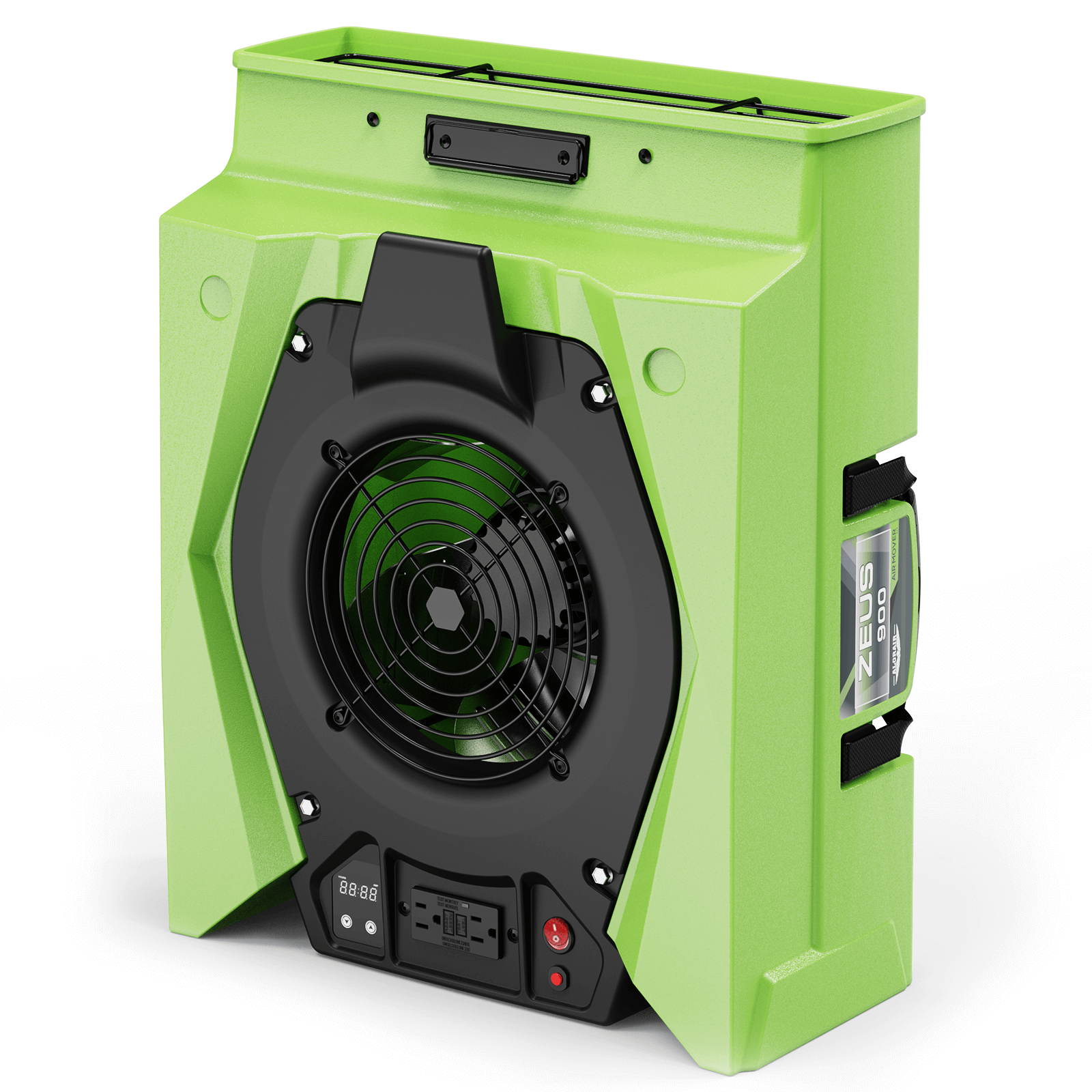
AlorAir® Zeus 900 Air Mover
![AlorAir® Zeus 900 Air Mover]()
![AlorAir® Zeus 900 Air Mover]()
![AlorAir® Zeus 900 Air Mover]()
![AlorAir® Zeus 900 Air Mover]()
Air Flow
950 CFM
Power
1.8 Amps
Speed Control
8-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
21.6" D x17.3" W x9.8" H
-
AlorAir® 600 CFM Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® 600 CFM Air Mover Blower Fan]()
![AlorAir® 600 CFM Air Mover Blower Fan]()
![AlorAir® 600 CFM Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air flow
600 CFM
Speed Control
3 Speed Control
Sound Pressure Level
< 65 dBA
Unit Dimensions
11.81x9.41x12.52in
-
AlorAir® GE4000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE4000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
4000 CFM
Wattage
1000 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
18.6"D x 16"W x 20.2"H
-
AlorAir® GE4000HTC Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE4000HTC Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
4000 CFM
Wattage
1000 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
18.6"D x 15.98"W x 20.2"H
-
AlorAir® GE4000TC Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE4000TC Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
4000 CFM
Wattage
1000 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
18.6"D x 16"W x 20.2"H
-
AlorAir® GE3000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE3000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
3000 CFM
Wattage
623 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.24"D x 14.02"W x 16.04"H
-
AlorAir® GE4000T Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE4000T Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
4000 CFM
Wattage
1000 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
18.6"D x 16"W x 20.2"H
-
AlorAir® GE3000HTC Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE3000HTC Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
3000 CFM
Wattage
623 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.24"D x 14.02"W x 16.06"H
-
AlorAir® GE3000TF Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE3000TF Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
3000 CFM
Wattage
623 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.8"D x 14.02"W x 15.98"H
-
AlorAir® GE3000T Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE3000T Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
3000 CFM
Wattage
623 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.24"D x 14.02"W x 16.06"H
-
AlorAir® GE2000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE2000HCW Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
2000 CFM
Wattage
224 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.24"D x 14.02"W x 16.06"H
-
AlorAir® GE2000TF Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE2000TF Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
2000 CFM
Wattage
224 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.8"D x 14.02"W x 15.98"H
-
AlorAir® GE2000T Air Mover Blower Fan
![AlorAir® GE2000T Air Mover Blower Fan]()
Air Flow
2000 CFM
Wattage
224 Watts
Speed Control
3-Speed Control
Unit Dimensions
17.24"D x 14.02"W x 16.06"H
-
AlorAir® Air Drying System
![AlorAir® Air Drying System]()
Floor Area
40.2 Square Feet
Capacity
50 Pints
Special Feature
Continuous Draining
Product Dimensions
13.9"D x 13.3"W x 12.21"H
Air Mover
-
AlorAir® Storm SLGR 850X
![AlorAir® Storm SLGR 850X]()
Capacity
180 PPD at Saturation, 85 PPD@AHAM
Size for
2300 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
21" D×11.6" W×17.3" H
-
AlorAir® Storm SLGR 1600X
![AlorAir® Storm SLGR 1600X]()
Capacity
275 PPD at Saturation, 160 PPD@AHAM
Size for
4000 sq.ft
Draining
Pump Drainage
Unit Dimensions
31.9" D ×20" W ×18" H
SLGR Dehumidifiers
-
AlorAir® Ventirpro 720
![AlorAir® Ventirpro 720]()
Power
115 V 60 Hz; 0.7 A
AirFlow
720 CFM
Material
Galvanized Sheet
Operating Humidity
5 to 80% RH
-
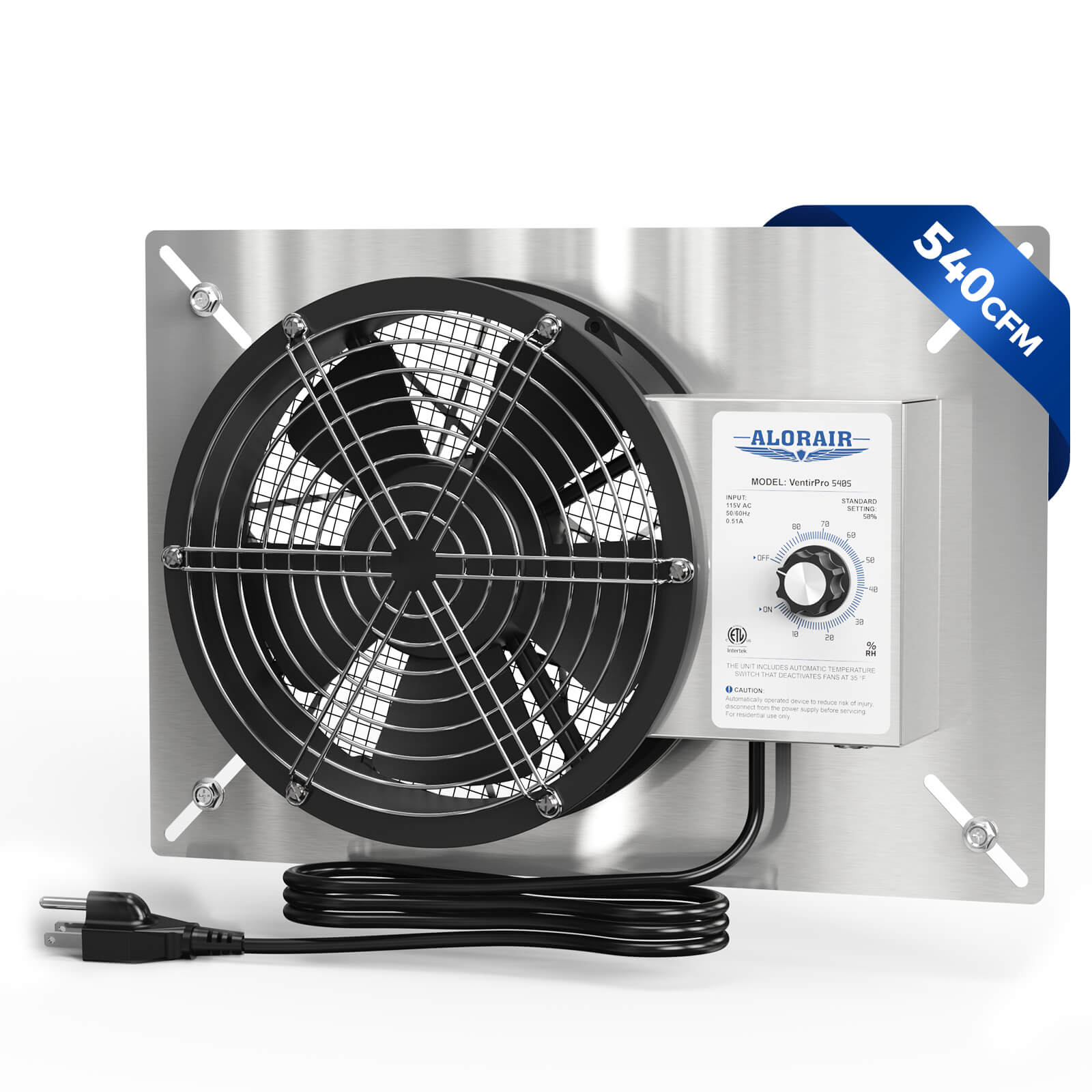
AlorAir® Ventirpro 540
![AlorAir® Ventirpro 540]()
Power
115 V 60 Hz; 0.51 A
AirFlow
540 CFM
Material
Galvanized Sheet
Operating Humidity
5 to 80% RH
-
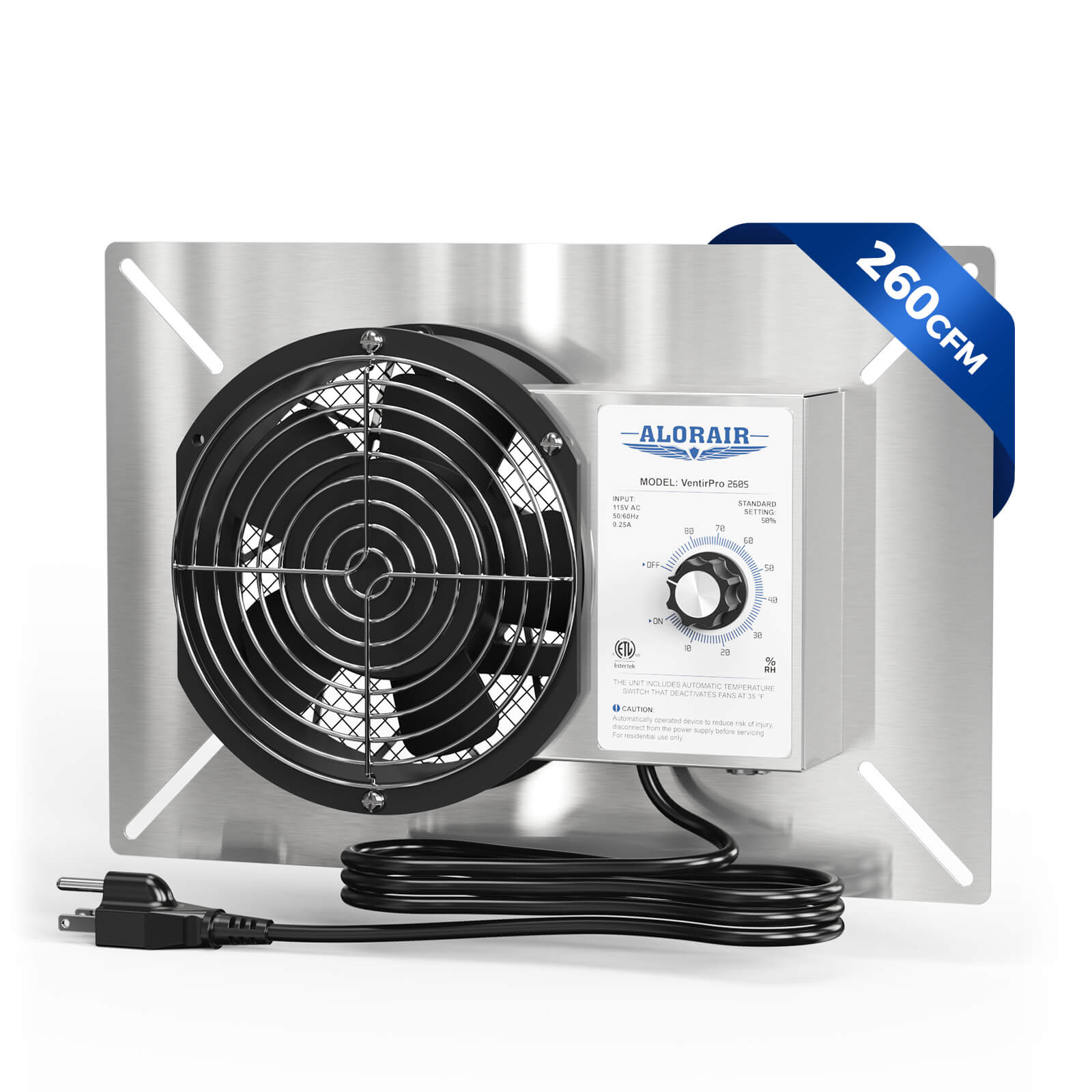
AlorAir® Ventirpro 260
![AlorAir® Ventirpro 260]()
Power
115 V 60 Hz; 0.25 A
AirFlow
260 CFM
Material
Galvanized Sheet
Operating Humidity
5 to 80% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirMax 780SD
![AlorAir® VentirMax 780SD]()
Power
115 V/ 60 Hz, 0.65 A
AirFlow
780 CFM
Operation
Button
Operating Humidity
1 to 99% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirMax 570SD
![AlorAir® VentirMax 570SD]()
Power
115 V/ 60 Hz, 0.52 A
AirFlow
570 CFM
Operation
Button
Operating Humidity
1 to 99% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirMax 300SD
![AlorAir® VentirMax 300SD]()
Power
115 V 60 Hz; 0.38 A
Airflow
300 CFM
Operation
Button
Operating Humidity
1 to 99% RH
-
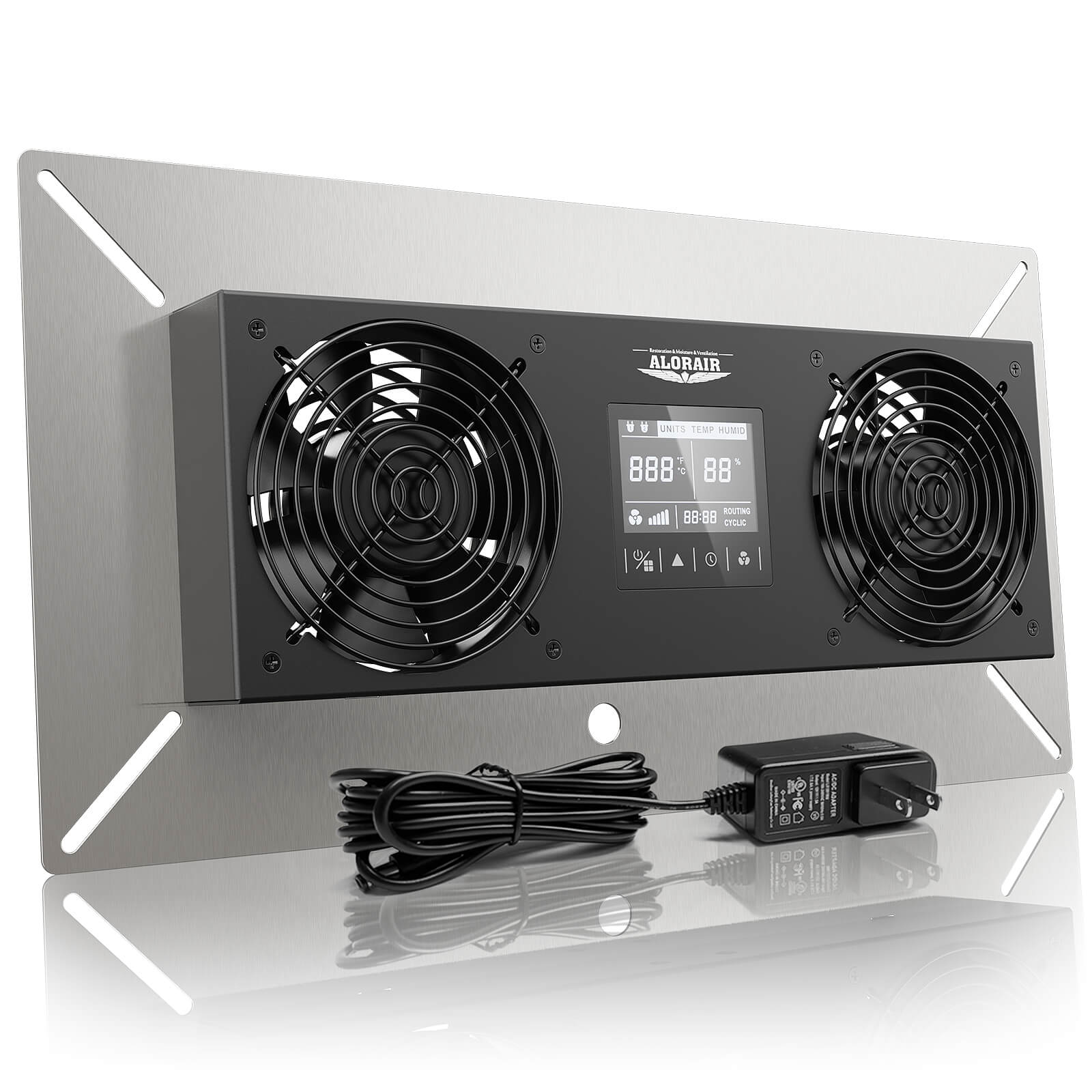
AlorAir® VentirPro-S2
![AlorAir® VentirPro-S2]()
Power
100 to 230V AC, 0.8A
Airflow
0-240 CFM (Air-out)
Noise
0-48 dBA
Operating Humidity
20 to 100% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirPro 260S
![AlorAir® VentirPro 260S]()
Power
115 V 60 Hz; 0.25 A
AirFlow
260 CFM
Material
Stainless Steel
Operating Humidity
5 to 80% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirPro 540S
![AlorAir® VentirPro 540S]()
Power
115 V/ 60 Hz, 0.51 A
Airflow
540 CFM
Material
Stainless Steel
Operating Humidity
5 to 80% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirPro 720S
![AlorAir® VentirPro 720S]()
Power
115 V/ 60 Hz, 0.7 A
Airflow
720 CFM
Material
Stainless Steel
Operating Humidity
5 to 80% RH
-
AlorAir® VentirMax 300S
![AlorAir® VentirMax 300S]()
Power
115V/60 Hz, 0.38 A
Airflow
300 CFM
Operation
Knob
Operating humidity
10-80%
-
AlorAir® VentirMax 570S
![AlorAir® VentirMax 570S]()
Power
115V/60 Hz, 0.52 A
Airflow
570 CFM
Operation
Knob
Operating humidity
10-80%
-
AlorAir® VentirMax 780S
![AlorAir® VentirMax 780S]()
Power
115V/60 Hz, 0.65 A
Airflow
780 CFM
Operation
Knob
Operating humidity
10-80%
Ventilation Fans
-
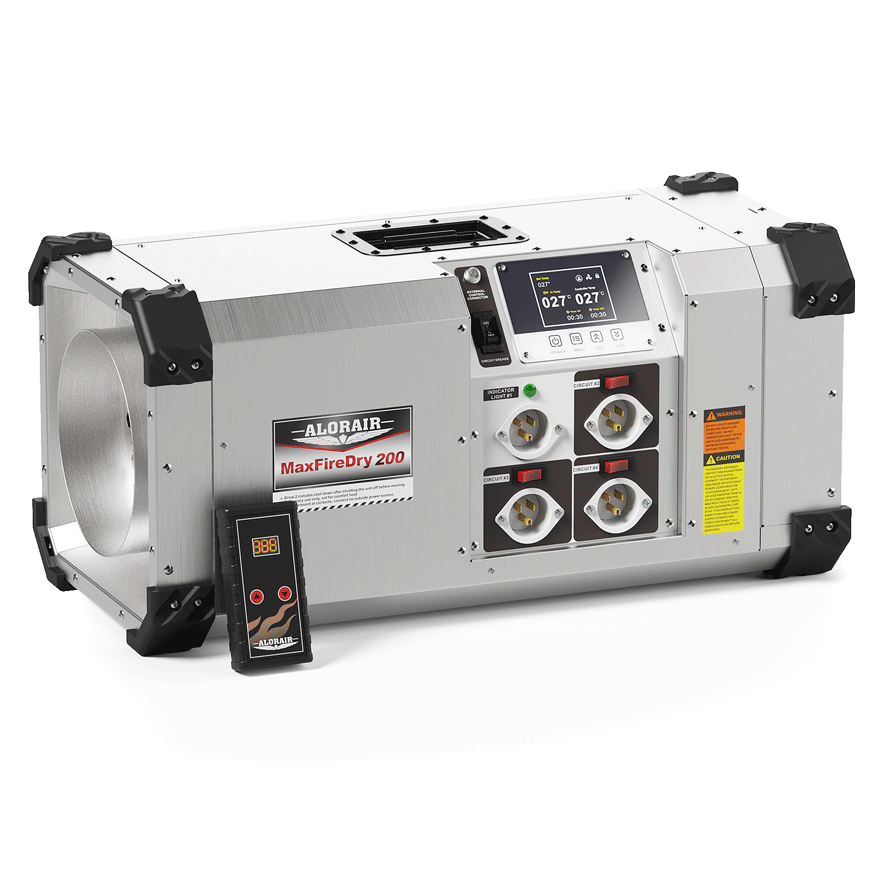
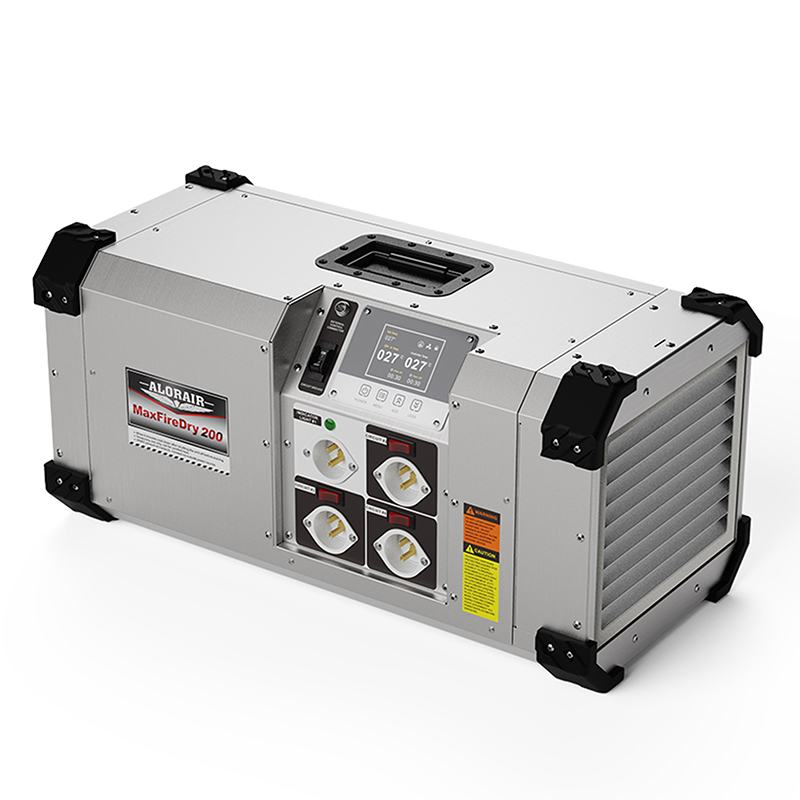
AlorAir® MaxFireDry 200
![AlorAir® MaxFireDry 200]()
Heat Output
20,000 BTUs
Airflow
250 CFM
Size for
Up to 430 Sq.Ft.
Features
PTC heating wires and Remote Control
Electric Heat Drying Systems
-
AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 10mil 10'x50'
![AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 10mil 10'x50']()
-
AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 10mil 10'x65'
![AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 10mil 10'x65']()
-
AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 10mil 10'x100'
![AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 10mil 10'x100']()
-
AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 12mil 10'x100'
![AlorAir® Vapor Barrier 12mil 10'x100']()
-
AlorAir® Crawl Space Vapor Barrier
![AlorAir® Crawl Space Vapor Barrier]()
Crawl Space Encapsulation and Repair
-
- Shop
Product Categories
-
Crawl Space & Basement Dehumidifiers
![Crawl Space & Basement Dehumidifiers]()
-
Whole House Dehumidifiers
![Whole House Dehumidifiers]()
-
Commercial & Industrial Dehumidifiers
![Commercial & Industrial Dehumidifiers]()
-
Commercial HEPA Air Scrubbers
![Commercial HEPA Air Scrubbers]()
-
Woodshop Air Filtration System
![Woodshop Air Filtration System]()
-
Air Mover
![Air Mover]()
-
SLGR Dehumidifiers
![SLGR Dehumidifiers]()
-
Ventilation Fans
![Ventilation Fans]()
-
Electric Heat Drying Systems
![Electric Heat Drying Systems]()
-
Filter & Other Accessories
![Filter & Other Accessories]()
-
Crawl Space Encapsulation and Repair
![Crawl Space Encapsulation and Repair]()
-
Wifi Dehumidifier
![Wifi Dehumidifier]()
-
-
Applications
Applications
-
Managing Air

-
Basement Dehumidification

-
Carpet Cleaning

-
Crawl Space Dehumidification
-
Fire Damage Restoration

-
Flood Dehumidification

-
Mold Removal

-
Water Damage Restoration

-
Indoor Swimming Pool

-
Grow Room & Tent Optimization

-
Pharmaceutical Production

-
Supermarket Grocery & Retail

-
Warehouse & Storage

-
Laboratory & Cleanrooms

-
Basement Wine Cellar

-
Gyms & Fitness Center

-
Guest Rooms & Hotels

-
- Support
- Learning
- Community
- Blog
- Distributor
-


-
-


Controlling Humidity for Optimal Indoor Grow Rooms: A Dehumidifier Solution
Recommend Products: AlorAir Storm Series,AlorAir® Sentinel Series.
AlorAir's dehumidification solutions ensure the yield and quality of indoor crop cultivation in agricultural facilities.


Indoor grow rooms have gained significant popularity in recent years, especially with the rise of vertical farming and hydroponic systems. These innovative farming methods solve the challenges of limited farmland and contaminated soil. Businesses and companies are cultivating fresh and healthy food in the heart of urban spaces by converting disused factories, storage facilities, or shipping containers into multi-story gardens.
Creating the Ideal Growing Climate for Indoor Agriculture
In these indoor farming environments, maintaining ideal climate conditions is crucial for the success of plant growth and maximizing yields. While outdoor farming benefits from favorable natural climate conditions, controlling the indoor environment becomes more challenging. Factors such as lighting, temperature, and humidity need to be carefully regulated to simulate optimal growing conditions throughout the different stages of plant growth.
Optimal Controlled Humidity Levels for All Flowering Stages
One of the key factors that significantly impact plant growth in indoor grow rooms is humidity. Maintaining a controlled humidity level is essential to ensure healthy plant development and prevent the risk of mold infestation. However, different phases of plant growth require specific humidity conditions.
During the germination and propagation phases, plants thrive in a relatively high-humidity environment of about 70 to 80% relative humidity (RH). This moisture enables the development of strong roots, as cuttings draw water from the air through their leaves.
As the plants progress to the growth phase, the humidity requirement decreases to around 50 to 80% RH as water consumption shifts to the developing root system. In the flowering phase, it is crucial to maintain a lower humidity level of 40 to 60% RH to minimize the risk of mold on the dense leaves and blossoms.
Optimize every growth stage of the plant to ensure maximum yield
Optimal climate conditions and humidity levels are essential for the healthy growth of plants. To ensure maximum high-quality harvest and prevent costly crop failures, a reliable dehumidification solution is necessary. Instead of complex dehumidifiers that complicate maintenance and increase costs, focus on the essentials: durability, high dehumidification performance, energy efficiency, low-temperature reliability, and scalability.
Whether it's a grow tent, a repurposed shipping container, or a large indoor farm, the Crawlspace series dehumidifiers, with capacities ranging from 35 to 235 pints, offer the performance, capacity, and reliability that portable devices sold in retail can't match. They ensure overall success in improving plant health, productivity, and the operation of the grow room.
Key advantages of AlorAir crawlspace dehumidifiers include:
Cost-effective investment.
High dehumidification capacity for quick and efficient moisture control.
GPP control/RH control for precise humidity control at different stages of plant growth.
Energy Star and ETL certifications ensure safety and energy efficiency.
Built-in MERV-8 filter improves air quality and reduces the risk of botrytis.
Gravity drainage/pump drainage options for flexible installation in multi-level farms.
Automatic defrost system ensures efficient operation even in late-flowering stages.
Robust steel housing and durable structure provide long-term value and minimal maintenance.
Compact design saves storage space.
Optional remote controller allows for remote monitoring of your growing space.
Flexible installation options including suspension, standalone, or ducted installation.
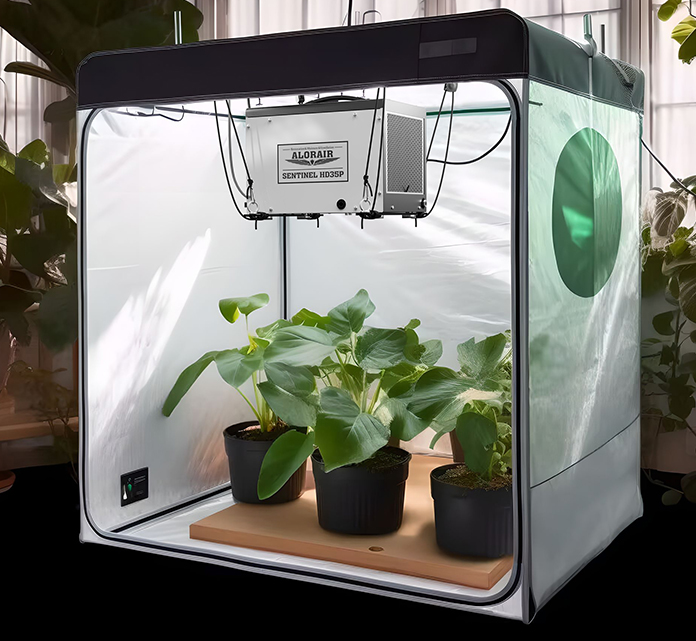
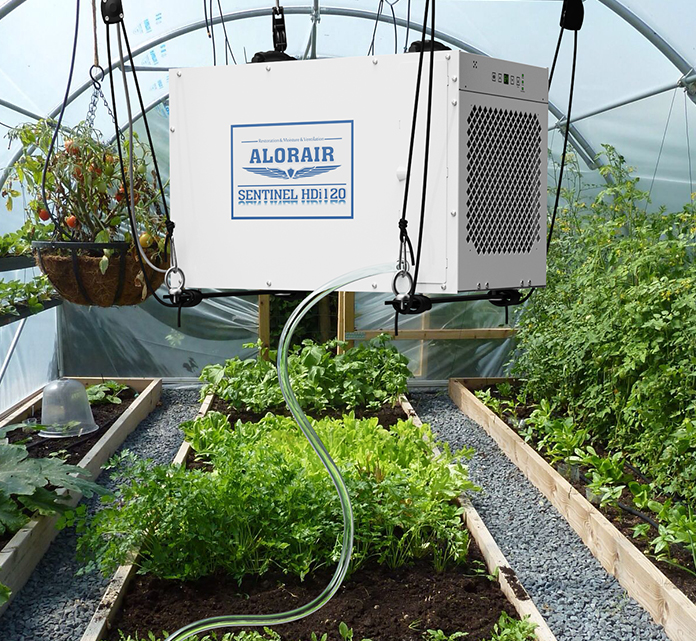
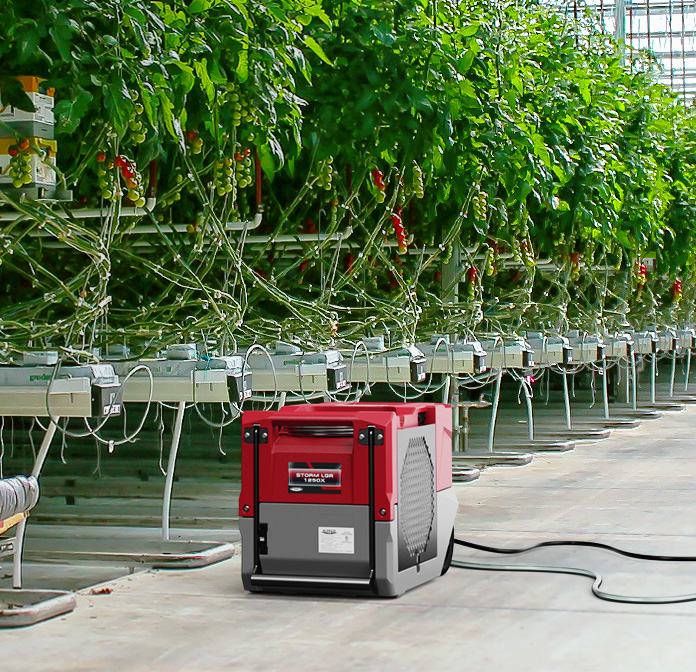



AlorAir commercial dehumidifiers are the upgraded choice for vertical farming
When planting in a large room, we know that plants are easily affected by low VPD and high relative humidity. Therefore, choosing a large-capacity industrial dehumidifier is the best choice for moisture regulation, and can take care of the needs of each plant.
AlorAir offers a series of commercial dehumidifiers, including the most powerful model SLGR, providing a powerful air circulation in your planting space, creating an environment that drives transpiration at the optimum rate, and helps prevent disease outbreaks.
Key features of AlorAir commercial dehumidifiers include:
Diverse models to meet the budget requirements of every grower.
Rugged and durable design with a molded plastic housing and heavy-duty structure.
SLGR pre-cooling technology elevates dehumidification performance to new levels.
WI-FI control allows easy monitoring of humidity conditions in your space.
Powerful condensate pump handles complex indoor drainage requirements.
Automatic defrost system provides efficient performance even in low-temperature conditions.
MERV-8 filter prevents the formation of harmful condensate.
High mobility for easy transportation to designated job sites.
Discuss wih AlorAir dehumidifier expert
AlorAir dehumidifiers allow you to take control of your own growth environment. You can achieve maximum dehumidification and VPD control, along with the best mobility and remote monitoring capabilities. In addition, you will receive top-tier products and professional support. If you have any confusion about equipment selection, please contact our sales team. We look forward to creating a comfortable plant growth environment with you.
AlorAir Crawlspace Dehumidifiers Recommended for Grow Room and Grow Tent

Condensing Dehumidifier, Stationary - Designed for Modern Home Consumers
AlorAir Commercial Dehumidifiers Recommended for Large Vertical farming, Aquaponics

Condensation Dehumidifiers, Mobile ‑ SLGR Series

Condensation Dehumidifiers, Mobile ‑ LGR Performance




-(1).png)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.HDi90.png)
.HD90.png)



.jpg)


.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)













.jpg)






.jpg)




















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)








.jpg)
.jpg)













.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)
















-.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)




.jpg)





 Exclusive
offers promotions
Exclusive
offers promotions